Bacteria are microscopic, single-celled organisms that live in almost every environment on Earth. They are prokaryotes, which means they do not have a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. Instead, their DNA is circular and located in a region called the nucleoid. Bacteria have different shapes, such as rods, spheres, and spirals. They also have different ways of obtaining energy and nutrients, such as photosynthesis, fermentation, or respiration. Some bacteria are beneficial for humans, plants, and animals, while others can cause diseases or infections. Here is an essay of approximately 1000 words about bacteria cells:
“`
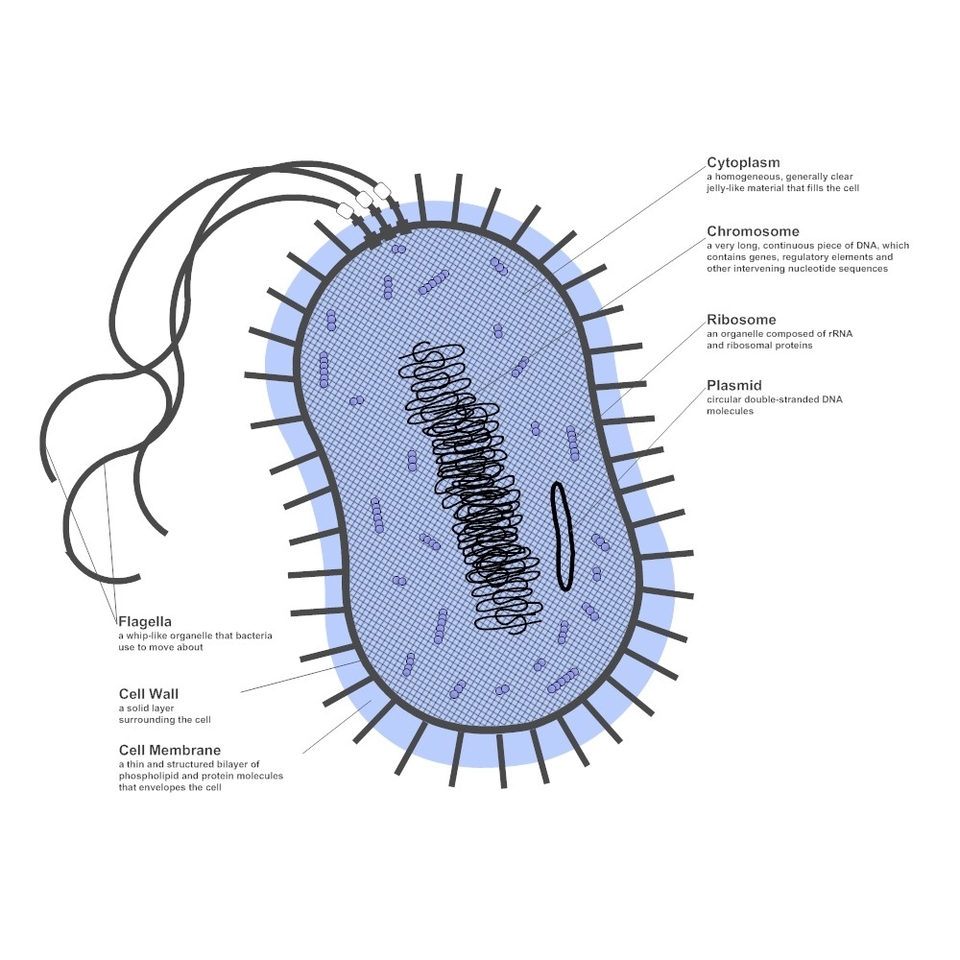
Bacteria are one of the most diverse and abundant groups of organisms on the planet. They are found in almost every habitat, from the deep sea to the human gut. They are also the oldest living forms of life, dating back to at least 3.5 billion years ago. Bacteria are single-celled organisms that belong to the domains Bacteria and Archaea, which are distinct from the domain Eukarya that includes animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Bacteria are prokaryotes, which means they do not have a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria or chloroplasts. Instead, they have a simple cell structure that consists of a plasma membrane, a cell wall, cytoplasm, ribosomes, and DNA.
The plasma membrane is a thin layer of phospholipids and proteins that surrounds the cell and regulates the passage of substances in and out of the cell. The cell wall is a rigid layer of peptidoglycan, a polymer of sugars and amino acids, that provides shape and protection to the cell. Some bacteria have an additional outer membrane that contains lipopolysaccharides, which are molecules that trigger immune responses in animals. Some bacteria also have structures that extend from the cell surface, such as flagella, pili, and fimbriae. Flagella are long, whip-like appendages that help the cell move by rotating. Pili and fimbriae are shorter, hair-like projections that help the cell attach to surfaces or exchange genetic material with other cells.
The cytoplasm is the fluid inside the cell that contains water, salts, enzymes, and other
