See the below image for the Biologys diagram.

Charts, Graphs and Diagrams
See the below image for the Newtons first law of motion diagram. Newton’s first law is often referred to as the principle of inertia . Newton’s first (and second) laws are valid only in an inertial reference frame. The second law states that the rate of change of momentum of a body over time is directly proportional to the force applied, and occurs in the same direction as the applied force.
Everyday Applications of Newton’s First Law. The force of the road on the locked wheels provides the unbalanced force to change the car’s state of motion, yet there is no unbalanced force to change your own state of motion. Thus, you continue in motion, sliding along the seat in forward motion.
We can think of this law as preserving the status quo of motion. Newton’s first law of motion states that there must be a cause—which is a net external force—for there to be any change in velocity, either a change in magnitude or direction. An object sliding across a table or floor slows down due to the net force of friction acting on the object.
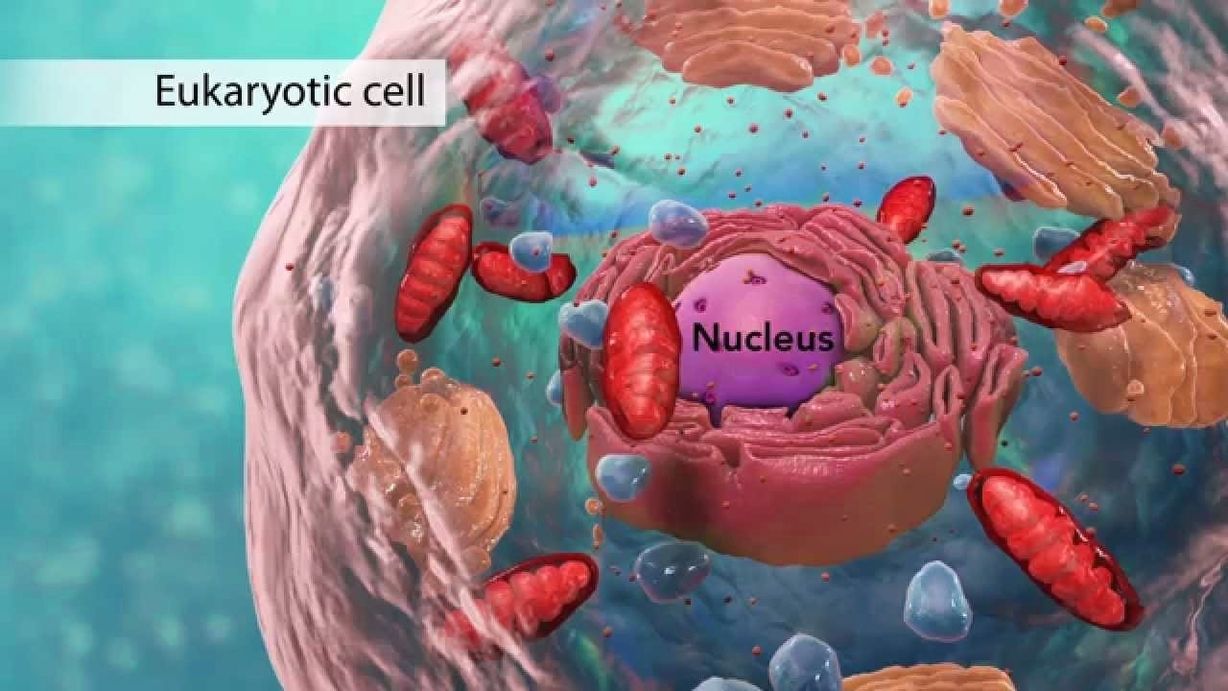
See the below image for the Biology cell structure youtube diagram. Biology: Cell Structure I Nucleus Medical Media. This animation by Nucleus shows you the function of plant and animal cells for middle school and high school biology, including organelles like the nucleus, nucleolus, DNA (chromosomes), ribosomes, mitochondria, etc. Also included are ATP molecules, cytoskeleton, cytoplasm, microtubules, proteins,…
The cell theory, which is one of the fundamental tenets of biology, states that all living things are composed of cells and that cells are the basic units of life. Comment on simran singh’s post Non-cellular life refers …”
If you are interested in understanding how cells are photographed, you might be interested in the Khan videos in “Introduction to the cell” https://www.khanacademy.org/science/high-school-biology/hs-cells , specifically Microscopy. Comment on Katy’s post It is an illustration.
