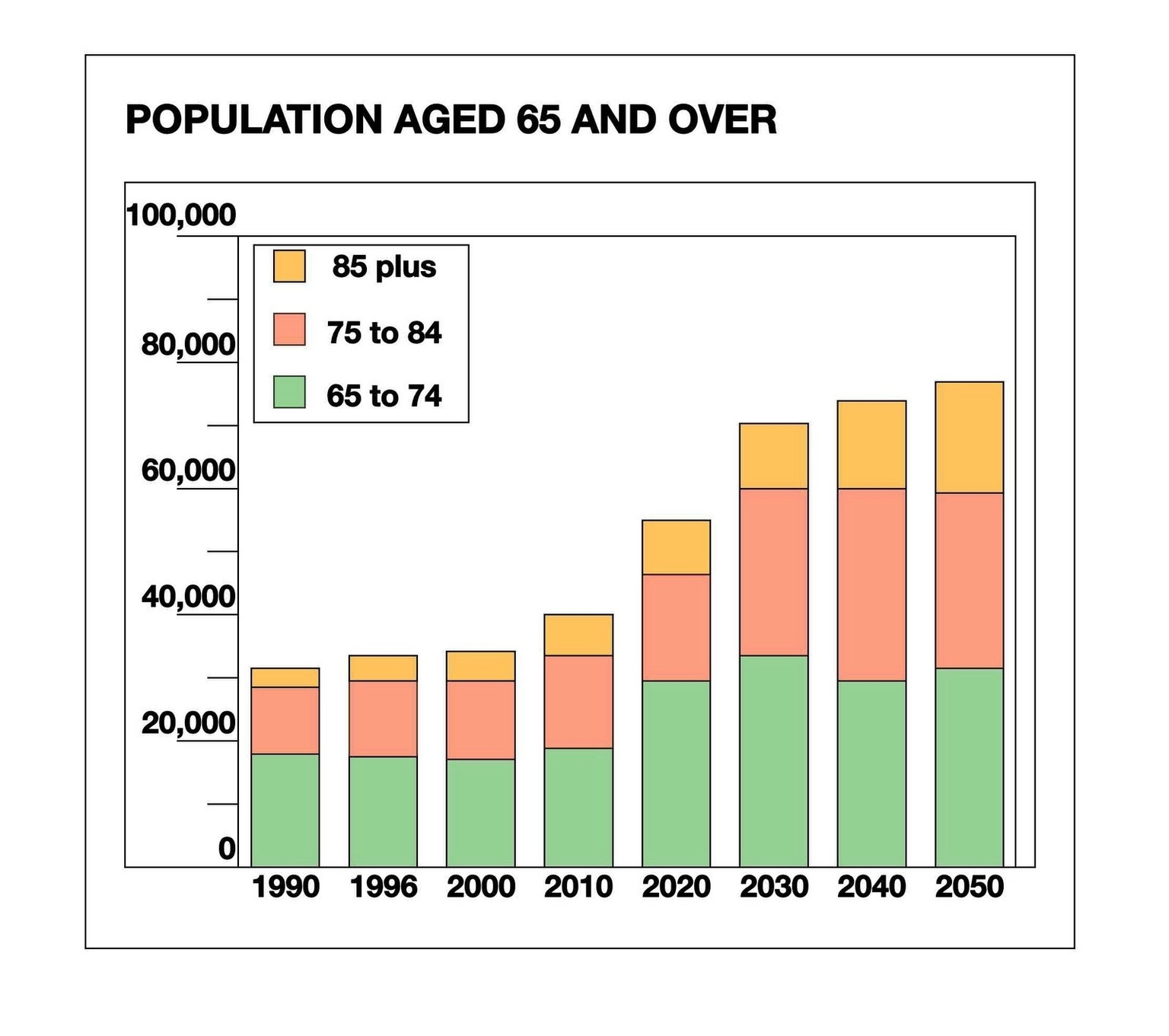
The world’s population is ageing at an unprecedented rate, and this demographic shift poses significant challenges to health and social systems worldwide. By 2050, the proportion of the world’s population over 60 years will nearly double from 12% to 22%. In Canada, the aging of the population is expected to have a significant impact on the country’s economy, society, and health care system over the next 25 to 30 years.
As people age, they are more likely to experience several conditions at the same time. Common health conditions in older age include hearing loss, cataracts and refractive errors, back and neck pain and osteoarthritis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, diabetes, depression, and dementia. The emergence of several complex health states commonly called geriatric syndromes is also common in older age. They are often the consequence of multiple underlying factors and include frailty, urinary incontinence, falls, delirium, and pressure ulcers.
The aging population is also associated with an increased risk of chronic diseases such as dementias, heart disease, type 2 diabetes, arthritis, and cancer. These are the nation’s leading drivers of illness, disability, death, and health care costs.
The United Nations Decade of Healthy Ageing (2021-2030) seeks to reduce health inequities and improve the lives of older people, their families, and communities through collective action in four areas: changing how we think, feel and act towards age and ageism; developing communities in ways that foster the abilities of older people; delivering person-centered integrated care and primary health services responsive to older people; and providing older people who need it with access to quality long-term care.
In conclusion, the aging population is a global phenomenon that poses significant challenges to health and social systems worldwide. The United Nations Decade of Healthy Ageing aims to reduce health inequities and improve the lives of older people, their families, and communities through collective action in four areas.
