Biodiversity is the variety of life on Earth, and it is essential for the functioning of ecosystems and the provision of ecosystem services. Agriculture is one of the main drivers of biodiversity loss, as it converts natural habitats into monocultures, degrades soil quality, pollutes water resources, and contributes to climate change. However, agriculture can also be part of the solution, if it is managed in a way that supports and enhances biodiversity both in and around farms.
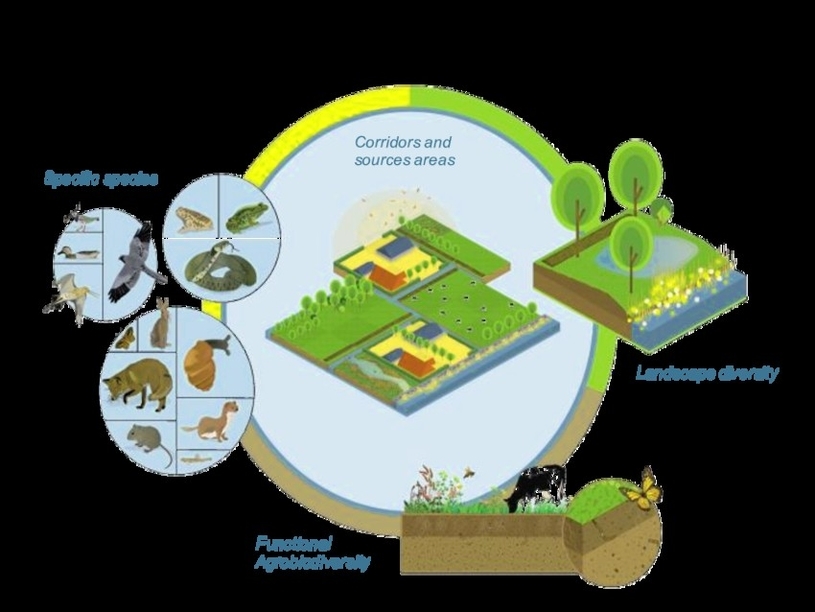
Four interconnected pillars for biodiversity in and around agriculture are:
– Functional agrobiodiversity: This refers to the diversity of plants, animals, and microorganisms that perform ecological functions within agricultural systems, such as pollination, pest control, nutrient cycling, and soil formation. Functional agrobiodiversity can improve crop productivity, resilience, and quality, as well as reduce the need for external inputs such as fertilizers and pesticides. Examples of practices that enhance functional agrobiodiversity include intercropping, crop rotation, cover cropping, agroforestry, and organic farming.
– Landscape diversity: This refers to the diversity of land use types and spatial patterns within and around farms, such as crop fields, pastures, hedgerows, woodlands, wetlands, and ponds. Landscape diversity can provide habitats and resources for wildlife, as well as buffer zones and corridors for connectivity and dispersal. Landscape diversity can also increase the aesthetic, cultural, and recreational value of agricultural landscapes,
