Vertebrates are a subphylum of chordates, which are animals that have a notochord, a dorsal nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail at some point in their life cycle. Vertebrates are characterized by having a backbone, or vertebral column, which is made up of individual bones called vertebrae. They also have a muscular system consisting primarily of bilaterally paired masses and a central nervous system partly enclosed within the backbone. The subphylum is one of the best known of all groups of animals.
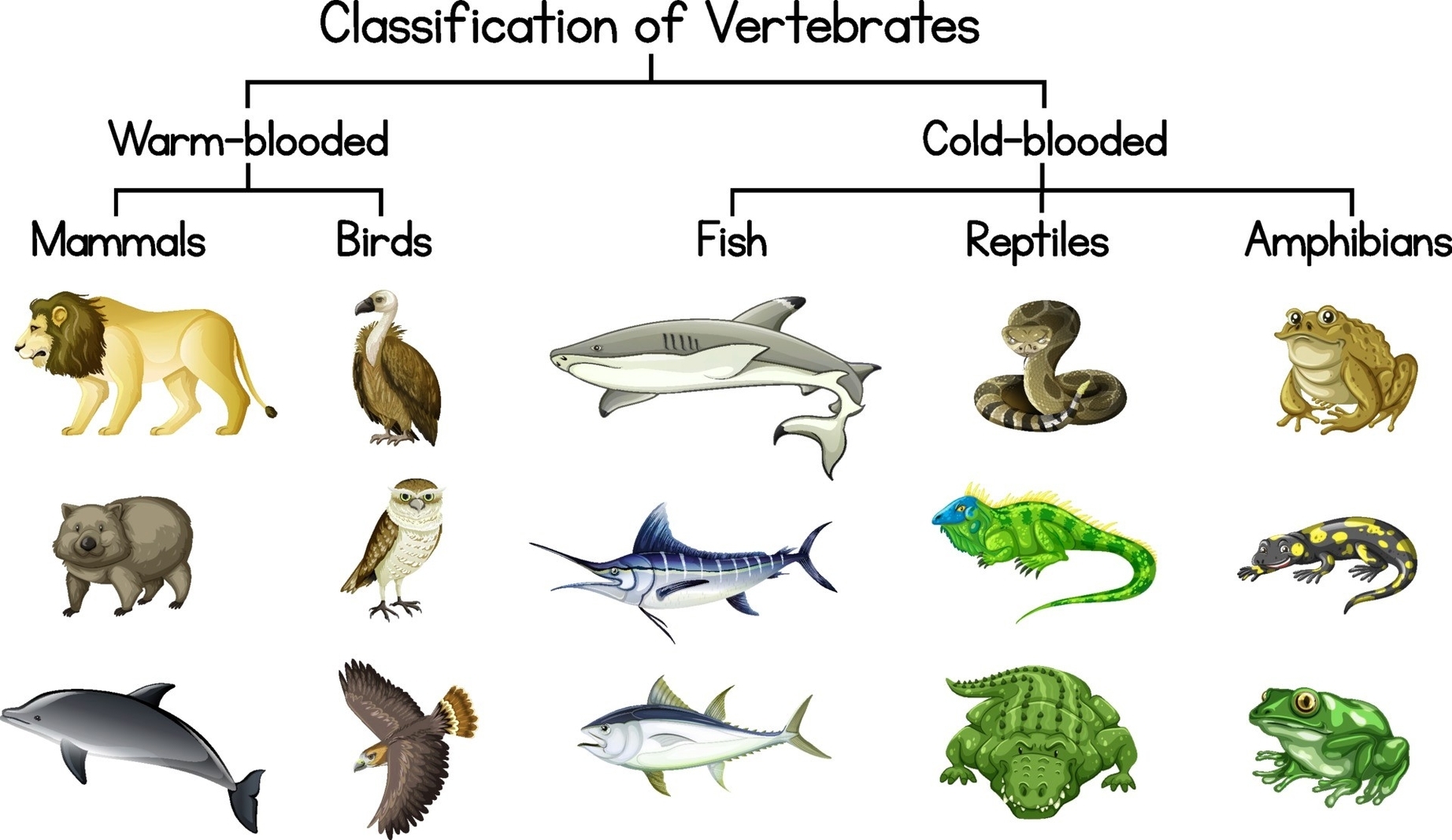
Vertebrates are classified into nine classes: hagfish, lampreys, cartilaginous fish, ray-finned fish, lobe-finned fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. Each class is distinguished by unique characteristics, such as the presence of jaws, the type of scales, the number of limbs, the type of reproduction, and the structure of the heart.
Hagfish and lampreys are the most primitive vertebrates and are jawless fish. They lack paired fins and scales, and their skeletons are made of cartilage rather than bone. Cartilaginous fish, such as sharks and rays, have a skeleton made of cartilage, five to seven gill slits on the sides of their heads, and a lateral line system that detects vibrations in the water. Ray-finned fish, such as salmon and trout, have a bony skeleton and fins supported by bony rays. They also have a swim bladder that helps them control their buoyancy.
Lobe-finned fish, such as coelacanths and lungfish, have fleshy fins that are supported by bones. They are the closest living relatives of tetrapods, which are four-limbed vertebrates. Amphibians, such as frogs and salamanders, are tetrapods that have moist skin and lay their eggs in water. They undergo metamorphosis from a larval stage to an adult stage, and they breathe through their skin as well as their lungs.
Reptiles, such as snakes and lizards, are tetrap
