Market equilibrium is a state of balance between the supply and demand of a particular good or service. It is the point at which the quantity of goods or services that consumers are willing to buy is equal to the quantity that producers are willing to sell at a given price. When the market is in equilibrium, there is no tendency for prices to change. The market-clearing price has been achieved, and the quantity of goods or services exchanged is at its maximum.
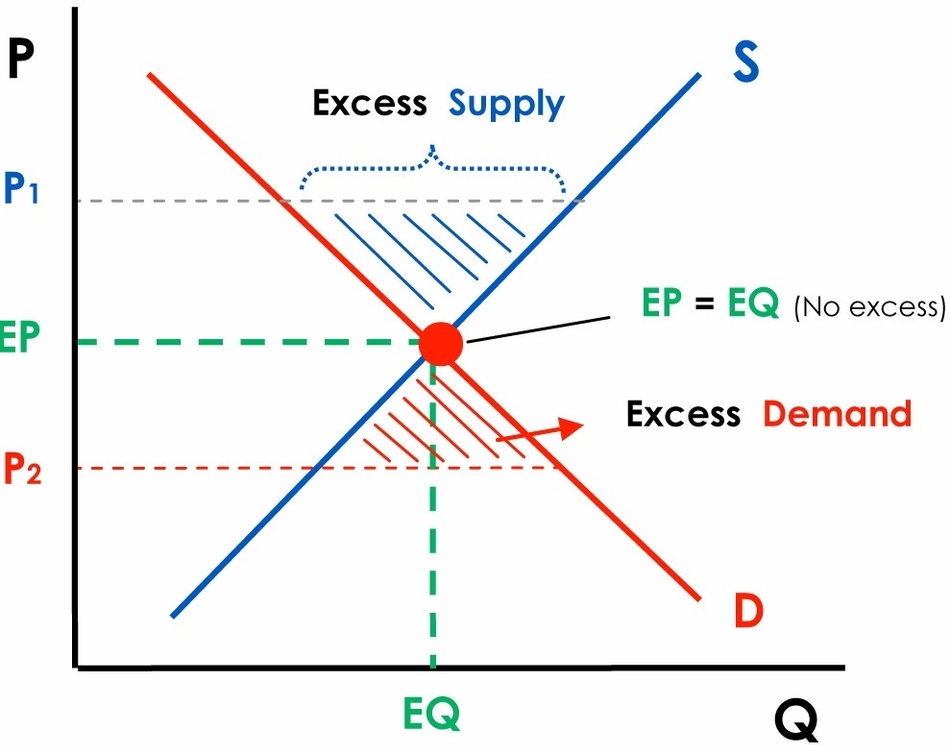
The price mechanism refers to how supply and demand interact to set the market price and amount of goods sold. At most prices, planned demand does not equal planned supply. This is a state of disequilibrium because there is either a shortage or surplus, and firms have an incentive to change the price. Market equilibrium can be shown using supply and demand diagrams. In the diagram, the equilibrium price is the point where the supply and demand curves intersect. The equilibrium quantity is the quantity of goods or services exchanged at that price.
If the price is below the equilibrium, there is a shortage of goods or services. Firms will put up prices and supply more. As the price rises, there will be a movement along the demand curve, and less will be demanded. Therefore, the price will rise to the equilibrium price until there is no shortage, and supply equals demand.
If the price is above the equilibrium, there is a surplus of goods or services. Firms will reduce prices and supply less. This would encourage more demand, and therefore the surplus will be eliminated. The new market equilibrium will be at a lower price and a higher quantity of goods or services exchanged.
Market equilibrium can be influenced by changes in demand or supply, and it affects the price mechanism. An increase in demand would shift the demand curve to the right, leading to a new equilibrium at a higher price and quantity of goods or services exchanged. An increase in supply would lead to a lower price and more quantity sold.
In conclusion, market equilibrium is a fundamental concept in economics that describes the balance between supply and demand. It is the point at which the quantity of goods or services that consumers are willing to buy is equal to the quantity that producers are willing to sell at a given price. The price mechanism refers to how supply and demand interact to set the market price and amount of goods sold. Market equilibrium can be shown using supply and demand diagrams, and it can be influenced by changes in demand or supply. Understanding market equilibrium is essential for businesses and policymakers to make informed decisions about pricing, production, and resource allocation.
