Smart Agriculture is a term that refers to the use of advanced technologies and data-driven methods to optimize and improve the sustainability of agricultural production. Smart Agriculture aims to address the interlinked challenges of food security, climate change, and profitability in the agri-food sector. Some of the technologies that are used for Smart Agriculture include artificial intelligence (AI), automation, the Internet of Things (IoT), sensors, robots, and satellite-based global positioning systems (GPS).
mart Agriculture is based on the concept of precision agriculture, which dates back to the 1980s and focuses on the variability of soil and crop conditions within a field. Precision agriculture uses data from yield monitors, GPS mapping, and soil sampling to apply the right amount of inputs (such as fertilizer, water, and pesticides) to the right place at the right time. Precision agriculture helps to increase crop yields, reduce costs, and minimize environmental impacts.
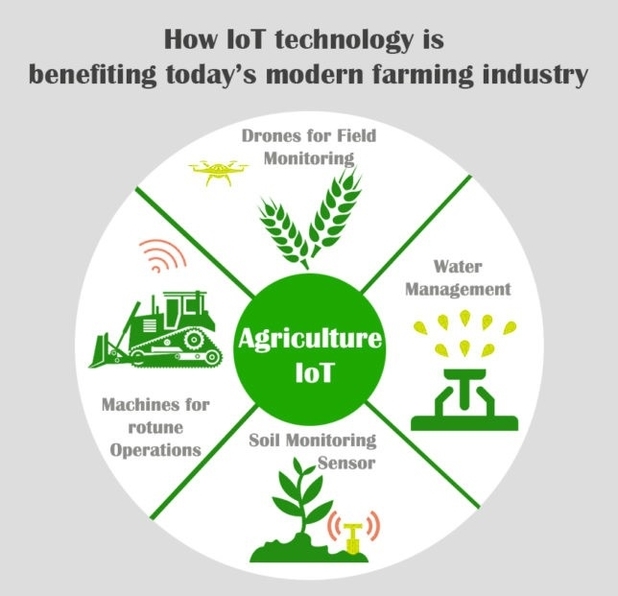
mart Agriculture goes beyond precision agriculture by integrating more technologies and data sources to enable real-time monitoring, analysis, and decision-making for farm operations. Smart Agriculture leverages AI to process large amounts of data from various sources, such as sensors, drones, satellites, weather stations, and farm management software. AI can also provide insights and recommendations for farmers, such as optimal planting dates, irrigation schedules, pest control strategies, and harvest times. AI can also automate some of the farm tasks, such as seeding, weeding, spraying, and harvesting, using robots and autonomous vehicles.
mart Agriculture also uses IoT to connect different devices and systems on the farm, such as sensors, cameras, machines, and mobile phones. IoT enables data collection and transmission, as well as remote control and coordination of farm activities. IoT can also facilitate traceability and transparency of the food supply chain, by providing information on the origin, quality, and safety of the food products.
The benefits of Smart Agriculture are manifold. Smart Agriculture can help to:
– Increase productivity and quality of food production, by optimizing the use of inputs, enhancing crop and livestock performance, and reducing losses and waste.
– Enhance resilience and adaptation to climate change, by improving the management of weather and climate risks, diversifying the production systems, and increasing the use of climate-resilient crop varieties and practices.
– Reduce greenhouse gas emissions and environmental impacts, by lowering the use of fossil fuels,