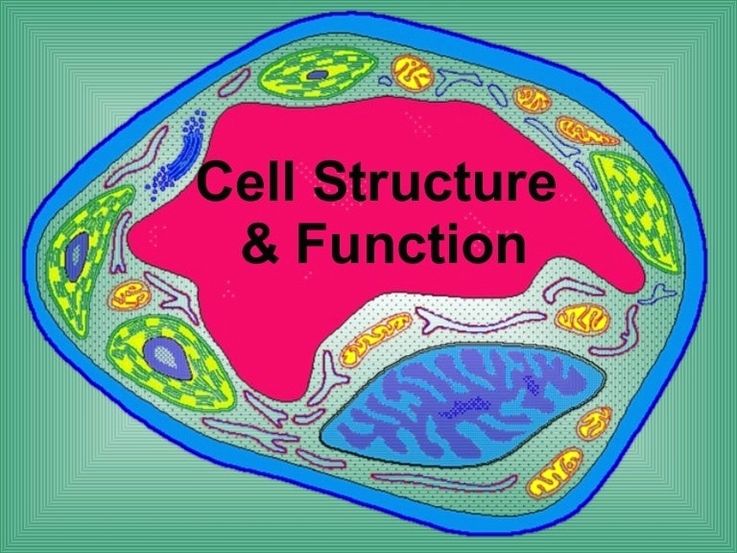
See the below image for the Biology cell structure function diagram. The cell structure comprises individual components with specific functions essential to carry out life’s processes. These components include- cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and cell organelles. Read on to explore more insights on cell structure and function.
The cell function is to keep all of the functions of the body performing as intended. This includes keeping toxins out of the body, help to break down waste, make nutrients and act as barriers within organelles.
Biology: Cell Structure I Nucleus Medical Media. This animation by Nucleus shows you the function of plant and animal cells for middle school and high school biology, including organelles like the nucleus, nucleolus, DNA (chromosomes), ribosomes, mitochondria, etc. Also included are ATP molecules, cytoskeleton, cytoplasm, microtubules, proteins,…
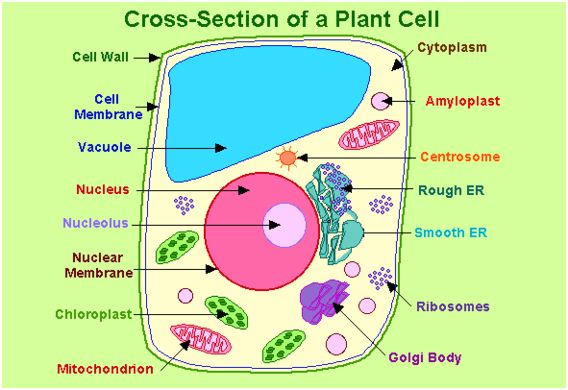
See the below image for the Cross section of a plant cell diagram. CROSS SECTION OF A LEAF. Spongy Mesophyll: These cells are smaller than those of the palisade mesophyll and are found in the lower part of the leaf. They also contain chloroplasts, but not quite as many. These cells have large air spaces between them that allow carbon dioxide and oxygen to diffuse between them.
The parts of a plant cell and plant cell components, which will be discussed, are plant cell wall, plant cell membrane, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, rough endoplasmic reticulum, vacuole, nucleus, peroxisomes, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, and plastids. The outermost portion of a plant cell is the cell wall.
It is located outside the cell membrane. It comprises proteins, polysaccharides and cellulose. The primary function of the cell wall is to protect and provide structural support to the cell. The plant cell wall is also involved in protecting the cell against mechanical stress and to provide form and structure to the cell.
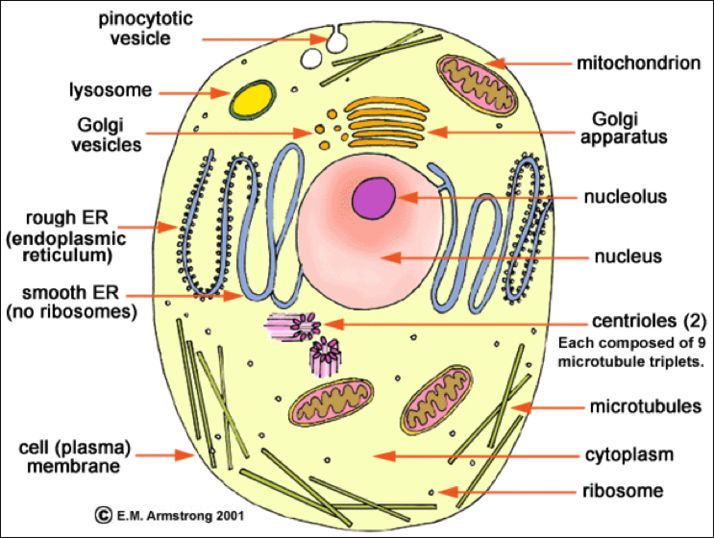
See the below image for the Cell structure image diagram. Browse 11,533 cell structure stock photos and images available, or search for plant cell structure or human cell structure to find more great stock photos and pictures.
