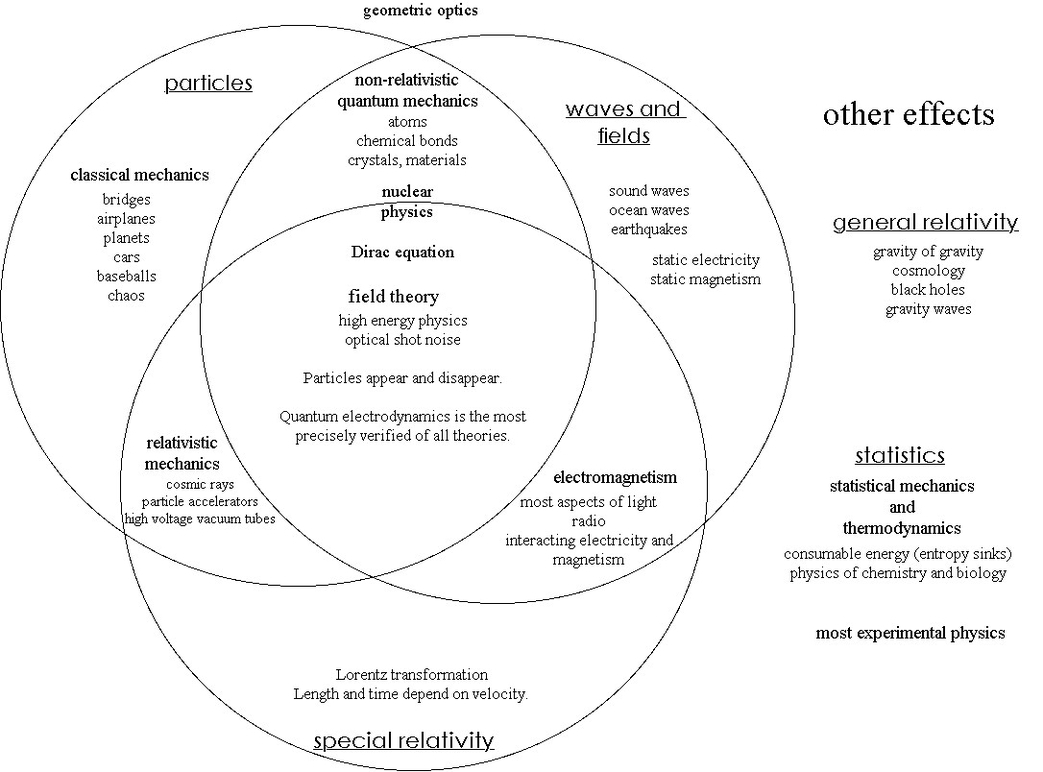
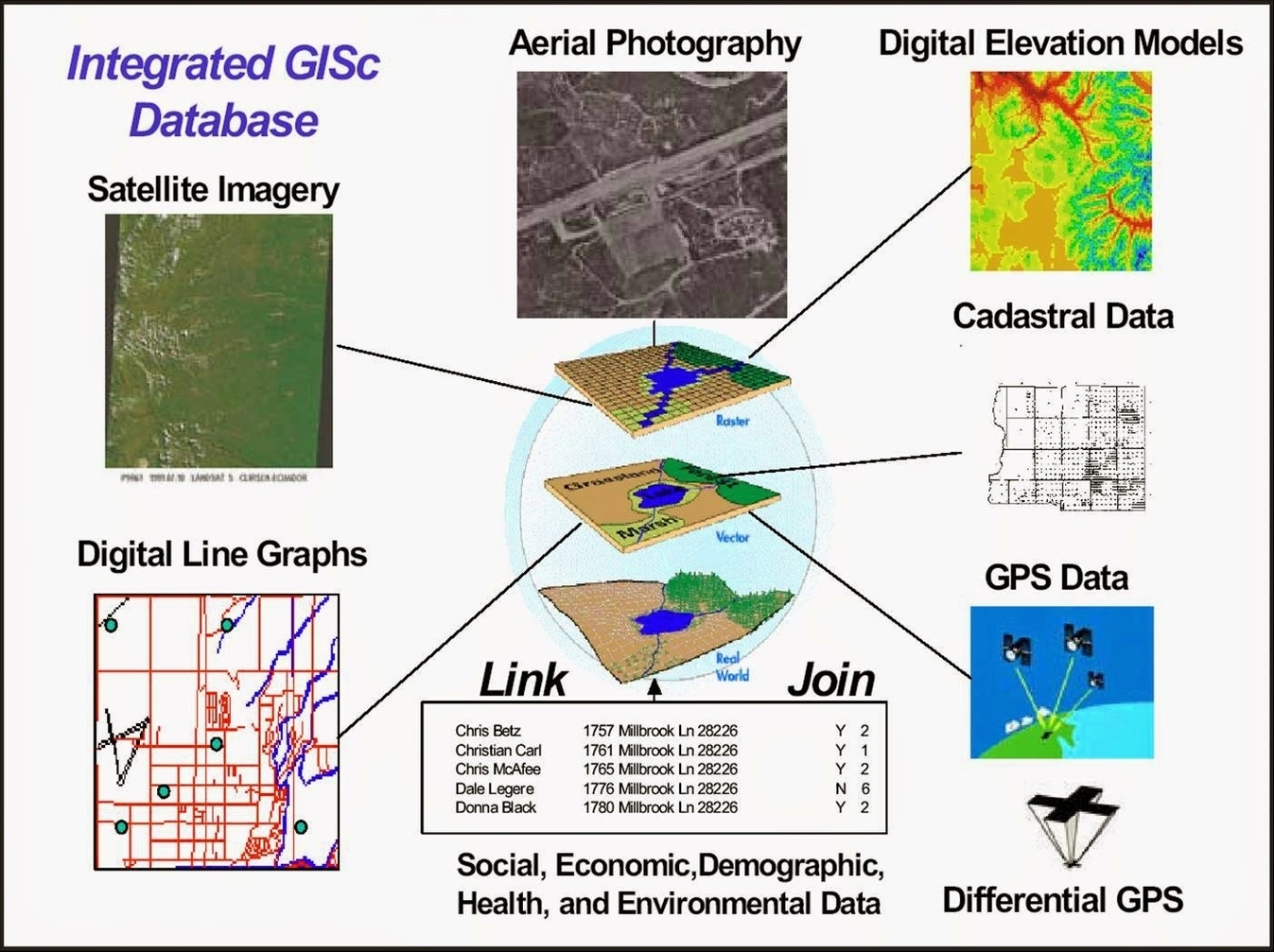
Smart farming is a practice in agricultural production that involves using technology like IoT, robotics, drones, and AI, among others, to manage farms, increase output, and reduce environmental impacts. Smart farming is also known as smart agriculture, digital agriculture, or e-agriculture. Here is an essay of approximately 1000 words on smart farming:
“`mart farming: An overview
The world population is expected to reach 8.5 billion by 2030 and 9.7 billion by 2050, according to the United Nations. This poses a huge challenge for the global food system, which needs to increase production by 70% by 2050 to meet the growing demand. However, the current agricultural practices are not sustainable, as they consume large amounts of natural resources, contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, and degrade the environment. Moreover, the agricultural sector faces various risks and uncertainties due to climate change, pests and diseases, market fluctuations, and regulatory pressures.
To address these challenges, smart farming has emerged as a promising solution that leverages advanced technologies and data-driven farm operations to optimize and improve sustainability in agricultural production. Smart farming can be defined as the adoption of technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), automation, the Internet of Things (IoT), drones, robotics, sensors, and cloud computing, among others, to collect, store, analyze, and share electronic data and information in agriculture. Smart farming aims to enhance the efficiency, productivity, profitability, and quality of agricultural products, while minimizing the environmental impacts and resource use.
mart farming can be applied to various aspects of the agricultural value chain, such as crop production, livestock management, aquaculture, forestry, and horticulture. Some examples of smart farming applications are:
– Precision agriculture: This involves the use of GPS, satellite imagery, remote sensing, and soil and crop sensors to monitor the spatial and temporal variability of soil, water, weather, and crop conditions, and to provide site-specific recommendations for inputs such as fertilizers, pesticides, irrigation, and seeds. Precision agriculture can help farmers to