Economics is a social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. It is concerned with how individuals, businesses, governments, and other organizations allocate resources to satisfy their needs and wants. The field of economics is divided into two main branches: microeconomics and macroeconomics.
Microeconomics is the study of how individuals and firms make decisions about the allocation of resources. It examines how prices are determined in markets, how consumers make choices about what to buy, and how firms decide what to produce and how much to charge for their products. Microeconomics also studies how government policies, such as taxes and regulations, affect the behavior of individuals and firms.
Macroeconomics, on the other hand, is the study of the economy as a whole. It examines the performance of the economy in terms of growth, inflation, and unemployment. Macroeconomists study the factors that determine the level of economic activity, such as government spending, interest rates, and international trade. They also analyze the effects of economic policies, such as monetary and fiscal policy, on the overall economy.
Economics is a broad field that encompasses many different topics. Some of the key concepts in economics include supply and demand, opportunity cost, comparative advantage, and market failure. Supply and demand is the fundamental principle that underlies all economic activity. It states that the price of a good or service is determined by the interaction of buyers and sellers in a market. Opportunity cost is the value of the next best alternative that must be given up in order to pursue a certain action. Comparative advantage is the ability of one country or individual to produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost than another country or individual. Market failure occurs when the market fails to allocate resources efficiently, leading to a suboptimal outcome.
Economics has many real-world applications. It is used to analyze and understand a wide range of issues, such as the causes of inflation and unemployment, the effects of government policies on the economy, and the impact of international trade on domestic industries. Economists work in a variety of settings, including academia, government, and the private sector. They use a variety of tools and techniques, such as statistical analysis, mathematical modeling, and game theory, to study economic phenomena.
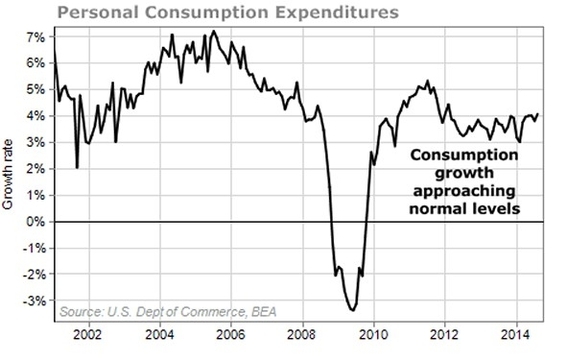
In conclusion
