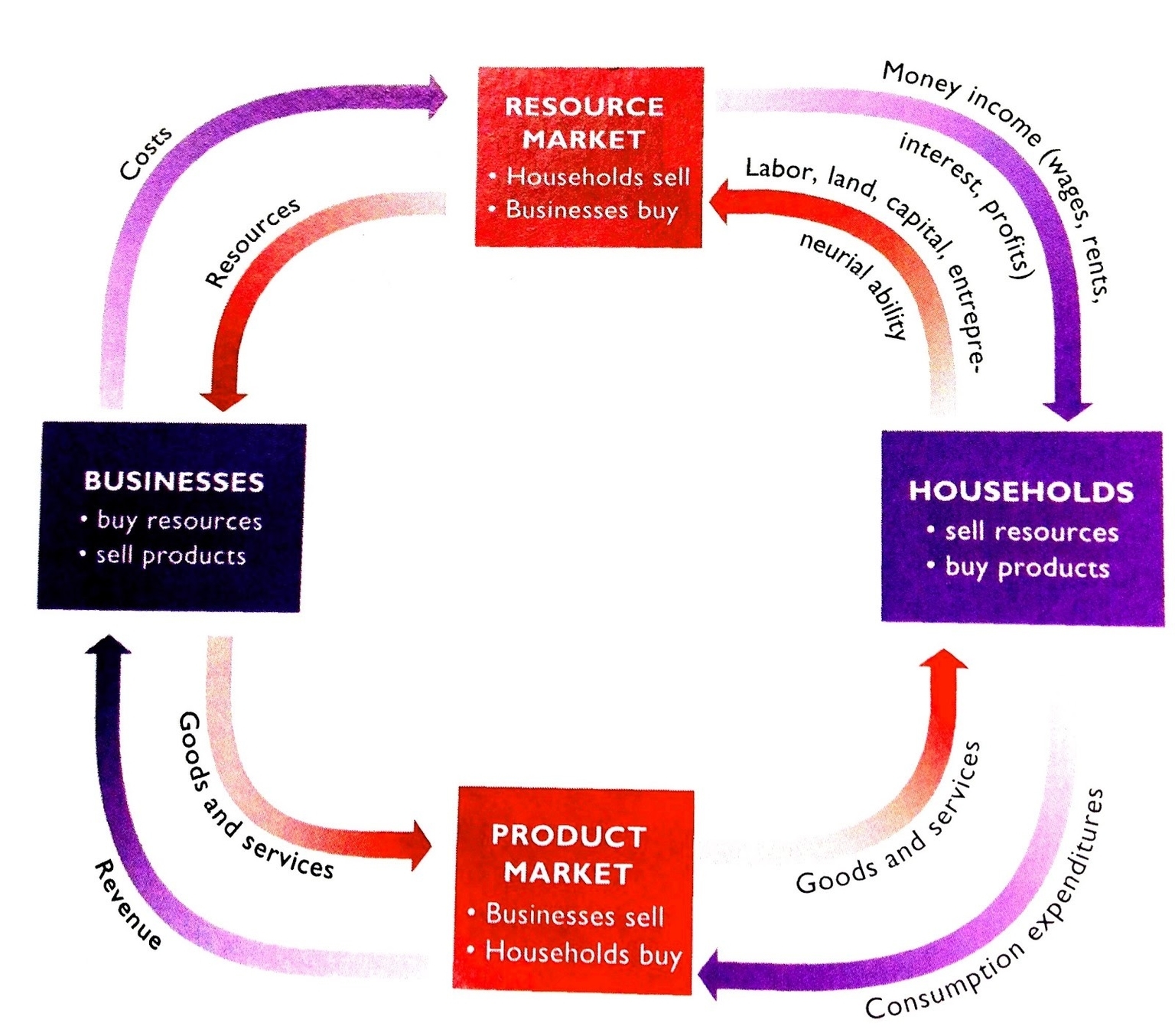
The Circular Flow Model is a fundamental concept in macroeconomics that describes how money, goods, and services move between sectors in an economic system . The model is used to measure a country’s national income or GDP by tracking the flows of money between the sectors . The model is also known as the Circular Flow of Income .
The basic circular flow model consists of two sectors: households and businesses . In this model, money flows from households to businesses as consumer expenditures in exchange for goods and services produced by the businesses. The money then flows back from businesses to households for the labor that individuals provide . This model is the most basic circular flow model of an economy .
In reality, there are more parties participating in a more complex structure of circular flows. The five-sector model consists of households (the public sector), businesses, government, the foreign sector, and the financial sector . Money flows from households and businesses to the government in the form of taxes in this model . The government pays back in the form of government expenditures through subsidies, benefit programs, public services, etc. . The foreign sector involves the import and export of goods and services, and the financial sector includes banks and other financial institutions .
The circular flow model has been widely applied in different studies, with significant impacts on the understanding of economics . Here are some examples of the significance of the model:
1. National Income Accounting: The circular flow model is used to measure a country’s national income or GDP by tracking the flows of money between the sectors . This helps economists understand the overall health of an economy.
2. International Trade: The circular flow model is used to explain the impact of international trade on an economy . The model shows how imports and exports affect the circular flow of money and goods between sectors.
3. Fiscal Policy: The circular flow model is used to explain the impact of fiscal policy on an economy . Fiscal policy refers to the government’s use of taxes and spending to influence the economy. The model shows how changes in government spending and taxation
