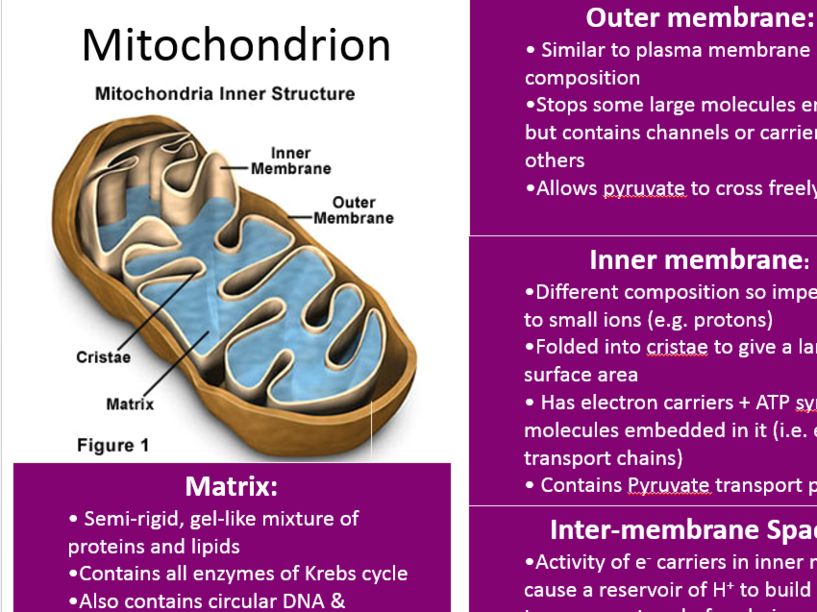
See the below image for the Miitochondrion diagram. The mitochondrion ( / ˌmaɪtəˈkɒndrɪən /, plural mitochondria) is a double membrane-bound organelle found in most eukaryotic organisms. Some cells in some multicellular organisms lack mitochondria (for example, mature mammalian red blood cells ).
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Mitochondrion. Lane, Nick (2016). The Vital Question: Energy, Evolution, and the Origins of Complex Life. WW Norton & Company.
Mitochondria are small membrane-bound organelles that are usually about 1 – 10 microns in length. They can be spherical or rod-shaped. The mitochondrion is enclosed by two membranes that separate it from the cytosol and the rest of the cell components.
