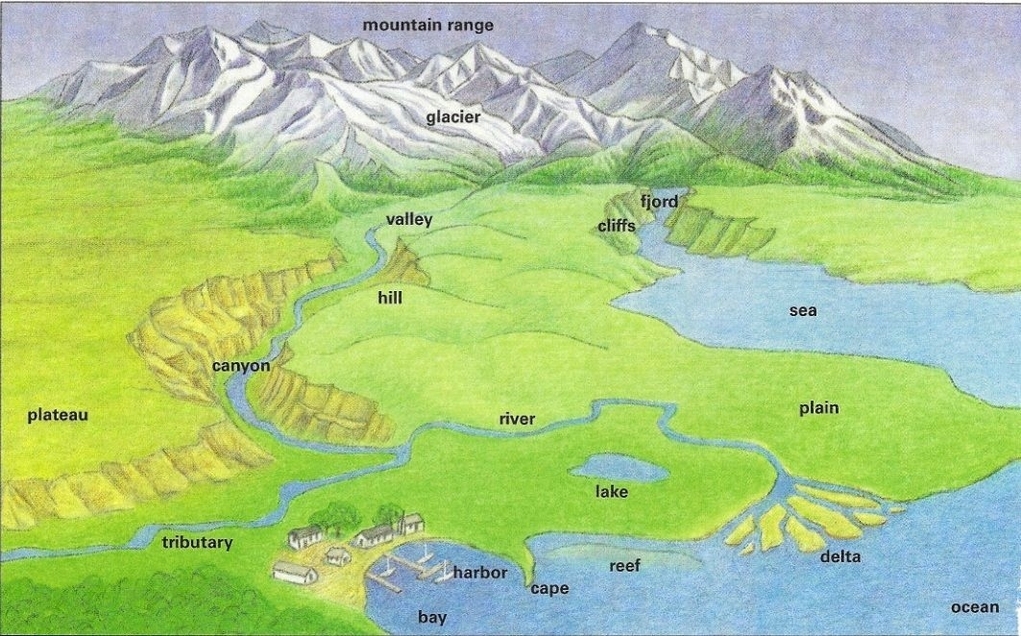
Physical features are the natural characteristics of the Earth’s surface, such as mountains, valleys, rivers, lakes, and oceans. They are shaped by various forces, such as plate tectonics, erosion, weathering, and climate. Physical features influence the distribution and diversity of life on Earth, as well as the human activities and cultures that develop in different regions.
Landforms are the specific shapes and forms of the Earth’s surface, such as hills, plateaus, canyons, and deltas. They are classified into three main types: mountains, plains, and plateaus. Mountains are high, steep, and rugged landforms that rise above the surrounding land. They are formed by the collision, folding, or volcanic activity of tectonic plates. Plains are flat or gently rolling landforms that cover large areas of land. They are formed by the deposition of sediments by rivers, glaciers, or wind. Plateaus are elevated landforms that have a flat or slightly sloping surface. They are formed by the uplift of large blocks of land or by the erosion of surrounding land.
Bodies of water are the areas of water that cover most of the Earth’s surface, such as oceans, seas, lakes, rivers, and streams. They are classified into two main types: saltwater and freshwater. Saltwater bodies of water are the oceans and seas that contain high concentrations of dissolved salts and minerals. They cover about 71% of the Earth’s surface and are connected by currents and tides. Freshwater bodies of water are the lakes, rivers, streams, and ponds that contain low concentrations of dissolved salts and minerals. They cover about 1% of the Earth’s surface and are mainly fed by precipitation and runoff.
Physical features, landforms, and bodies of water are interrelated and interdependent. They affect and are affected by each other in various ways. For example, mountains can influence the climate and precipitation of a region, as well as the flow and direction of rivers. Rivers can carve out valleys and canyons, as well as deposit sediments and nutrients in deltas and lakes. Lakes can provide habitats for aquatic life, as well as sources of water for irrigation and drinking. Oceans can moderate the temperature and humidity of the land, as well as transport heat and moisture across the globe.
Physical features, landforms, and bodies of water are also important for human society and civilization. They provide natural resources, such as water, minerals, soil, and energy. They offer opportunities for recreation, tourism, and exploration. They pose challenges and hazards, such as floods, droughts, landslides, and earthquakes. They shape the history, culture, and identity of different peoples and nations. They inspire the imagination, creativity, and curiosity of human beings.
In conclusion, physical features, landforms, and bodies of water are the essential components of the Earth’s surface. They are the result of complex and dynamic processes that occur within and on the Earth. They are the basis of the natural environment and the human environment. They are the source of beauty and wonder, as well as of problems and solutions. They are the subject of study and discovery, as well as of appreciation and preservation. They are the physical features of our planet.
