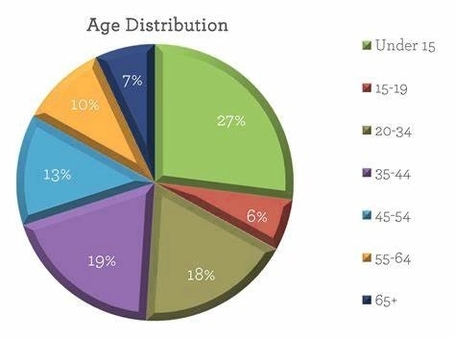
Age distribution pie charts are a type of graph that displays the proportion of different age groups in a population. The chart is circular in shape, with each slice representing a different age group. The size of each slice is proportional to the percentage of the population that falls within that age group. The chart is divided into sections, with each section representing a different age group. The sections are arranged in a circular pattern, with the youngest age group at the center and the oldest age group at the outer edge.
The age distribution pie chart is a useful tool for analyzing population demographics. It can be used to identify trends in population growth, as well as to compare the age distribution of different populations. For example, an age distribution pie chart might show that a population has a high proportion of young people, indicating that the population is growing rapidly. Alternatively, it might show that a population has a high proportion of elderly people, indicating that the population is aging.
According to Statistics Canada, age pyramids are dynamic applications that allow users to see the evolution of the age structure of the Canadian population over a given time period and for selected geographies . The age pyramid is a type of age distribution graph that displays the percentage of the population in each age group, with males on one side and females on the other. The age pyramid is divided into sections, with each section representing a different age group. The sections are arranged in a pyramid shape, with the youngest age group at the bottom and the oldest age group at the top.