World population growth is the change in the number of people living on Earth over time. It is influenced by factors such as birth rates, death rates, migration, and environmental changes. Here is a brief overview of world population growth in about 1000 words:
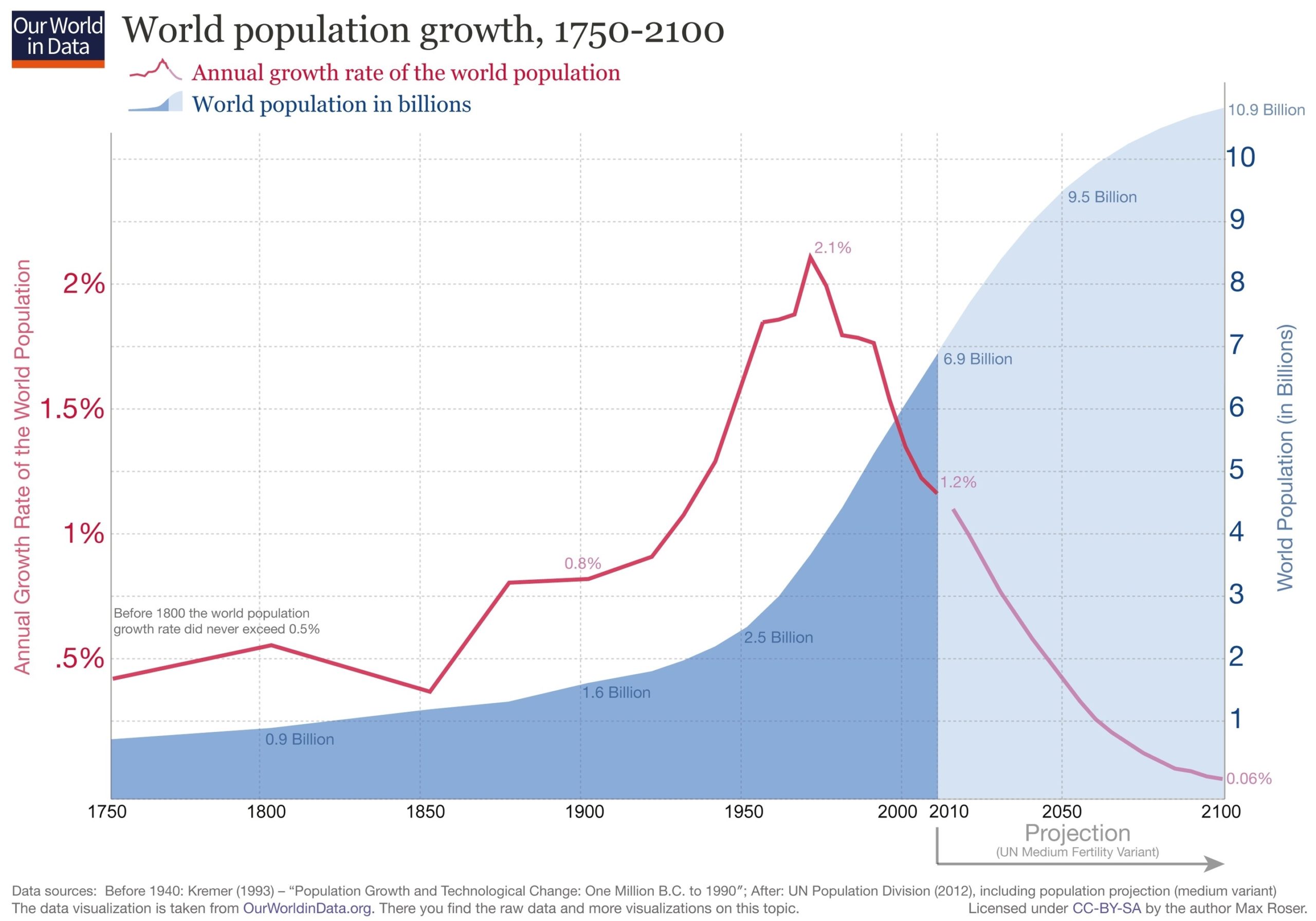
The world population has increased rapidly in recent centuries, reaching over 8 billion people in 2023. However, this growth is not evenly distributed across regions, countries, or demographic groups. Some areas of the world are experiencing faster population growth than others, and some are even facing population decline. Moreover, the age structure, sex ratio, and urbanization of the population vary widely across the world, with implications for social and economic development.
The main drivers of population growth are fertility and mortality. Fertility is the average number of children a woman has in her lifetime, and it depends on factors such as culture, education, health, and family planning. Mortality is the rate at which people die, and it depends on factors such as disease, violence, nutrition, and medical care. Migration is another factor that affects population growth, as people move from one place to another for various reasons, such as work, education, or safety.
The global fertility rate has declined significantly over the past decades, from about 5 children per woman in 1950 to about 2.4 in 2023. This is mainly due to the improvement of women’s education, health, and empowerment, as well as the availability and use of contraceptives. However, there are still large differences in fertility levels across regions and countries, ranging from 1.1 in South Korea to 6.9 in Niger. The global mortality rate has also declined over the past decades, from about 19 deaths per 1000 people in 1950 to about 7.5 in 2023. This is mainly due to the reduction of infectious diseases, child mortality, and maternal mortality, as well as the advancement of medical technology and public health. However, there are still large differences in mortality levels across
