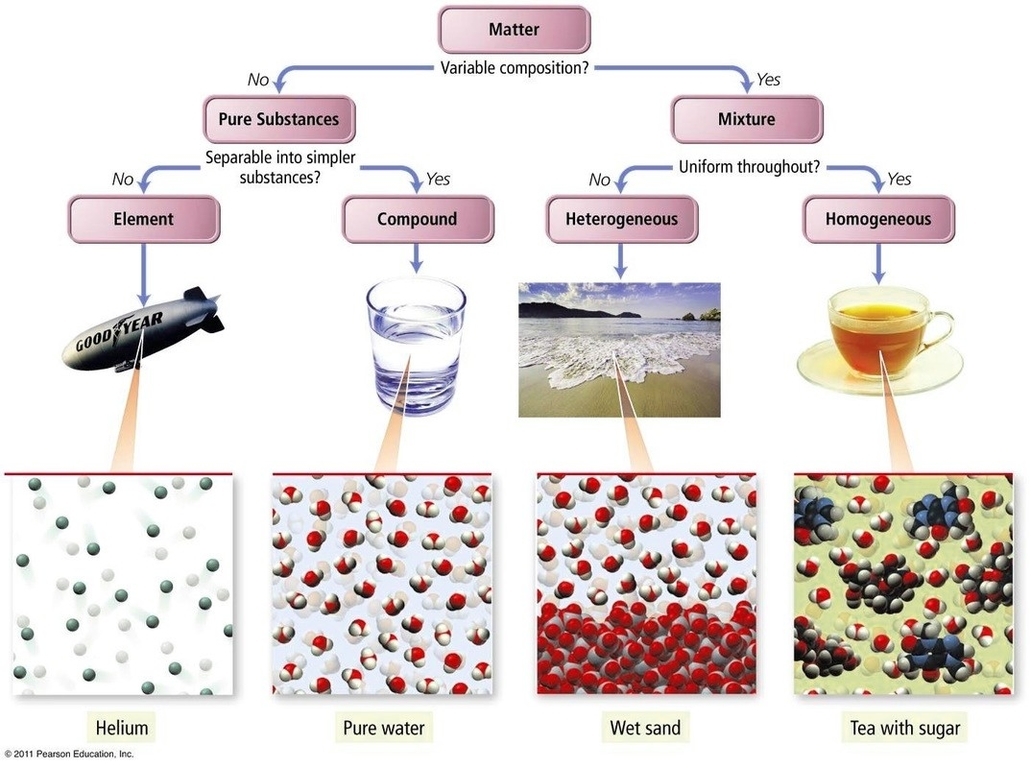
Pure substances and mixtures are two fundamental concepts in chemistry. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. It is classified into two broad categories: pure substances and mixtures. A pure substance is a single kind of matter that has a constant or uniform structure and cannot be broken down or transformed into new substances. Pure substances are further classified as elements and compounds. An element is a substance that consists of only one type or kind of atom. An element is a pure substance as it cannot be broken down or transformed into a new substance even by using some physical or chemical means. Elements are mostly metals, non-metals or metalloids. Compounds, on the other hand, are also pure substances when two or more elements are combined chemically in a fixed ratio. However, these substances can be broken down into separate elements by chemical methods.
Pure substances are mostly homogeneous in nature containing only one type of atom or molecule. These substances mainly have a constant or uniform composition throughout. The substances have fixed boiling and melting points. A pure substance usually participates in a chemical reaction to form predictable products. All elements are mostly pure substances. A few of them include gold, copper, oxygen, chlorine, diamond, etc. Compounds such as water, salt or crystals, baking soda amongst others are also grouped as pure substances.
A mixture is a physical combination of two or more pure substances in which each substance retains its own chemical identity. Mixtures are further divided into homogenous or heterogeneous mixture. A homogeneous mixture occasionally called a solution, is comparatively unvarying in configuration or constant. Every unit of the mixture is like every other unit. For instance, if you liquefy sugar in water and blend it really well, your concoction is essentially the same, no matter where you sample it. This mixture contains two or more chemical substances. A heterogeneous mixture is a concoction whose configuration varies from spot to spot within the sample. For example, if you put a little amount of sugar in a vessel, add some sand, and then shake the jar a couple of times, your concoction doesnt have the same configuration all throughout the jar.
Mixtures are classified as either homogeneous or heterogeneous. A homogeneous mixture is a mixture in which the composition is uniform throughout the mixture. In other words, the mixture has the same proportion of its components throughout. Examples of homogeneous mixtures include saltwater, air, and sugar solutions. A heterogeneous mixture is a mixture in which the composition is not uniform throughout the mixture. In other words, the mixture has different proportions of its components throughout. Examples of heterogeneous mixtures include sand and water, oil and water, and soil.
In summary, pure substances are substances that are made up of only one kind of particle and have a fixed or constant structure. Pure substances are further classified as elements and compounds. A mixture is a physical combination of two or more pure substances in which each substance retains its own chemical identity. Mixtures are further divided into homogenous or heterogeneous mixture. Homogeneous mixtures are uniform throughout the mixture, while heterogeneous mixtures are not uniform throughout the mixture..
