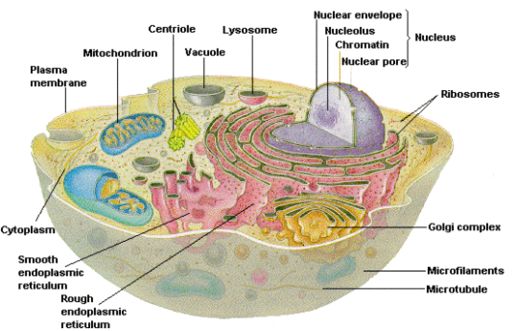
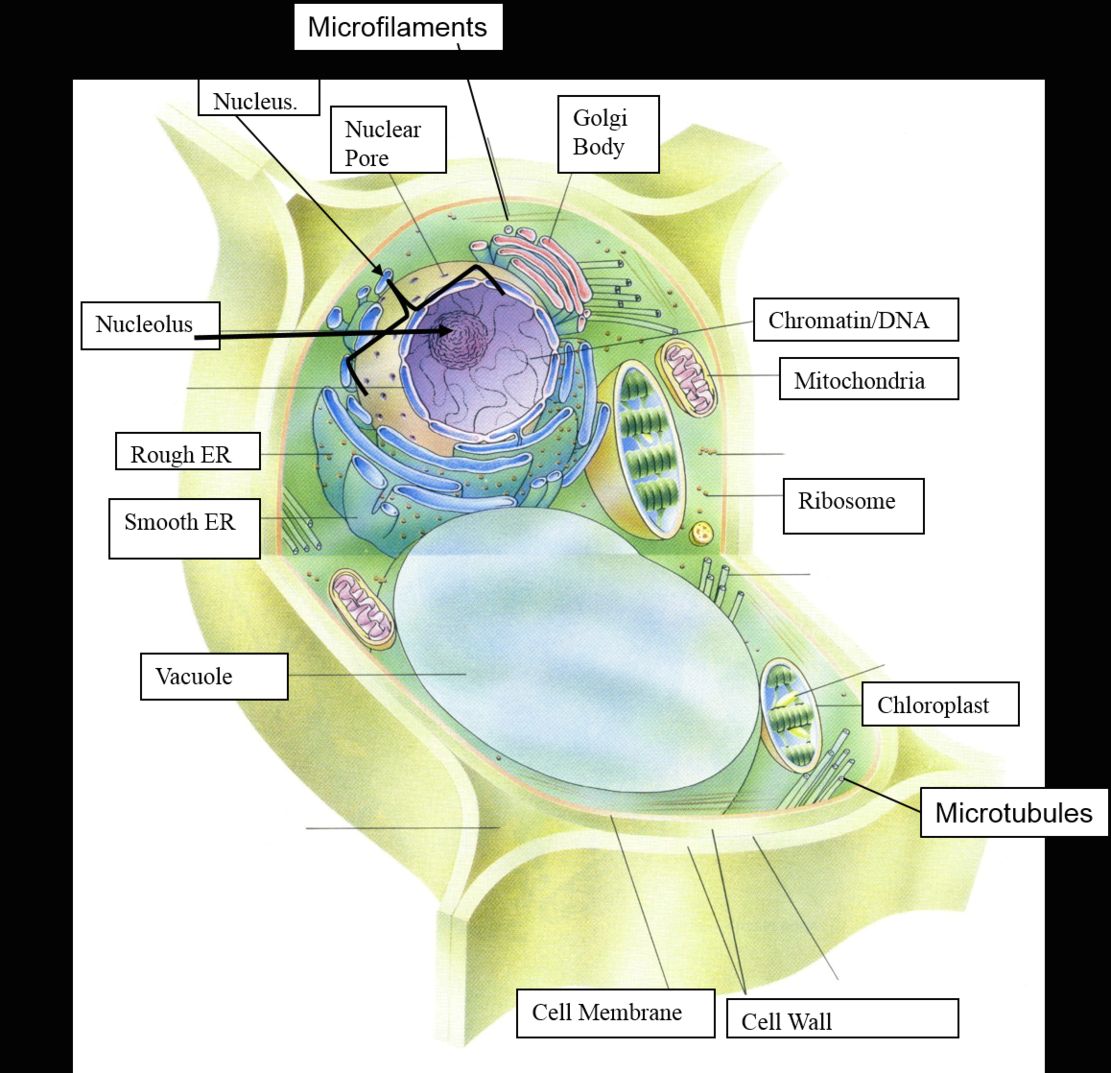
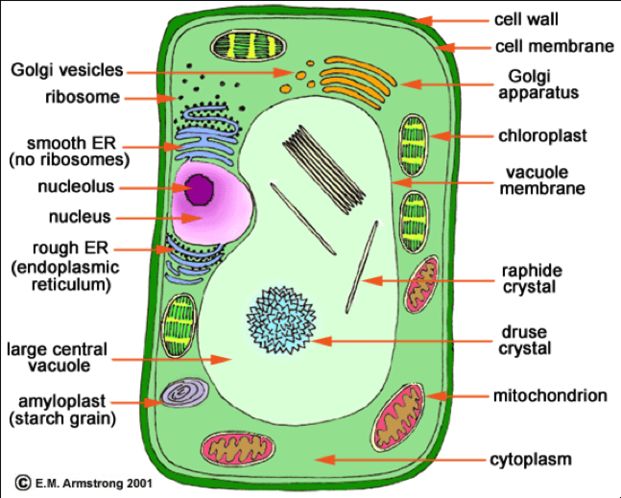
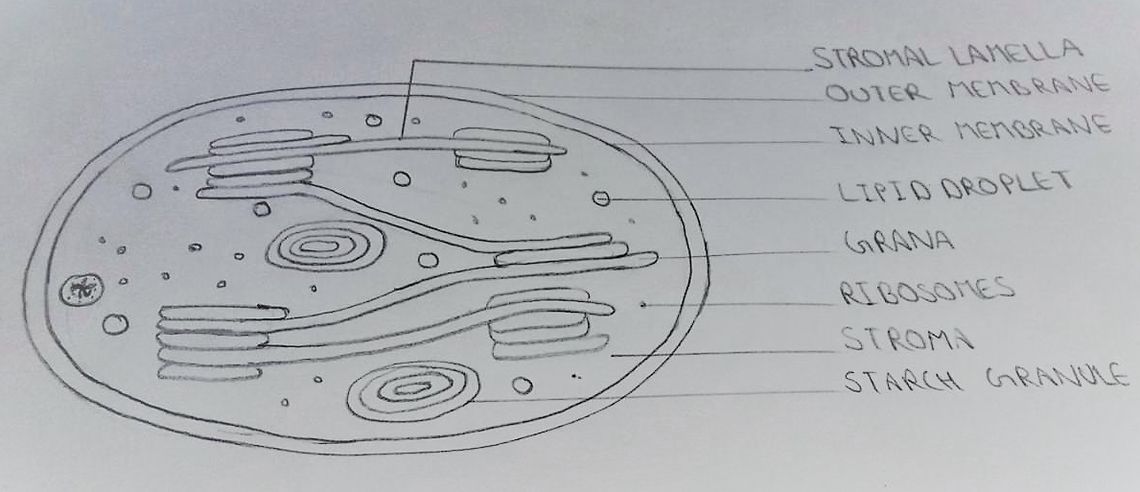
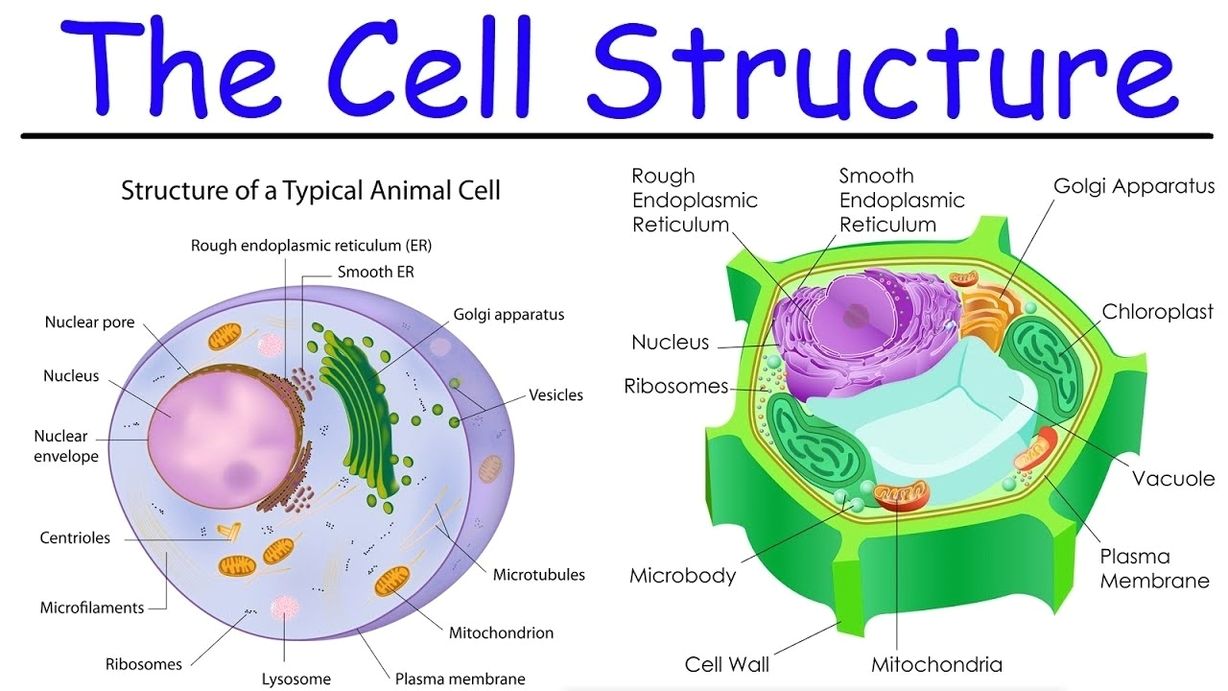
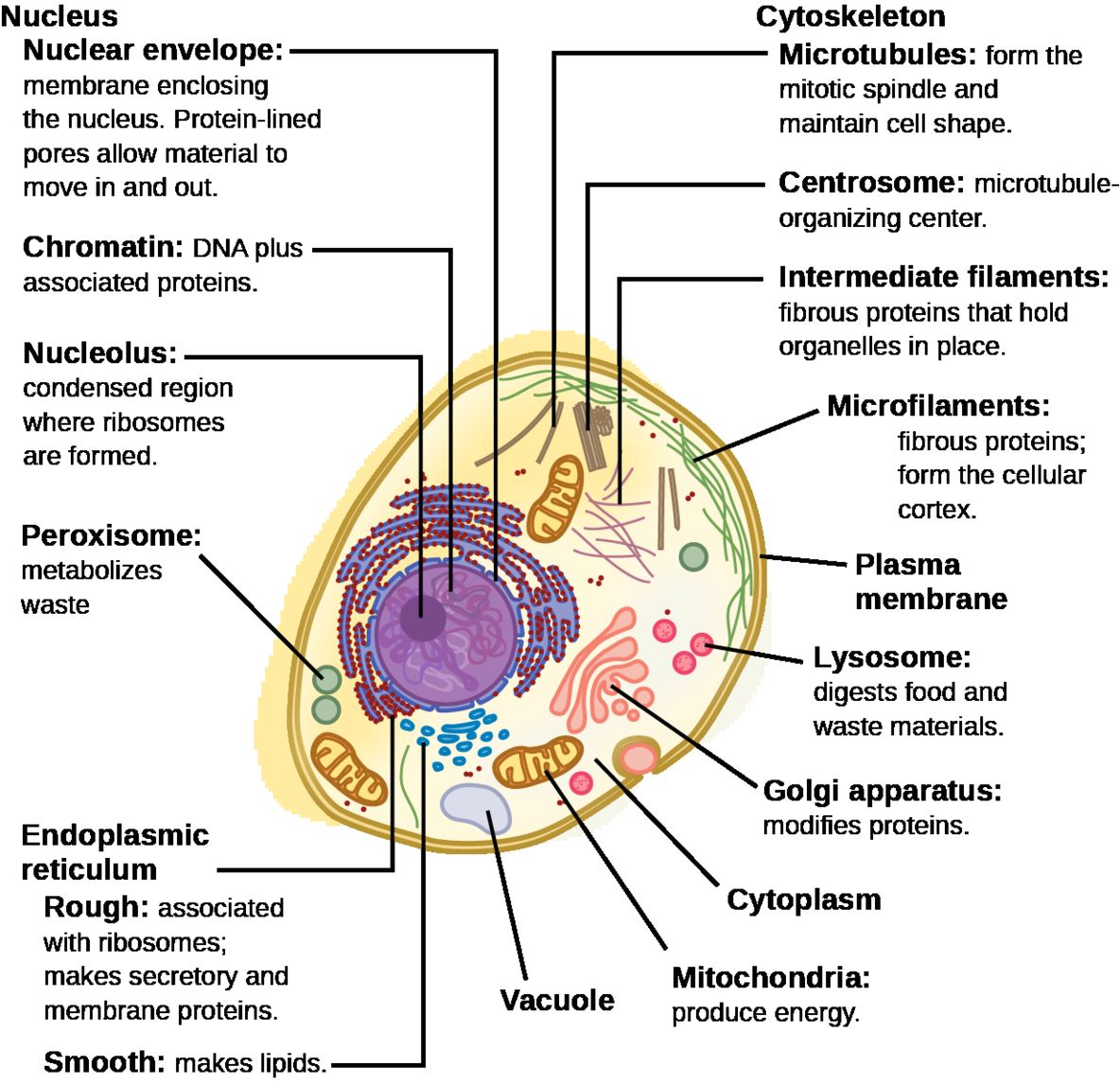
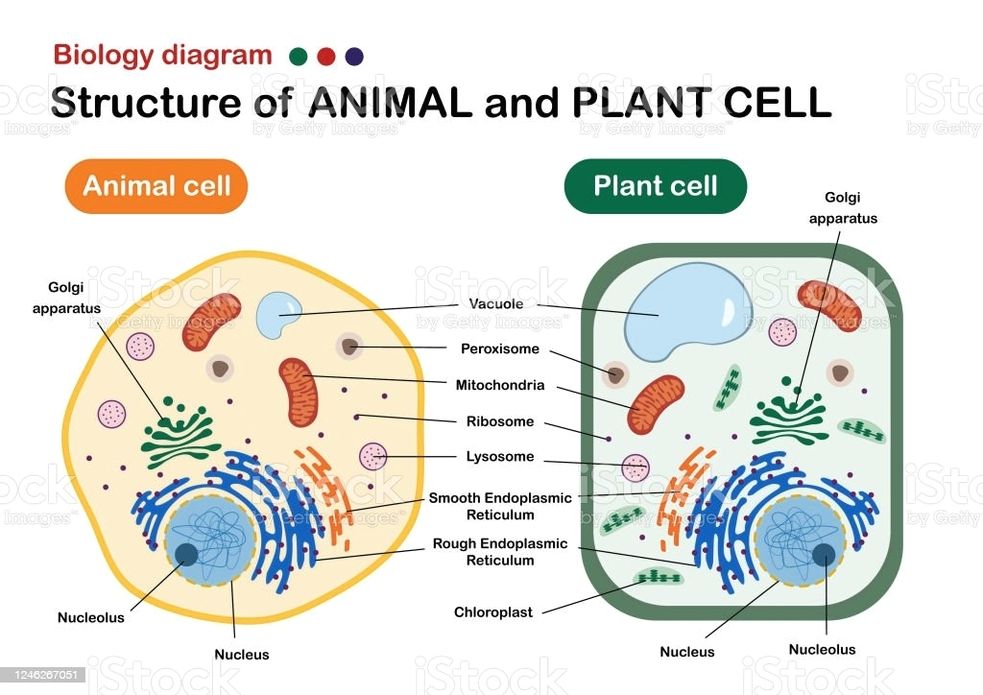
