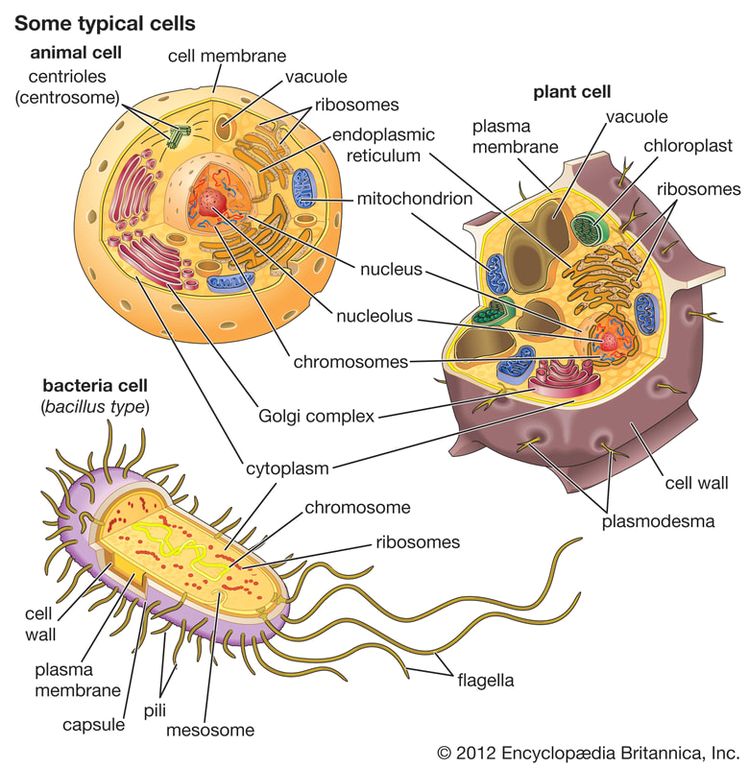
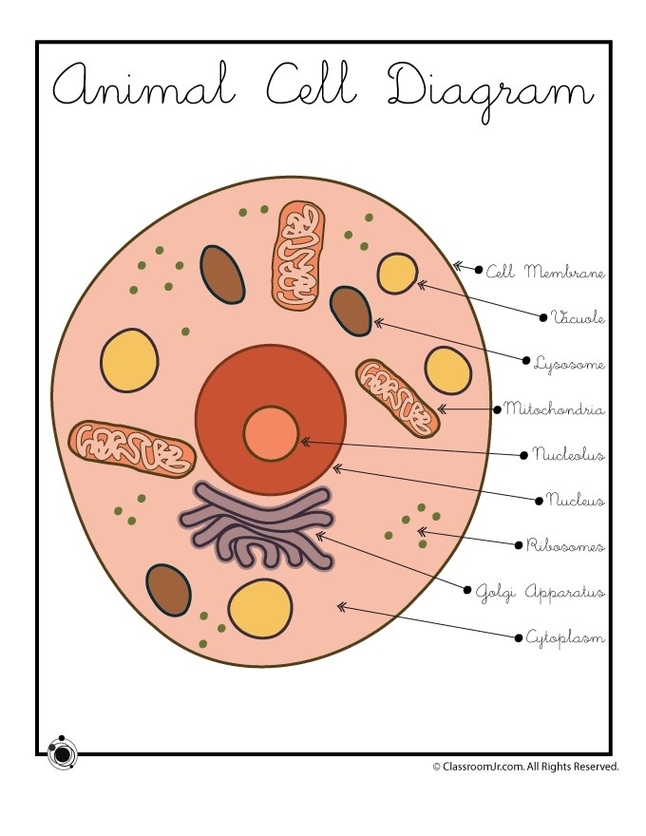
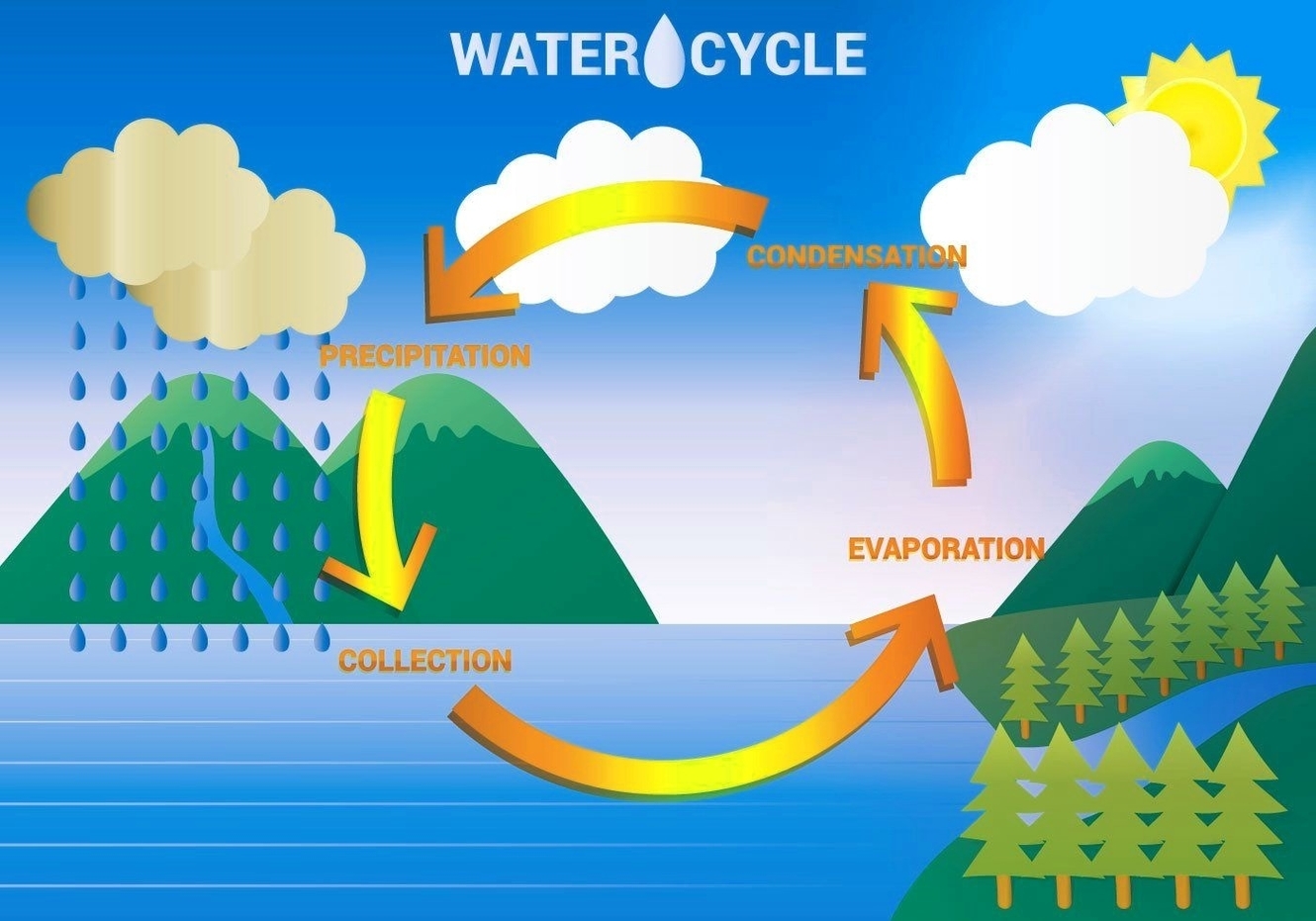
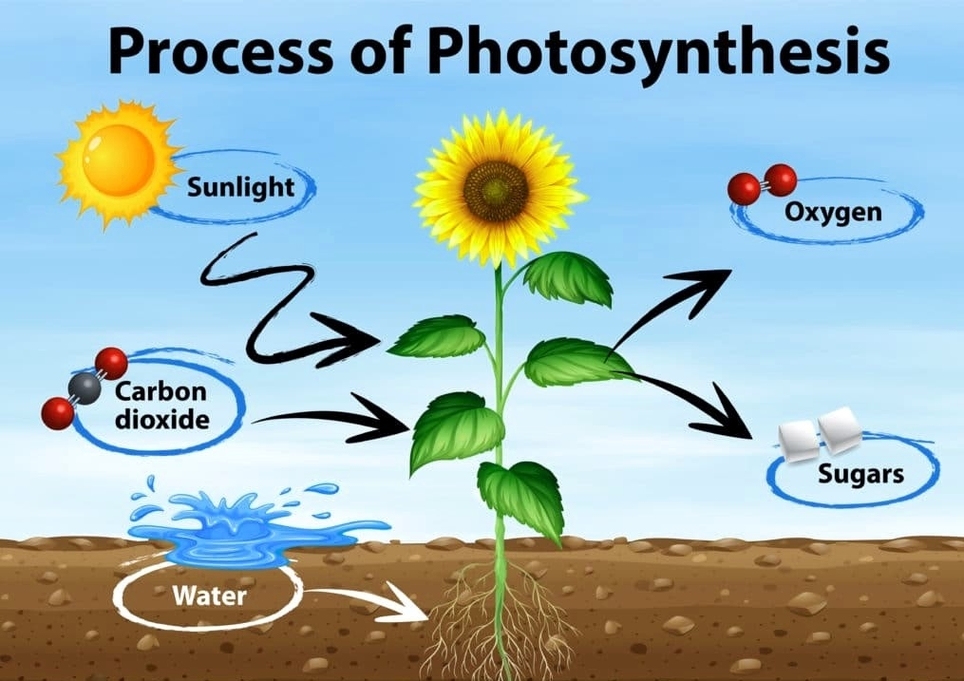
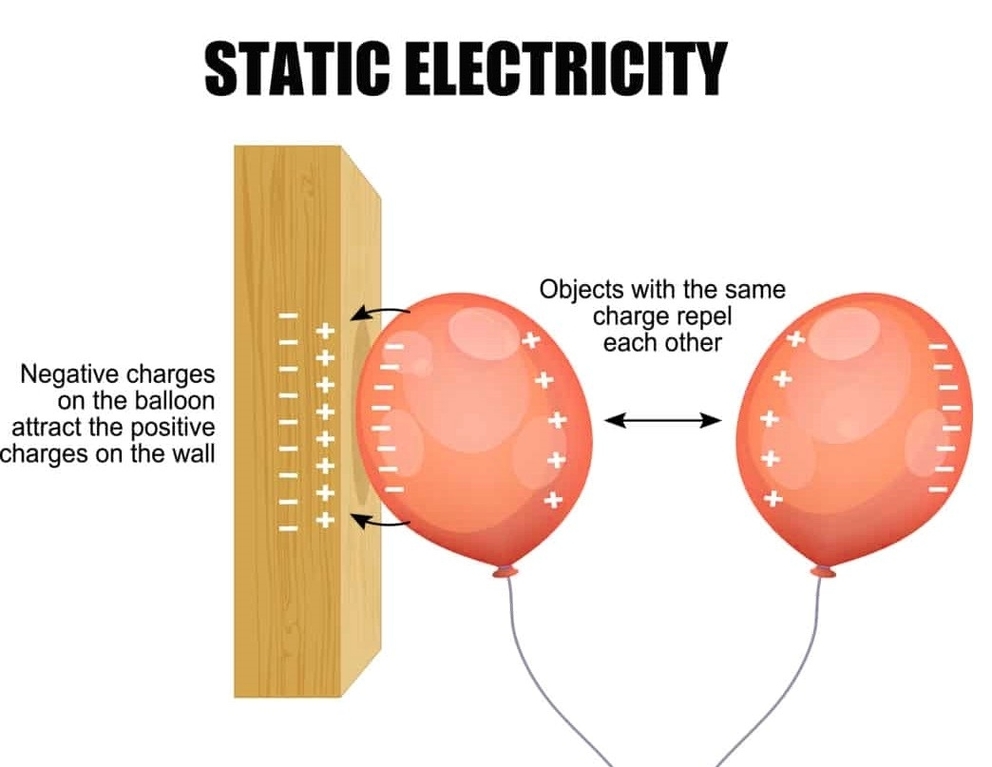
See the below image for the Cell types diagram. Types of Cells in the Human Body. 1 Stem Cells. Pluripotent stem cell. 2 Bone Cells. 3 Blood Cells. 4 Muscle Cells. 5 Fat Cells. More items
A cell type is a classification used to distinguish between morphologically or phenotypically distinct cell forms within a species. A multicellular organism may contain a number of widely differing and specialized cell types, such as muscle cells and skin cells in humans, that differ both in appearance and function yet are genetically identical.
Stem cells are cells that are yet to choose what they are going to become. Some differentiate to become a certain cell type, and others divide to produce more stem cells. They are found in both the embryo and some adult tissues, such as bone marrow. There are at least three primary types of bone cell: Osteoclasts, which dissolve bone.