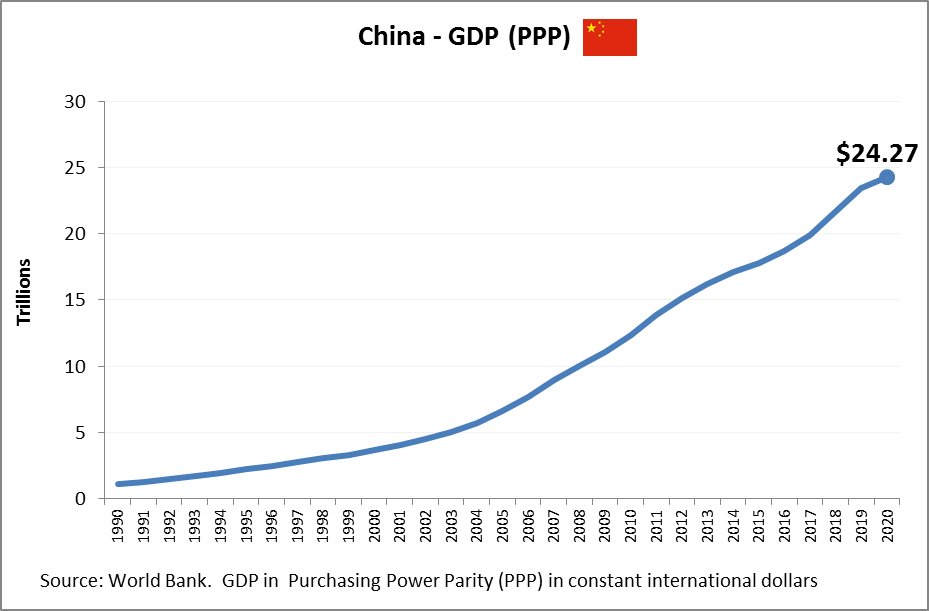
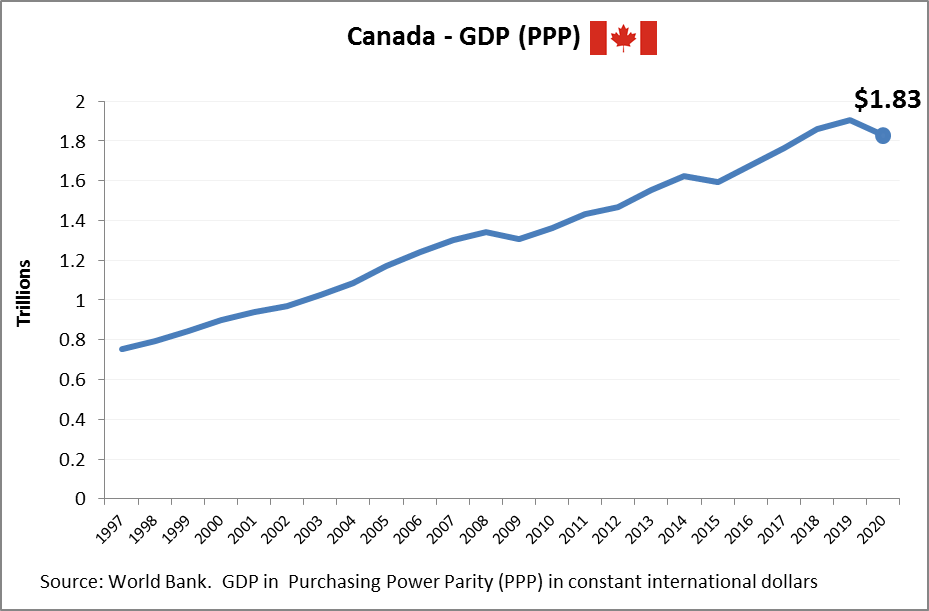
Germany economy size measured in Power Purchasing Parity, i.e. comparing relative standard of living and ability to afford goods and services. Germany’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) chart showing historical economic growth as measured in PPP international dollars.
Germany: Germany holds one of the highest GDP PPP totals in the world, representing Europes largest economy and a global export powerhouse. Its economic model is built on high-value manufacturing, engineering, and a strong Mittelstand (small and medium-sized enterprises). In terms of GDP PPP per capita, Germany also performs very well, signifying strong productivity and a high quality of life. The German economy benefits from deep integration within the EU and a reputation for efficiency and innovation. However, demographic shifts and energy transitions pose long-term challenges to sustaining its economic momentum.