See the below image for the Nucleus biology diagram. Her writing is featured in Kaplan AP Biology 2016. The cell nucleus is a membrane bound structure that contains the cell’s hereditary information and controls the cell’s growth and reproduction. It is the command center of a eukaryotic cell and is commonly the most prominent organelle in a cell.
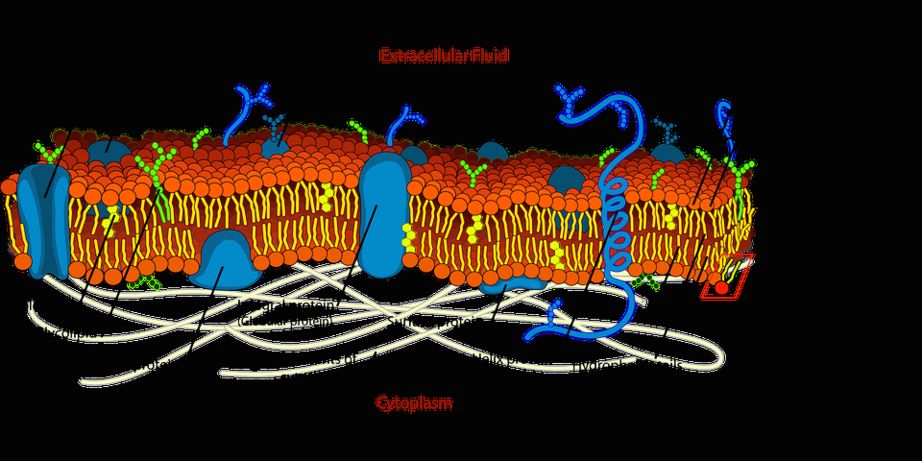
Properties. The nucleus is a membrane-bound structure that contains the cell’s hereditary information and controls the cell’s growth and reproduction. It is generally the most prominent organelle in the cell. It is surrounded by a structure called the nuclear envelope. This membrane separates the contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm.
Nucleus ensures equal distribution and exact copying of the genetic content during the process of cell replication. This is the main function of nucleus in animal cells. The nucleus sustains and controls the cell growth by orchestrating the synthesis of structural proteins in the cell.