AI Framework Agriculture is a term that refers to the use of artificial intelligence (AI) frameworks, such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Keras, to develop and deploy AI-based solutions for various agricultural challenges and opportunities. AI frameworks are software platforms that provide developers with tools and libraries to build and train AI models, such as deep neural networks, generative adversarial networks, and reinforcement learning agents. AI frameworks can also facilitate the integration of AI models with other technologies, such as the internet of things (IoT), blockchain, and drones, to create smart and sustainable farming systems.
AI frameworks can contribute to agriculture in many ways, such as:
– Intelligent Crop Planning: AI frameworks can enable the creation of AI models that can analyze weather forecasts, soil data, crop varieties, market conditions, and other factors to provide optimal crop planning recommendations for farmers at micro and macro levels.
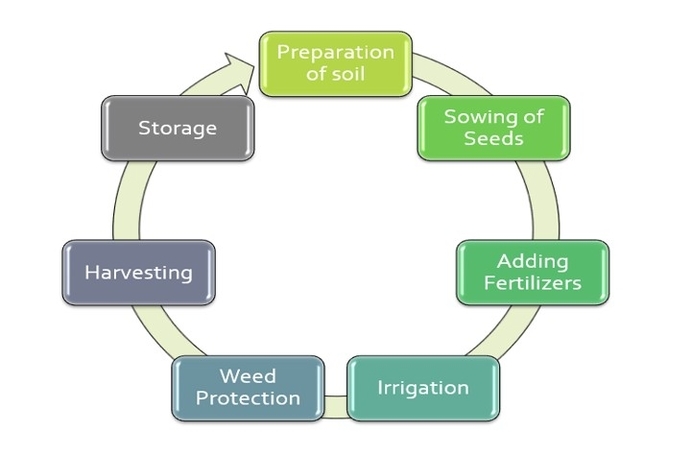
– Smart Farming: AI frameworks can support the development of AI models that can monitor and control various aspects of crop production, such as irrigation, fertilization, pest management, harvesting, and post-harvest processing, using sensors, drones, robots, and other devices.
– Farmgate-to-Fork: AI frameworks can facilitate the implementation of AI models that can enhance the supply chain efficiency and transparency of agricultural products, from farm to consumer, using blockchain, traceability systems, and smart contracts.
– Data-driven Agriculture: AI frameworks can empower the generation of AI models that can leverage big data and analytics to provide farmers with actionable insights and feedback on their farming practices, as well as enable data sharing and collaboration among different stakeholders in the agricultural sector.
AI frameworks have the potential to transform agriculture and address the global challenges of food security, climate change, and rural development. However, the use of AI frameworks also poses some ethical and social issues, such as data privacy, bias, accountability, and human-AI interaction. Therefore, it is important to develop and apply AI frameworks in agriculture with ethical and responsible principles, such as fairness, transparency, inclusivity, and sustainability.
(Word count: 298)