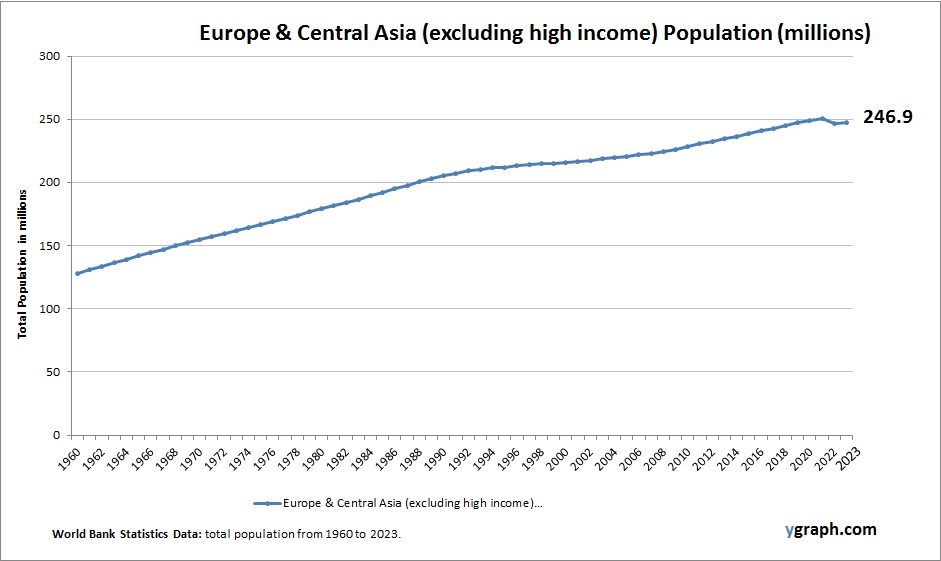
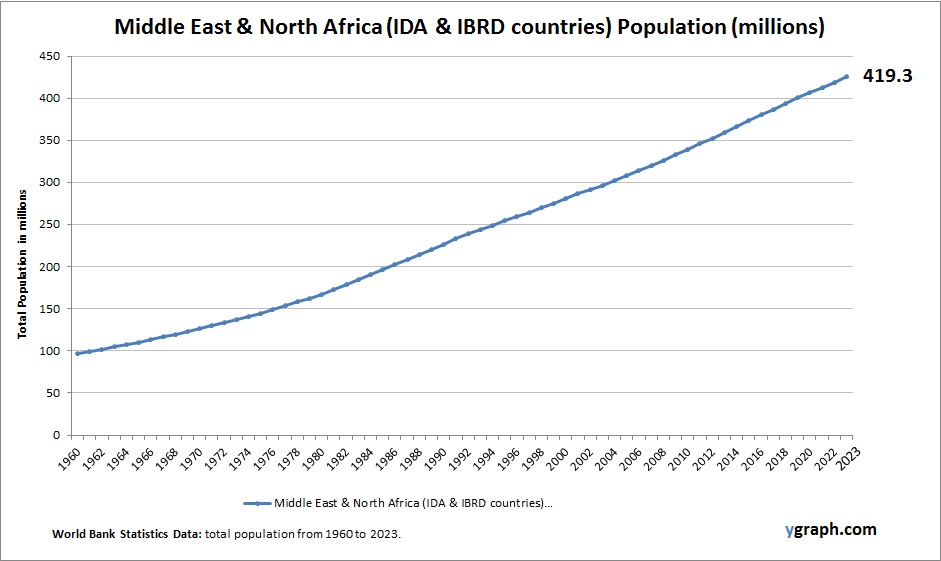
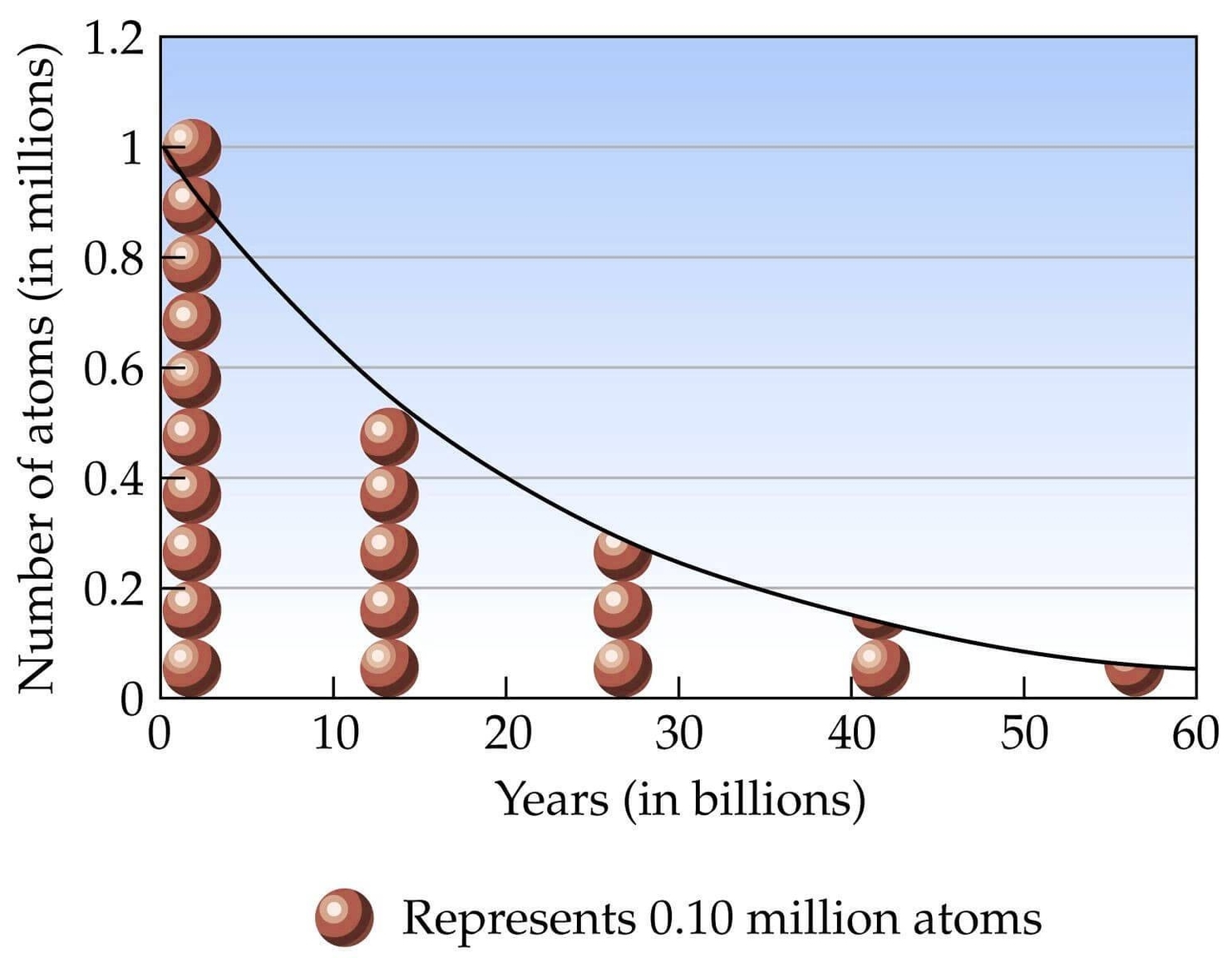
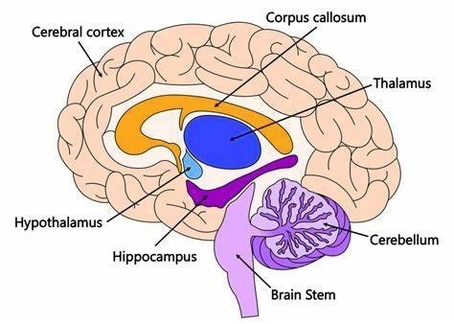
A Timeline Flow Chart Example is a visual representation that organizes events, milestones, or processes in chronological order, often using arrows or linear connections to show the progression over time. This type of chart is particularly effective for illustrating historical developments, project schedules, business growth, product launches, or policy changes in a way that is easy to follow and understand. Each point on the timeline typically includes a date or time reference alongside a brief description of the event, allowing viewers to grasp both the sequence and significance of each step. Unlike traditional timelines, which might simply place events on a straight line, a timeline flow chart integrates directional flow and sometimes branching paths, making it useful for showing dependencies, cause-and-effect relationships, or decision points within a process. For example, in an economics or GDP context, a timeline flow chart might trace the major financial reforms, economic crises, or growth spurts of a country over decades, linking them to changes in policy or global events. This layered structure not only helps highlight the progression but also clarifies how one stage leads to the next. As a tool, a timeline flow chart is versatile, intuitive, and ideal for presentations, reports, or educational content where clarity and sequence are critical.ow it can help you!.