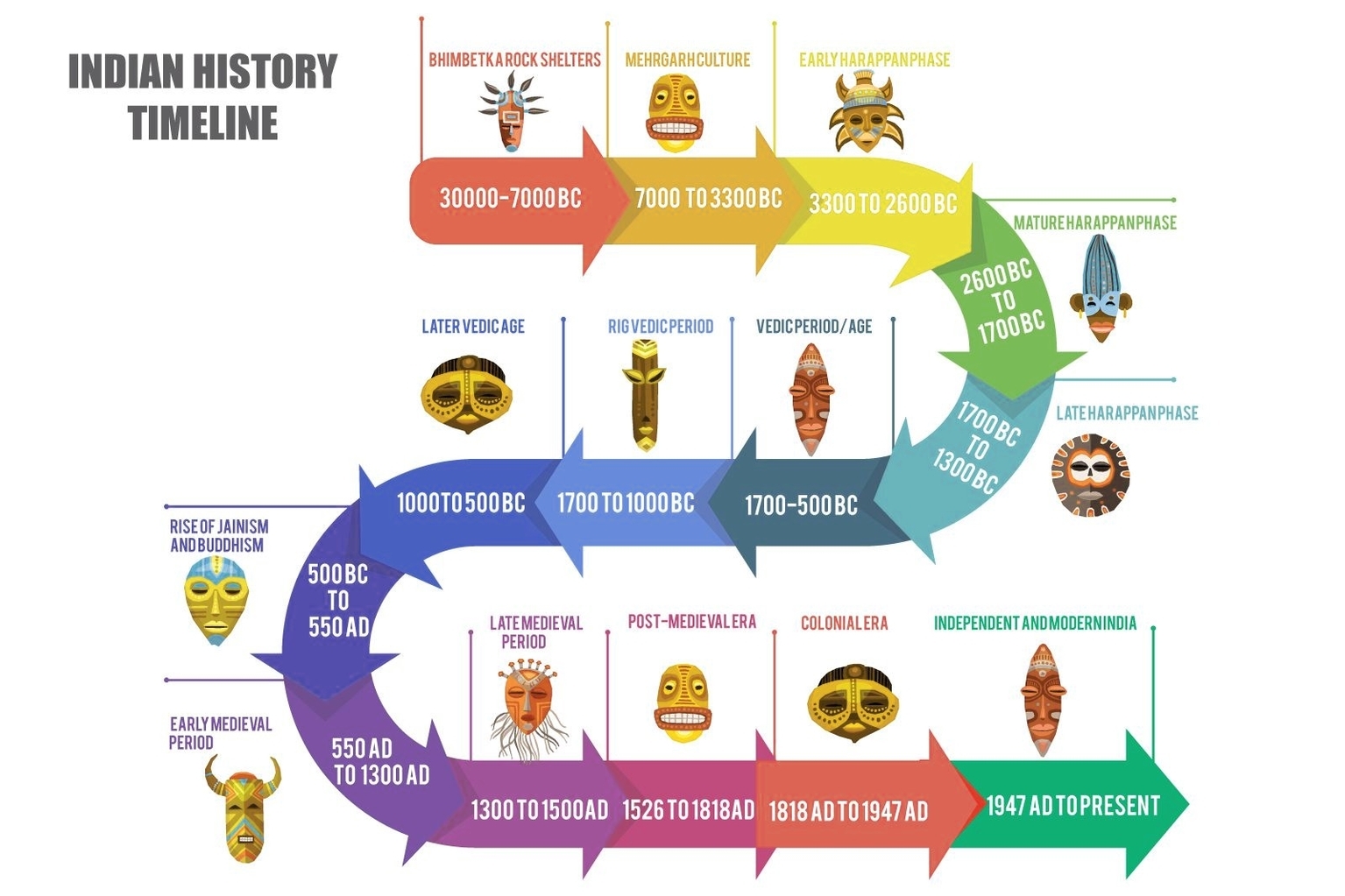
Indian history is a vast and diverse subject that spans thousands of years and covers many aspects of the subcontinent’s culture, politics, religion, and society. Here is a brief overview of some of the major periods and events in Indian history, based on the web search results:
– Prehistoric India (2 million BC 1500 BC): This period includes the emergence of early human ancestors, such as Homo erectus and Homo sapiens, who used stone tools and fire. The earliest evidence of human settlement in India is found in the Bhimbetka rock shelters, which date back to 30,000 BC. The Indus Valley Civilization, one of the oldest urban civilizations in the world, flourished from 3300 BC to 1300 BC, and developed a sophisticated system of writing, trade, and urban planning.
– Vedic India (1500 BC 500 BC): This period is marked by the arrival of the Indo-Aryan people, who brought with them the Vedic religion, the precursor of Hinduism. The Vedas, the oldest scriptures of Hinduism, were composed during this time. The Vedic society was divided into four varnas, or classes, based on occupation and birth. The Vedic people also established several kingdoms, known as janapadas, which later formed the basis of the Mahajanapadas, or great kingdoms.
– Classical India (500 BC 550 AD): This period witnessed the rise and fall of several empires and dynasties, such as the Mauryan Empire, the Kushan Empire, the Gupta Empire, and the Harsha Empire. These empires expanded their territories through conquest and diplomacy, and promoted art, literature, science, and culture. Some of the notable figures of this period include Ashoka, Chandragupta Maurya, Kanishka, Chandragupta II, and Harshavardhana. This period also saw the development of various schools of philosophy, such as Buddhism, Jainism, Hinduism, and Ajivika. The concept of zero, the decimal system, and the chess game were invented in India during this time.
– Medieval India (550 AD 1526 AD): This period is characterized by the invasion and rule of various foreign dynast
