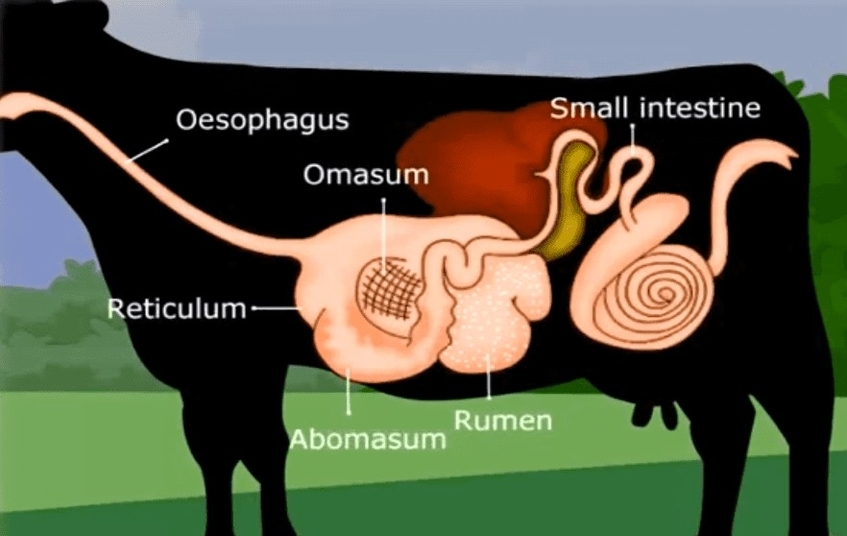
Ruminant Digestive System
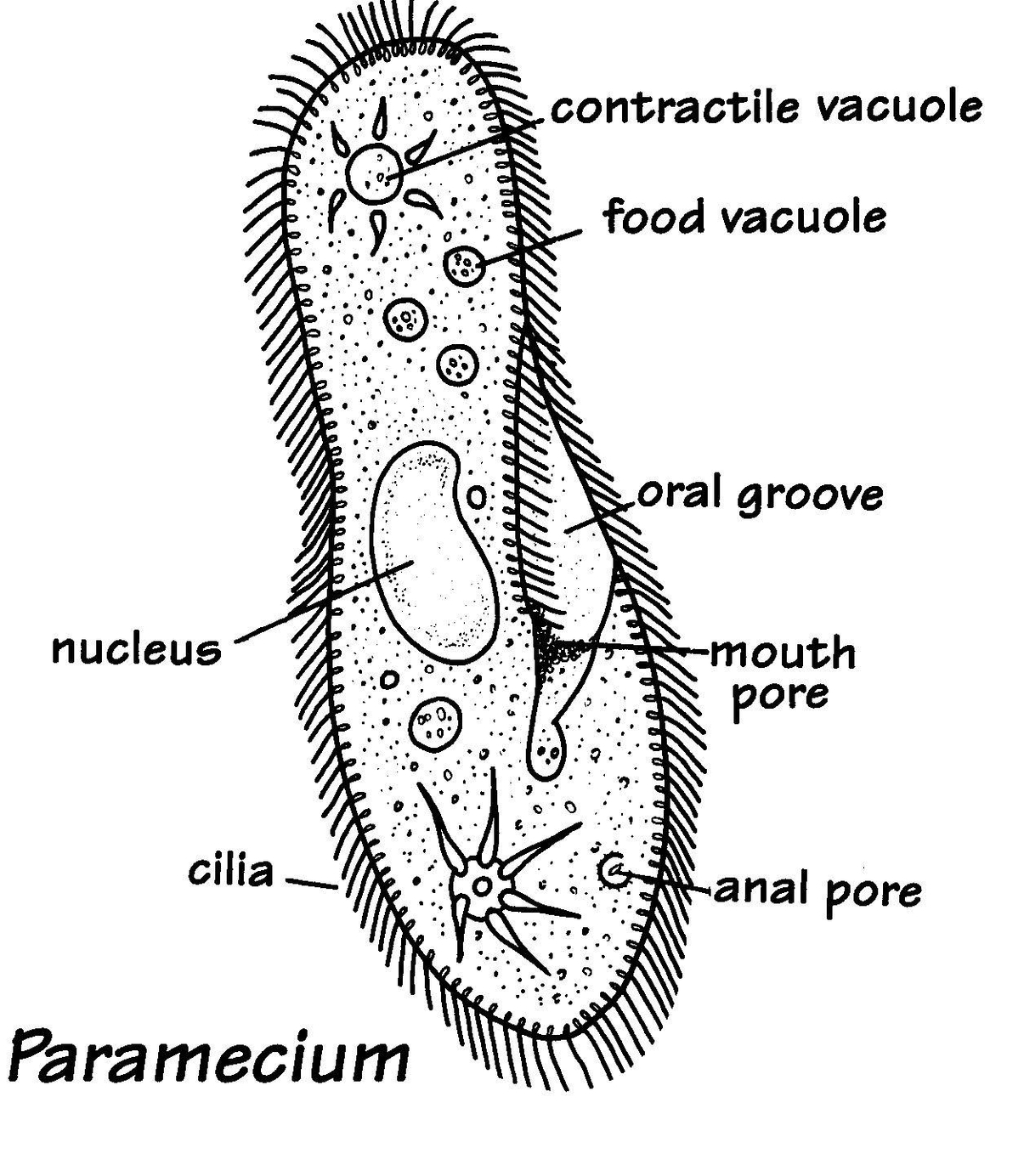
Ruminant animals are herbivores that have a unique digestive system that allows them to efficiently use fibrous plant material as their main source of energy. Ruminants include cattle, sheep, goats, deer, and camels. They have a four-compartment stomach that consists of the rumen, reticulum, omasum, and abomasum. Each compartment has a specific function in the digestion of feedstuffs.
The rumen is the largest and most important compartment of the ruminant stomach. It can hold up to 50 gallons of partially digested feed, water, and microbes. The rumen is a fermentation vat where bacteria, protozoa, and fungi break down complex carbohydrates, such as cellulose and hemicellulose, into simpler compounds, such as volatile fatty acids (VFAs), carbon dioxide, and methane. VFAs are the main source of energy for ruminants, and they are absorbed through the rumen wall into the bloodstream. The rumen also produces B vitamins, vitamin K, and amino acids from the microbial protein. The rumen microbes can use nonprotein nitrogen sources, such as urea and ammonia, to synthesize protein. The rumen is also involved in nitrogen recycling, where excess nitrogen is converted into urea and returned to the saliva or excreted in the urine.
The reticulum is the second compartment of the ruminant stomach. It is also known as the “honeycomb” because of its internal structure. The reticulum is connected to the rumen and functions as a sorting and mixing area. It separates the smaller, denser feed particles from the larger, lighter ones. The smaller particles are passed to the omasum, while the larger particles are regurgitated for further chewing. This process is called rumination or cud chewing, and it helps to reduce the particle size and increase the surface area of the feed for microbial digestion. Rumination also stimulates saliva production, which helps to buffer the rumen pH and provide water and minerals. Ruminants spend several hours a day ruminating, depending on the type and quality of feed they consume.
The omasum is the third compartment of the ruminant stomach. It is also known as the “manyplies” because of its many folds of tissue. The omasum acts as a filter and a pump. It filters out the water