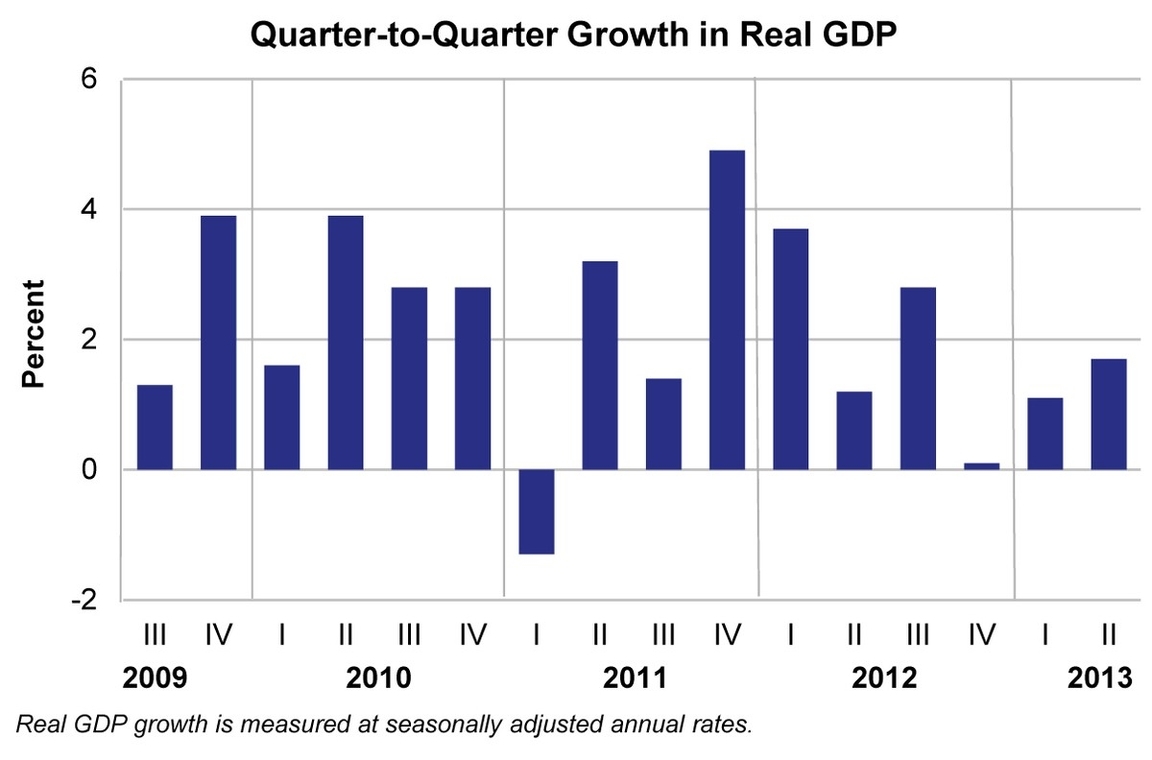
Real GDP, or gross domestic product, is a measure of the total value of goods and services produced in a country over a certain period of time, adjusted for inflation. Quarterly growth of real GDP indicates how fast the economy is expanding or contracting in a given quarter compared to the previous one. The U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) publishes quarterly estimates of real GDP, along with other economic indicators, such as corporate profits and GDP by industry.
According to the latest data from the BEA, the U.S. real GDP increased by 4.9 percent in the third quarter of 2023, after increasing by 2.1 percent in the second quarter and 2.2 percent in the first quarter. The increase in the third quarter was mainly driven by consumer spending and inventory investment, while imports, which subtract from GDP, also increased. The growth rate in the third quarter was higher than the average annual growth rate of 2.8 percent from 2013 to 2022.
The quarterly growth of real GDP is affected by various factors, such as consumer confidence, business investment, government spending, trade balance, and global events. For example, the COVID-19 pandemic caused a sharp contraction of 29.9 percent in the second quarter of 2020, followed by a rebound of 35.3 percent in the third quarter of 2020, as lockdown measures were eased and stimulus packages were implemented. The quarterly growth of real GDP also reflects the cyclical fluctuations of the economy, such as recessions and expansions.
The quarterly growth of real GDP is an important indicator of the economic performance and health of a country. It helps policymakers, businesses, and consumers make informed decisions and plan for the future. However, it is not the only measure of economic well-being, as it does not capture other aspects of social welfare, such as income distribution, environmental quality, and human development. Therefore, it should be complemented by other indicators that reflect the broader goals and values of society.
(Word count: 299)
