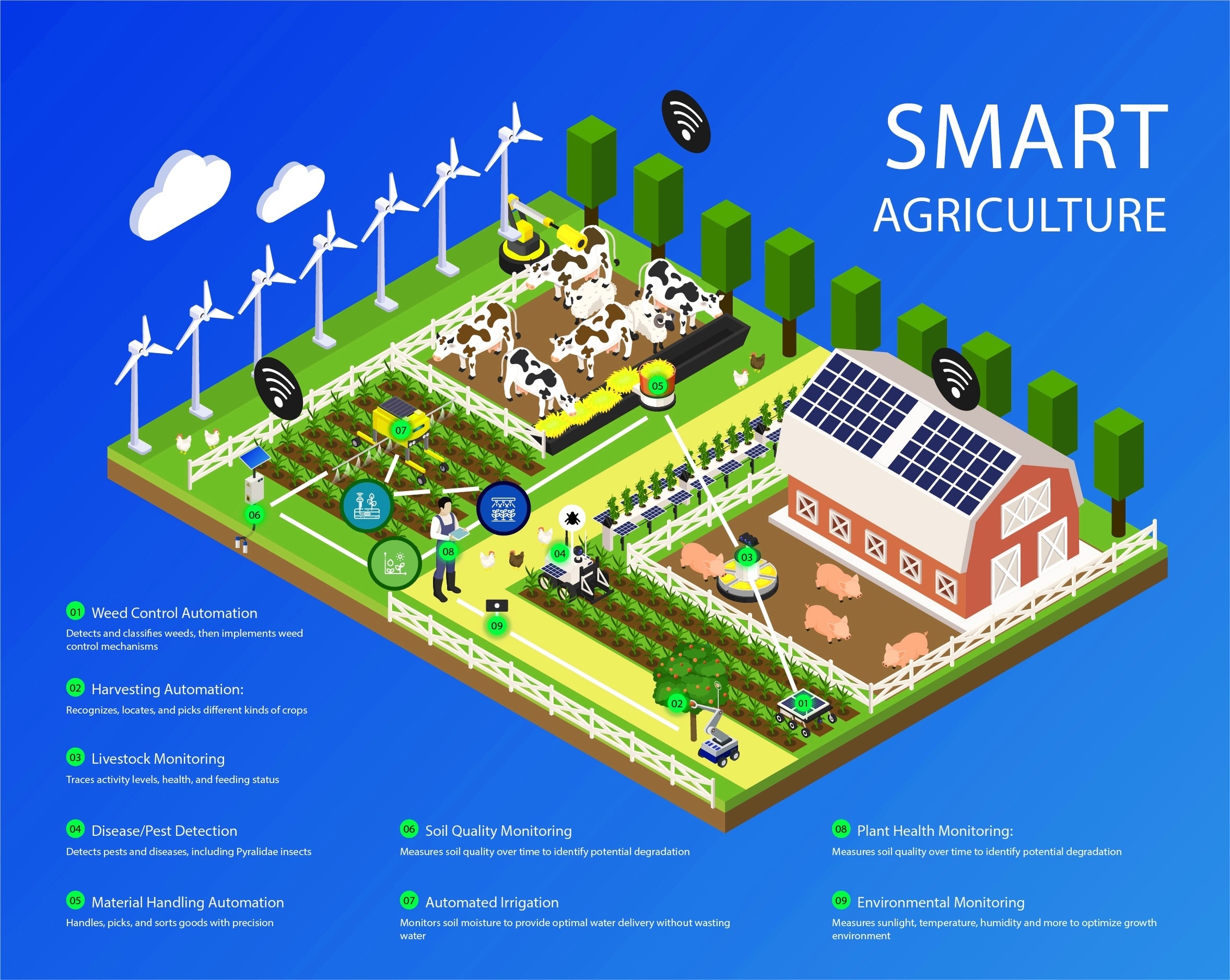
Smart agriculture is the application of technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud computing to improve the efficiency, productivity, and sustainability of farming practices. Smart agriculture aims to address the challenges of increasing food demand, climate change, labor shortage, and environmental impact in the agriculture sector. Here is a brief overview of how AI, IoT, and cloud computing can enable smart agriculture solutions:
– AI is the ability of machines to perform tasks that normally require human intelligence, such as perception, reasoning, learning, decision making, and problem solving. AI can help farmers to analyze data from various sources, such as sensors, satellites, drones, weather stations, and historical records, to optimize crop growth, yield, and quality. AI can also assist farmers in detecting pests, diseases, weeds, and nutrient deficiencies, and provide recommendations for the best management practices. AI can also automate tasks such as irrigation, fertilization, harvesting, and sorting, by using robots, drones, or autonomous vehicles.
– IoT is the network of physical objects that are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies that enable them to communicate and exchange data with other devices and systems over the internet. IoT can help farmers to monitor and control various aspects of their farms, such as soil moisture, temperature, humidity, pH, light, water level, and crop health, by using smart devices and wireless communication. IoT can also help farmers to track and manage their livestock, equipment, and resources, by using RFID tags, GPS, and cameras. IoT can also help farmers to reduce waste, energy consumption, and greenhouse gas emissions, by using smart meters, valves, and switches.
– Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services, such as servers, storage, databases, software, analytics, and intelligence, over the internet. Cloud computing can help farmers to store, process, and access large amounts of data from various sources, such as sensors, satellites, drones, weather stations, and historical records, by using cloud platforms and applications. Cloud computing can also help farmers to share and collaborate with other stakeholders, such as researchers, extension agents, suppliers, and consumers, by using cloud services and tools. Cloud computing can also help farmers to scale up or down their computing resources, depending on their needs and budget, by using cloud models and pricing.
In conclusion, smart agriculture is the integration of AI, IoT, and cloud computing technologies to enhance the performance and profitability of farming practices. Smart agriculture can benefit farmers by providing them with data-driven insights, recommendations, and automation, to improve their decision making, efficiency, and sustainability. Smart agriculture can also benefit the society and the environment by increasing food security, quality, and safety, while reducing resource consumption, waste, and pollution. Smart agriculture is expected to be a key driver for the digital transformation and innovation of
