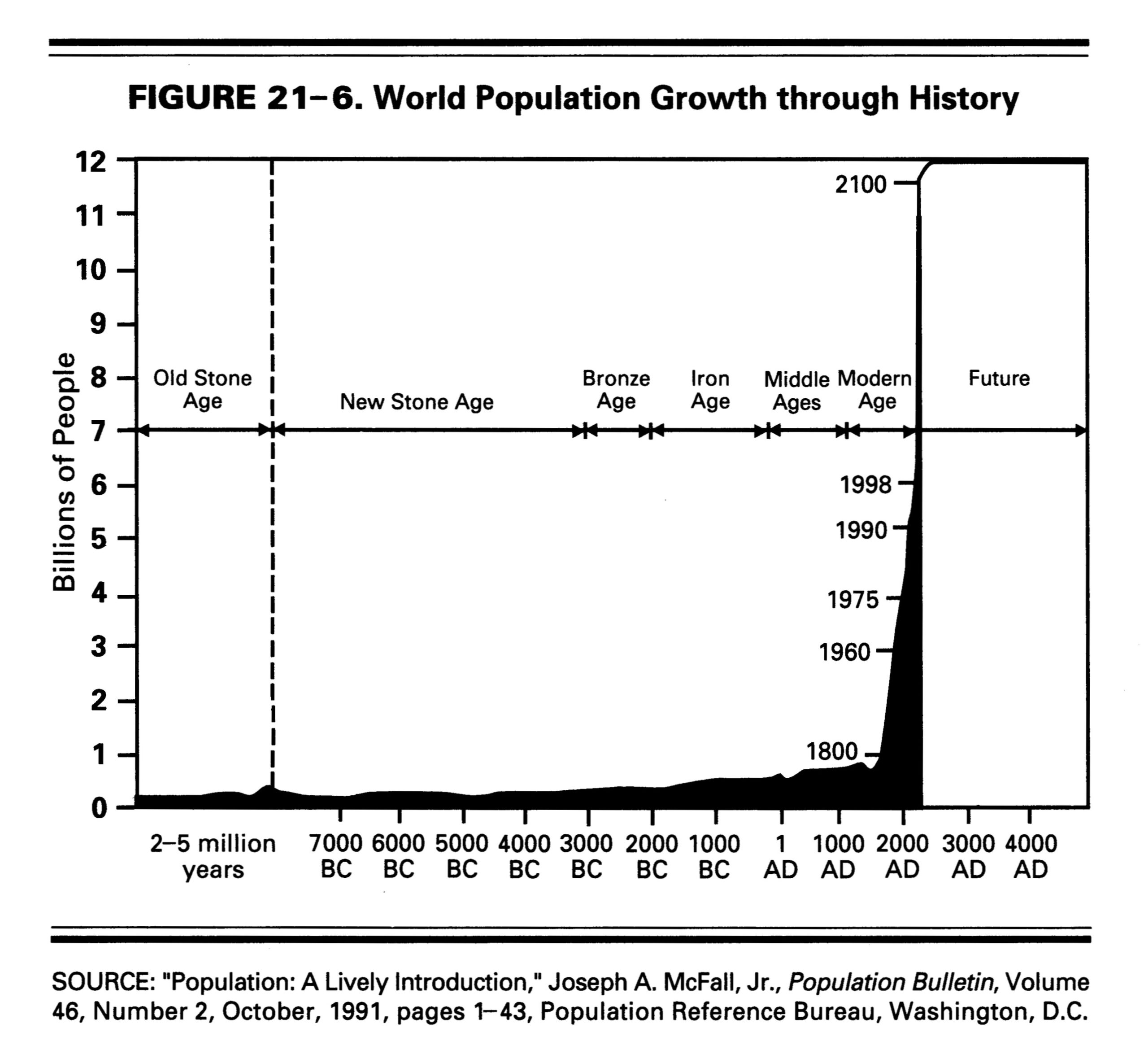
World Population Growth 4 is a hypothetical scenario that assumes a very low fertility rate and a very high mortality rate for the world population in the 21st century. According to this scenario, the world population would peak at 8.1 billion in 2024 and then decline rapidly to 2.3 billion by 2100. This would be a dramatic reversal of the historical trend of population growth, which has seen the world population increase from 1 billion in 1800 to 7.9 billion in 2021.
The main drivers of this scenario are the assumptions that the total fertility rate (TFR) – the average number of children per woman – will drop below the replacement level of 2.1 in all regions of the world, and that the life expectancy at birth will decrease significantly due to various factors, such as pandemics, wars, environmental degradation, and social unrest. The TFR is projected to decline from 2.5 in 2020 to 1.5 in 2050 and 1.2 in 2100, while the life expectancy is projected to decline from 72.6 in 2020 to 65.9 in 2050 and 58.4 in 2100.
The implications of this scenario are profound and complex, affecting various aspects of human society and the environment. Some possible consequences are:
– A rapid aging of the population, with the median age increasing from 30.9 in
