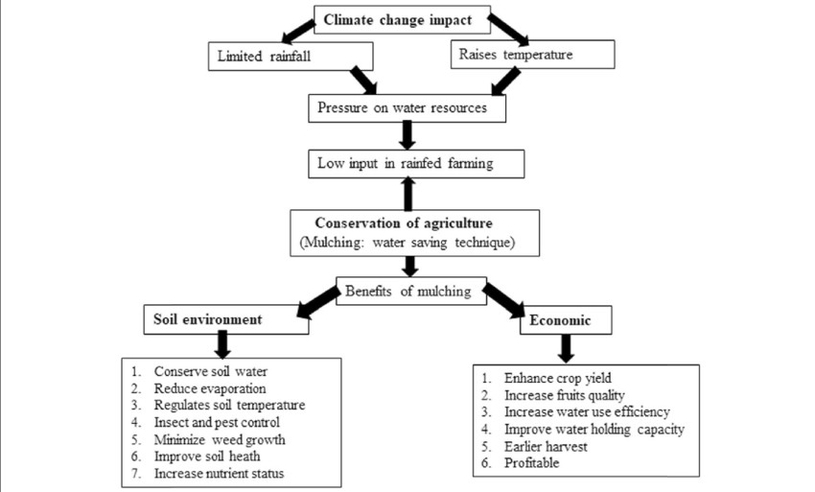
Conservation Agriculture (CA) is a farming system that aims to protect soil from erosion and degradation, and then increase crop yields. It promotes maintenance of a permanent soil cover, minimum soil disturbance, and diversification of plant species . CA is a sustainable approach method to improve agricultural production . The principles of CA are universally applicable to all agricultural landscapes and land uses with locally adapted practices . Soil interventions such as mechanical soil disturbance are reduced to an absolute minimum or avoided, and external inputs such as agrochemicals and plant nutrients of mineral or organic origin are applied optimally and in ways and quantities that do not interfere with, or disrupt, the biological processes . CA facilitates good agronomy, such as timely operations, and improves overall land husbandry for rainfed and irrigated production .
The benefits of CA are numerous. It can prevent losses of arable land while regenerating degraded lands . It enhances biodiversity and natural biological processes above and below the ground surface, which contribute to increased water and nutrient use efficiency and to improved and sustained crop production . CA is a base for sustainable agricultural production intensification. It opens increased options for integration of production sectors, such as crop-livestock integration and the integration of trees and pastures into agricultural landscapes .
CA is a management system that can prevent the loss of land suitable for cultivation and contribute to the restoration of degraded soils . It is a sustainable approach to agriculture that can help farmers to produce more food with fewer resources . CA is a promising solution to the challenges of food security and climate change . By adopting CA, farmers can reduce their environmental footprint and increase their resilience to climate change .
In conclusion, Conservation Agriculture is a sustainable approach to agriculture that can help farmers to produce more food with fewer resources. It promotes maintenance of a permanent soil cover, minimum soil disturbance, and diversification of plant species. The principles of CA are universally applicable to all agricultural landscapes and land uses with locally adapted practices. By adopting CA, farmers can reduce their environmental footprint and increase their resilience to climate change. CA is a promising solution to the challenges of food security and climate change..
