A fjord is a long, narrow, and deep inlet of the sea that is surrounded by steep cliffs. Fjords are formed by the erosion of glaciers that carved U-shaped valleys in the land. When the glaciers retreated, the sea filled the valleys and created fjords. Fjords are found in many regions of the world that have been glaciated, such as Norway, Chile, New Zealand, Canada, Greenland, and Alaska. Fjords have unique features and ecosystems that are influenced by the interaction of freshwater and saltwater, as well as the tides and currents. Fjords are also important for human activities, such as fishing, tourism, and transportation.
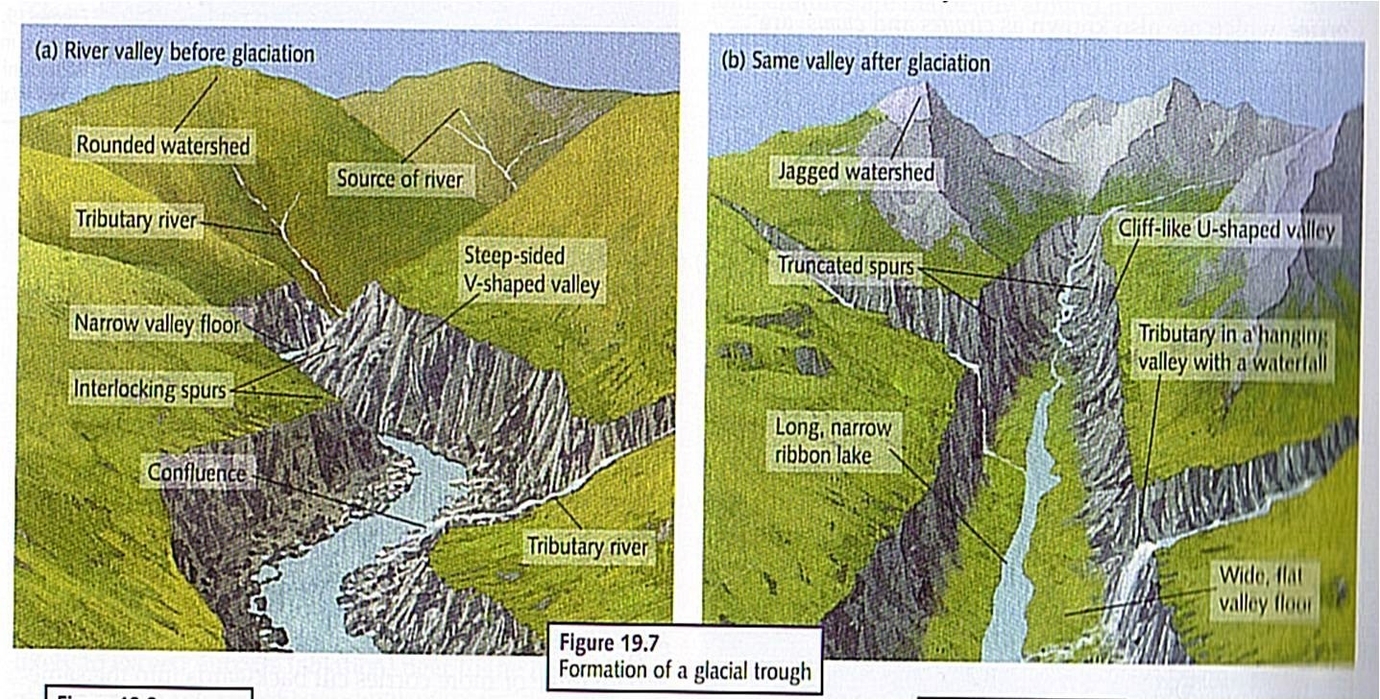
Fjords are the result of a long and complex process of glaciation, which is the formation and movement of glaciers. Glaciers are large masses of ice that accumulate on land over thousands of years. Glaciers can move slowly downhill due to gravity, or they can be pushed by the weight of the ice behind them. As glaciers move, they erode the underlying rock and soil by plucking, abrasion, and freeze-thaw action. Plucking occurs when the glacier freezes onto the bedrock and pulls out chunks of rock as it moves. Abrasion occurs when the rock fragments carried by the glacier scrape and polish the bedrock. Freeze-thaw action occurs when water seeps into cracks in the rock and expands when it freezes, breaking the rock apart.
Glaciers can create different types of landforms depending on the shape of the valley they occupy. In pre-glacial times, most valleys had a V-shaped cross-section, with a narrow bottom and sloping sides. When a glacier enters a V-shaped valley, it widens and deepens the valley by eroding the sides and bottom. This creates a U-shaped valley, with a flat bottom and steep sides. U-shaped valleys are also called glacial troughs. Sometimes, glaciers can erode the valley floor more than the sides, creating an overdeepened valley. This means that the valley floor is lower than the level of the sea. Overdeepening can occur due to several factors, such as variations in the hardness of the rock, the thickness and speed of the glacier, and the presence of subglacial water.
When the climate becomes warmer, glaciers start to melt and retreat. This exposes the land that was previously covered
