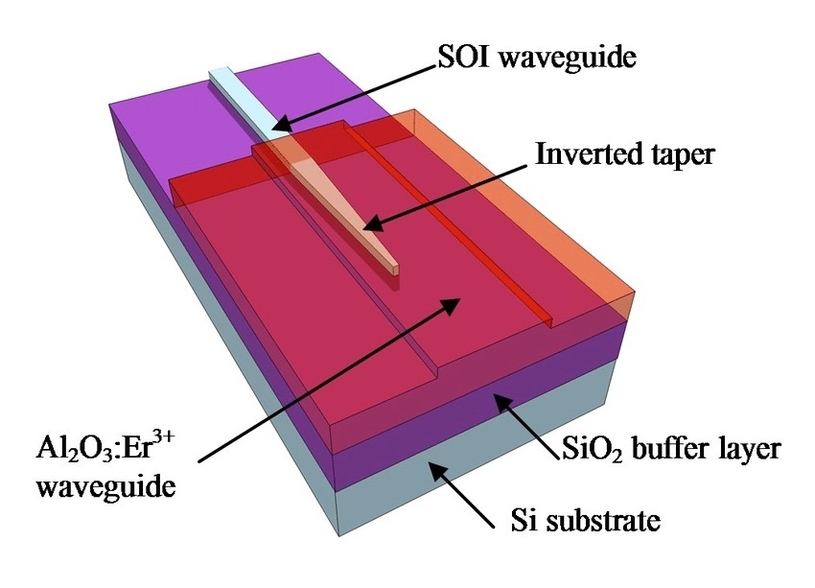
A silicon optical waveguide is a device that guides light along a path on a silicon chip. It is a key component of silicon photonics, which is the study and application of photonic systems that use silicon as an optical medium . Silicon waveguides can be readily fabricated from silicon-on-insulator (SOI) wafers using standard complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) processes . The basic structure of a silicon waveguide consists of a longitudinally extended high-index optical medium, called the core, which is transversely surrounded by low-index media, called the cladding . A guided optical wave propagates in the waveguide along its longitudinal direction.
There are two basic types of silicon waveguides: planar waveguides and nonplanar waveguides. In a planar waveguide, the core is sandwiched between cladding layers in only one direction, with an index profile n(x). The core of a planar waveguide is also called the film, while the upper and lower cladding layers are called the cover and the substrate . Planar waveguides are used for integrated photonics, such as laser chips . In a nonplanar waveguide, the index profile n(x, y) is a function of both transverse coordinates x and y. There are many different types of nonplanar waveguides that are differentiated by the distinctive features of their index profiles .
ilicon waveguides offer several advantages over other waveguide materials. They have a high refractive index, which allows for strong confinement of light in the waveguide . They are also compatible with CMOS processes, which makes them easy to integrate with other electronic components on a silicon chip . Silicon waveguides can be used for a wide range of applications, including optical interconnects, optical modulators, and optical sensors.
The design and optimization of silicon waveguides is an active area of research. Researchers are exploring new waveguide structures and materials to improve the performance of silicon waveguides. For example, slot waveguides are a type of silicon waveguide that have a low-index slot region between two high-index silicon layers. This structure allows for strong confinement of light in the slot region, which can be used for applications such as sensing and nonlinear optics . Silicon photonic wire waveguides are another type of silicon waveguide that have a submicron cross-section. These waveguides offer efficient media for nonlinear optical functions, such as wavelength conversion.
In conclusion, silicon optical waveguides are devices that guide light along a path on a silicon chip. They are a key component of silicon photonics, and can be readily fabricated from SOI wafers using standard CMOS processes. Silicon waveguides offer several advantages over other waveguide materials, including a high refractive index and compatibility with CMOS processes. They can be used for a wide range of applications, and researchers are exploring new waveguide structures and materials to improve their performance.