The structure of a cell includes various organelles that perform all crucial functions such as the production of energy, replication, transport of materials, etc. Cells of prokaryotes differ from eukaryotes based on their structure.
Diagram of the human cell illustrating the different parts of the cell. The cell membrane is the outer coating of the cell and contains the cytoplasm, substances within it and the organelle. It is a double-layered membrane composed of proteins and lipids.

See the below image for the Biology cell structure and functions diagram. The cell structure comprises individual components with specific functions essential to carry out life’s processes. These components include- cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and cell organelles. Read on to explore more insights on cell structure and function.
The cell function is to keep all of the functions of the body performing as intended. This includes keeping toxins out of the body, help to break down waste, make nutrients and act as barriers within organelles.
Cell Structure and Functions Every organ in our body performs a variety of different functions such as digestion, assimilation, and absorption. Similarly, in the plants too, there are different organs of the plant which performs specialized or specific functions. For instance, the roots of the plants help in the absorption of minerals and water.
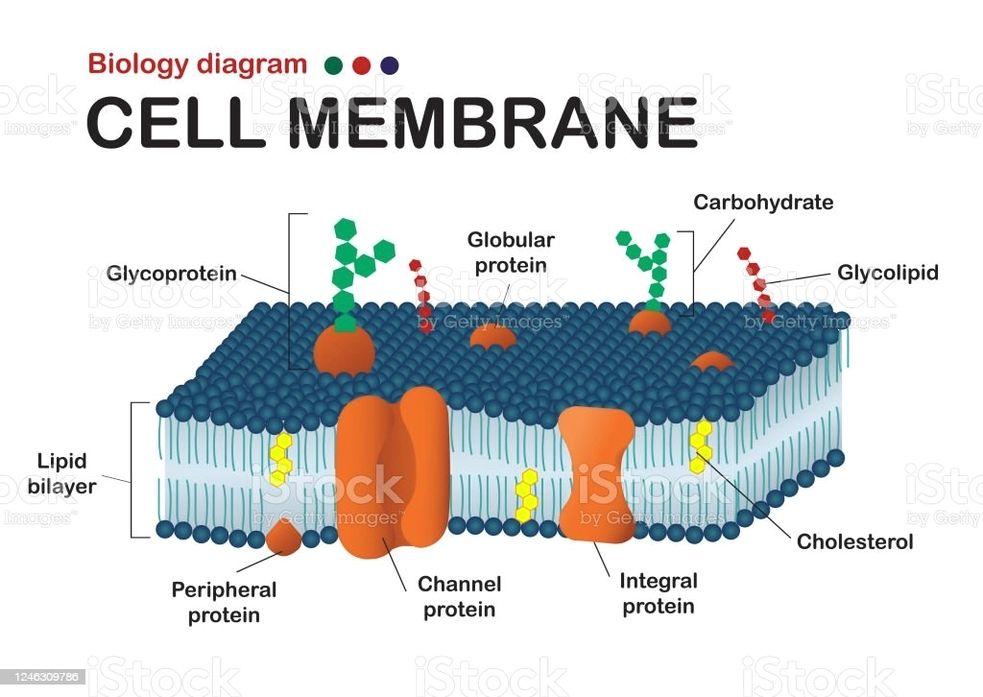
See the below image for the Cell membrane diagram. Cell Membranes – The Cell – NCBI Bookshelf The structure and function of cells are critically dependent on membranes, which not only separate the interior of the cell from its environment but also define the internal compartments of eukaryotic cells, including the nucleus and cytoplasmic organelles.
Its function is to protect the integrity of the interior of the cell by allowing certain substances into the cell, while keeping other substances out. It also serves as a base of attachment for the cytoskeleton in some organisms and the cell wall in others.
our editorial process. Regina Bailey. Updated October 07, 2019. The cell membrane (plasma membrane) is a thin semi-permeable membrane that surrounds the cytoplasm of a cell. Its function is to protect the integrity of the interior of the cell by allowing certain substances into the cell while keeping other substances out.