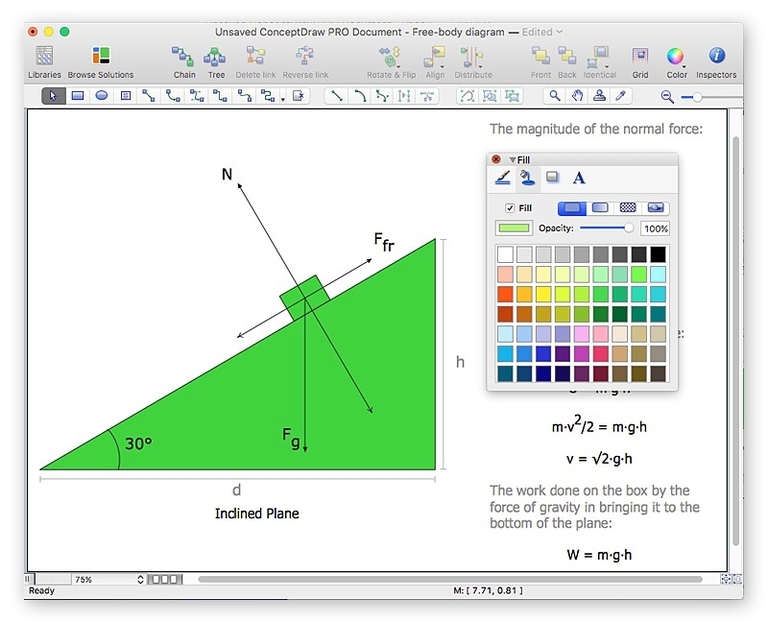
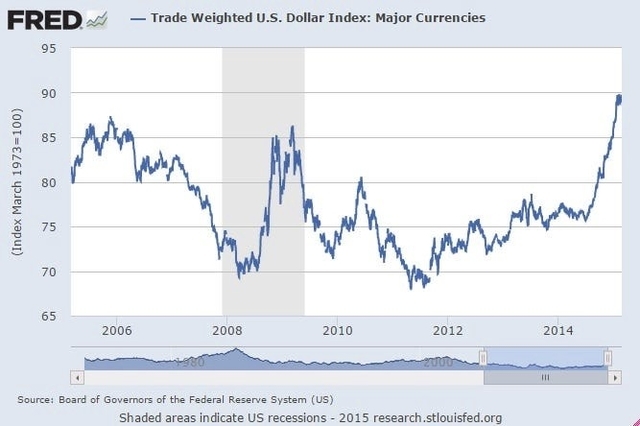
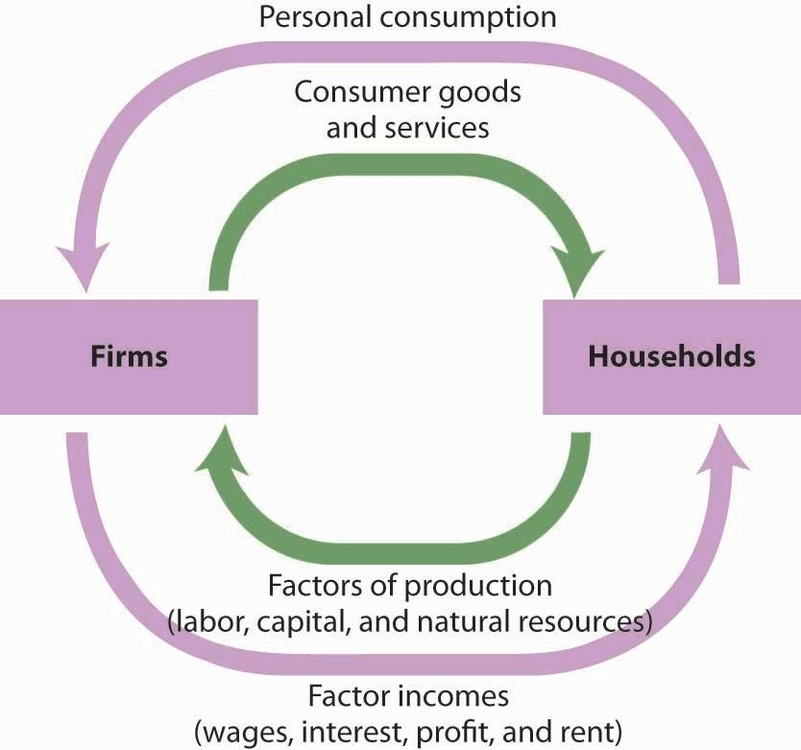
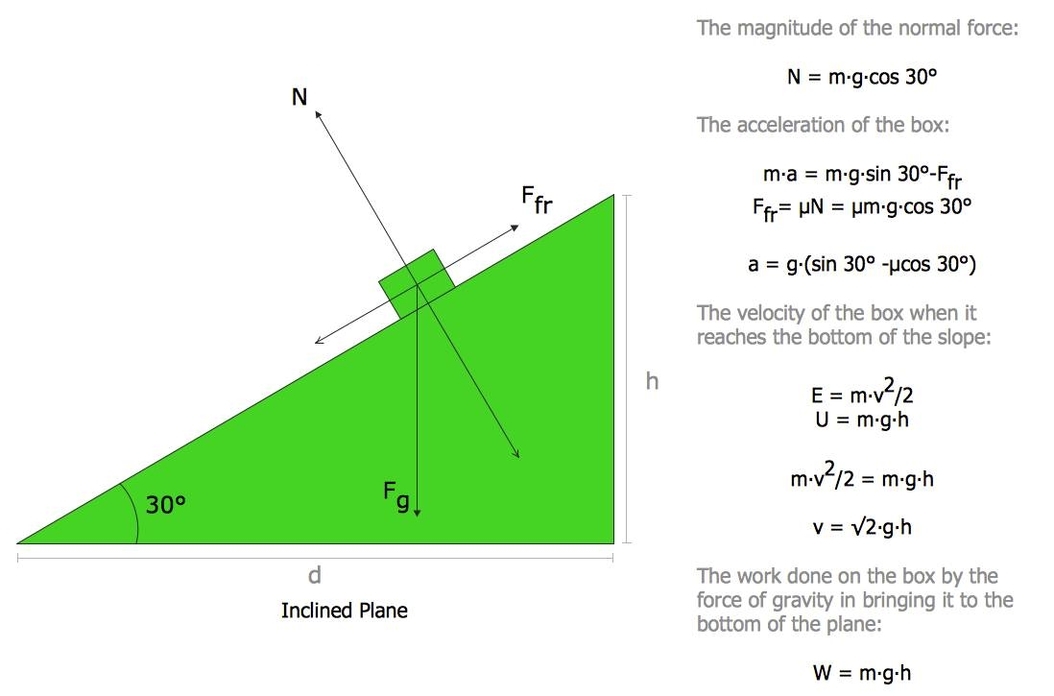
Drawing software is a computer program that allows users to create digital art. It is used by artists, designers, and illustrators to create a wide range of digital art, including illustrations, comics, animations, and more. There are many different types of drawing software available, ranging from simple, free programs to complex, professional-grade software.
According to a recent article on TechRadar, some of the best digital art and drawing software in 2024 include:
1. Adobe Photoshop: A professional-grade software that is widely used by artists and designers around the world. It offers a wide range of tools and features for creating digital art, including brushes, layers, and filters.
2. Corel Painter: A powerful digital painting software that is designed for professional artists. It offers a wide range of brushes and tools for creating realistic digital paintings.
3. Clip Studio Paint: A popular software that is used by many manga and comic artists. It offers a wide range of tools and features for creating comics, illustrations, and animations.
4. Krita: A free and open-source painting software that is designed for digital artists. It offers a wide range of brushes and tools for creating digital art, including illustrations, comics, and animations.
If you’re looking for free drawing software, TechRadar also recommends the following:
1. GIMP: A free and open-source image editing software that offers a wide range of tools and features for creating digital art.
2. Inkscape: A free and open-source vector graphics editor that is used for creating illustrations, logos, and other types of digital art.
3. Sketchpad: A free online drawing application that is suitable for all ages. It offers a wide range of tools and features for creating digital art, including brushes, layers, and filters.