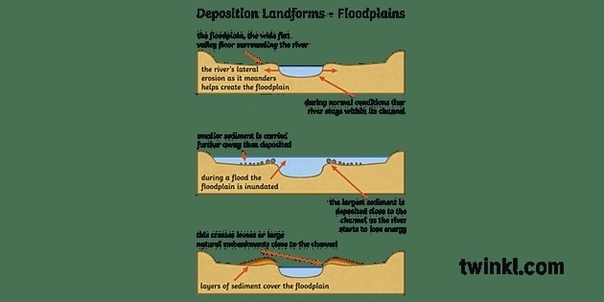
Deposition plan view rivers are rivers that have a sinuous or meandering shape in their plan view, meaning the map view of the river. They are formed and maintained by the erosion of the outer banks and the deposition of sediment on the inner banks of the river bends, creating point bars. Deposition plan view rivers are the most stable and efficient channel geometry to conduct water and sediment over any surface, as they minimize the variability of energy distribution in the river flow.
ome of the features and processes of deposition plan view rivers are:
– Wavelength and amplitude: These are the parameters used to describe the geometry of the meander bends. Wavelength is the distance between two successive bends in the same direction, and amplitude is the distance from the centerline of the channel to the apex of the bend.
– Meander neck: This is the narrow part of the meander bend, between adjacent reaches of the channel above and below the bend. Meander necks can be cut off by the river during floods, forming oxbow lakes.
– Point bar: This is the smooth and gently sloping body of sand on the inner bank of the meander bend, where sediment is deposited by the river. Point bars grow laterally as the river migrates across the floodplain, creating a characteristic scroll pattern of ridges and swales.
– Cut bank: This is the steep bank or cliff on the outer bank of the meander bend, where the river erodes the consolidated or semi-consolidated sediment. Cut banks are undercut by the river, causing the collapse of large masses of sediment into the channel.
– Flow-transverse profile: This is the cross-sectional profile of the river, showing the depth and velocity of the flow. The flow is deepest and fastest near the outer bank, where erosion occurs, and shallowest and slowest near the inner bank, where deposition occurs. The isovels, or lines of equal velocity, are asymmetrical and skewed toward the outer bank.
Deposition plan view rivers are influenced by various factors, such as the discharge, sediment load, slope, and valley width of the river, as well as the resistance and cohesion of the bank material. They are also affected by external factors, such as climate change, tectonic activity, human intervention, and vegetation. Deposition plan view rivers are dynamic and complex systems that constantly adjust to changing conditions, creating diverse and rich habitats for flora and fauna.
ources:
