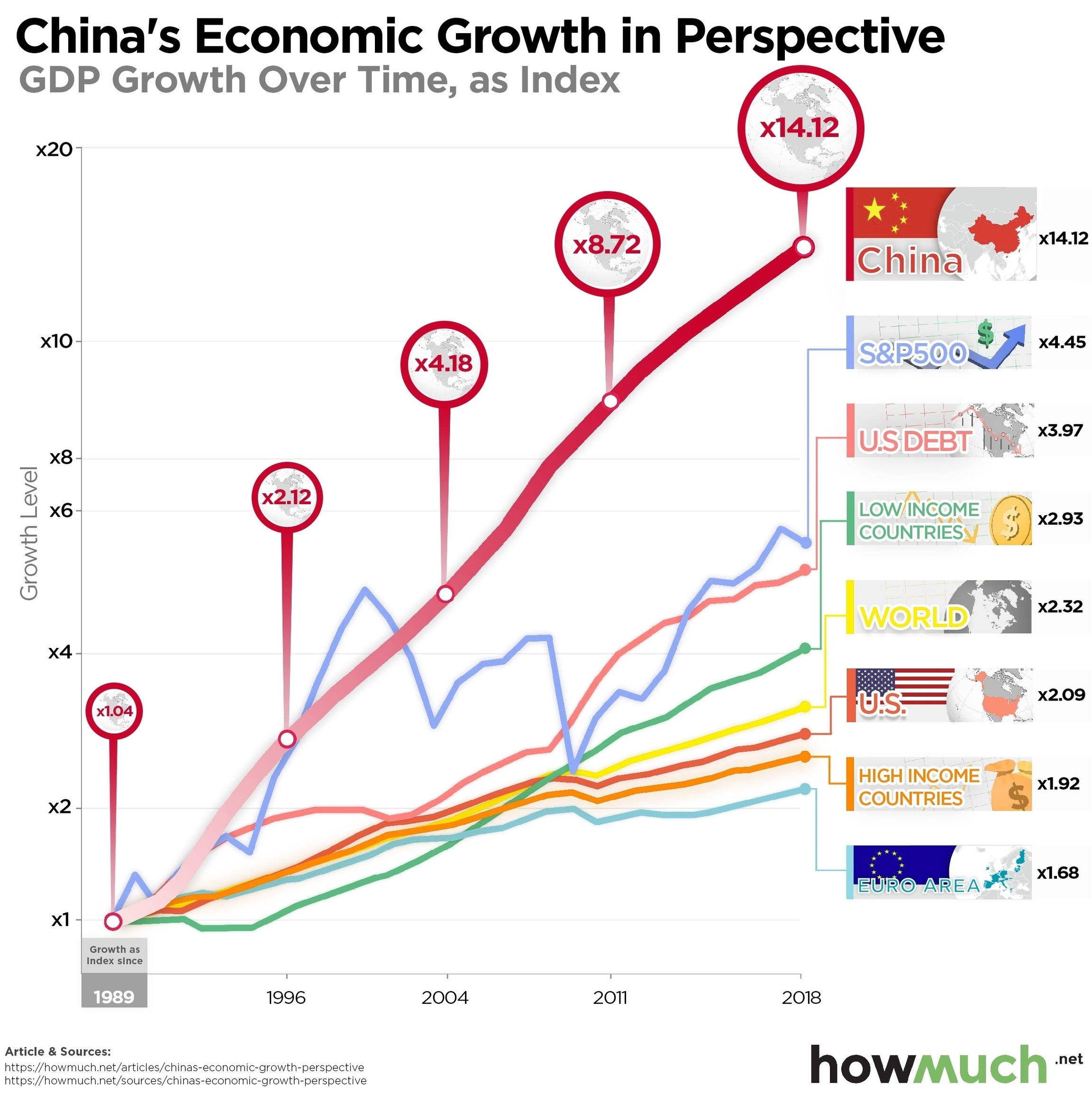
China’s economy has been growing at a rapid pace over the past few decades, making it one of the world’s largest economies. According to the World Bank, China’s GDP has grown at an average rate of 9.6% per year from 1979 to 2019. In 2020, China was the only major economy to experience GDP growth, with a 2.3% increase . The country’s GDP growth rate for 2021 was 21.33%, which is a significant increase from the previous year . The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has raised its forecast for China’s economic growth in 2022 to 5.4% .
China’s sustained growth can be attributed to its export relations, manufacturing sector, and low-wage workers . However, the country’s economic performance has been affected by the COVID-19 pandemic, with one of its worst economic performances in decades in 2022 . The government has set a modest GDP target of around 5% for 2023 .
In terms of GDP, China’s economy is the second-largest in the world, with a GDP of $17,963.17 billion in 2022 . The country’s manufacturing sector is one of the largest in the world, with a significant contribution to the country’s GDP .
In conclusion, China’s economic growth has been remarkable over the past few decades, with the country’s GDP growing at an average rate of 9.6% per year from 1979 to 2019. The country’s sustained growth can be attributed to its export relations, manufacturing sector, and low-wage workers. However, the COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the country’s economic performance, with one of its worst economic performances in decades in 2022. The government has set a modest GDP target of around 5% for 2023.
