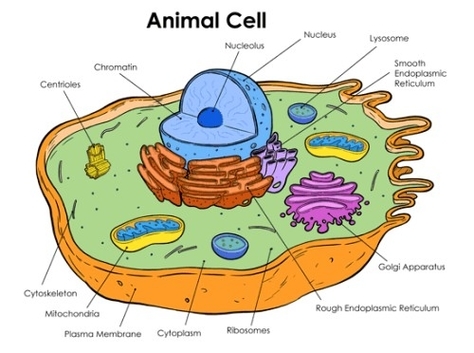
Animal Cell Definition: Animal cells, which are the fundamental units of life in the Animal Kingdom, are eukaryotic cells. This means that they contain a true (membrane-bound nucleus) along with other membrane-bound organelles.
An animal cell is a type of cell that differs from plant or fungi cells. Like plant and fungi cells, an animal cell is eukaryotic, but animal cells lack the cell wall structure found in plant and fungi cell types. Animal cells also do not contain chloroplasts as plant cells do, as animal cells are heterotrophic and do not perform photosynthesis.
Animal cells, which are the fundamental units of life in the Animal Kingdom, are eukaryotic cells. This means that they contain a true (membrane-bound nucleus) along with other membrane-bound organelles.
