Timeline Of Timeline
The concept of a timeline has been around for centuries, and it has been used to represent a wide range of information. A timeline is a graphical representation of a sequence of events, usually in chronological order. It is often used to illustrate the history of a particular subject, such as a person, a place, or an event. Timelines can be used to show the development of a particular field of study, the evolution of a species, or the history of a nation.
The Timeline of Timeline is a timeline that documents the history of the concept of a timeline itself. It is a meta-timeline, if you will. The Timeline of Timeline begins with the earliest known examples of timelines, which date back to ancient civilizations such as the Egyptians and the Greeks. These early timelines were often used to record historical events, such as the reigns of kings and queens, or the construction of important buildings.
As time progressed, the use of timelines became more widespread, and they began to be used to represent a wider range of information. For example, timelines were used to show the development of scientific theories, the history of art, and the evolution of technology. The Timeline of Timeline documents these developments, and shows how the concept of a timeline has evolved over time.
One of the most significant developments in the history of timelines was the invention of the printing press in the 15th century. This made it possible to produce large numbers of printed books, including books that contained timelines. The Timeline of Timeline documents the impact that the printing press had on the development of timelines, and how it made it possible for people to access information about historical events more easily.
Another important development in the history of timelines was the advent of the internet. The internet has made it possible to access vast amounts of information about historical events, and has made it easier than ever before to create and share timelines. The Timeline of Timeline documents the impact that the internet has had on the development of timelines, and how it has made it possible for people to collaborate on timelines and share them with others.
In conclusion,

Diagrams Physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, energy, and their interactions. It is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines, with its main goal being to understand how the universe behaves . The study of physics has led to many technological advancements that have transformed modern-day society, such as television, computers, domestic appliances, and nuclear weapons .
The field of physics is vast and encompasses a wide range of topics, including mechanics, thermodynamics, electromagnetism, optics, and quantum mechanics, among others . Each of these topics is concerned with different aspects of the physical world and has its own set of laws and principles that govern it.
Mechanics is the branch of physics that deals with the motion of objects and the forces that cause this motion . It is divided into two main branches: classical mechanics and quantum mechanics. Classical mechanics deals with the motion of macroscopic objects, while quantum mechanics deals with the behavior of subatomic particles .
Thermodynamics is the branch of physics that deals with the relationships between heat, work, and energy . It is concerned with the behavior of large systems and is used to study phenomena such as phase transitions, chemical reactions, and the behavior of gases .
Electromagnetism is the branch of physics that deals with the behavior of electrically charged particles and the electromagnetic fields that they create . It is concerned with phenomena such as electric and magnetic fields, electromagnetic waves, and the behavior of charged particles in electric and magnetic fields .
Optics is the branch of physics that deals with the behavior of light and its interactions with matter . It is concerned with phenomena such as reflection, refraction, diffraction, and interference .
Quantum mechanics is the branch of physics that deals with the behavior of matter and energy at the atomic and subatomic level . It is concerned with phenomena such as wave-particle duality, quantum entanglement, and the uncertainty principle .
In conclusion, physics is a vast and fascinating field that has contributed immensely to our understanding of the universe and has led to many technological advancements that have transformed modern-day society. The topics covered in physics are diverse and range from mechanics to quantum mechanics, each with its own set of laws and principles that govern it ..
Asian Countries Economic Recovery
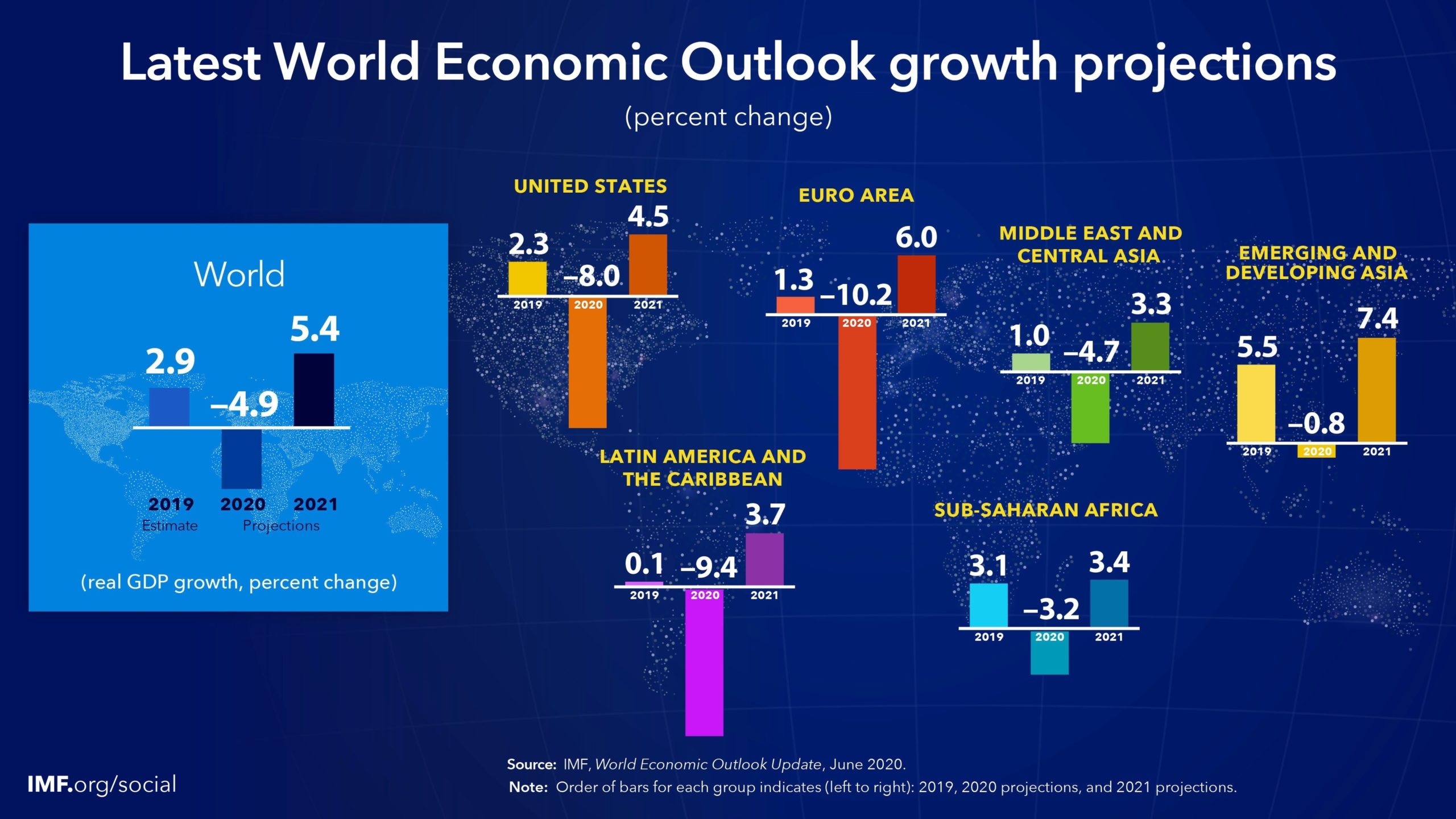
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the economies of Asian countries. While the pandemic has affected all countries, the impact has been more severe in some countries than others. The economic recovery of Asian countries has been a topic of discussion since the pandemic began. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has been closely monitoring the economic recovery of Asian countries. According to the IMF’s October 2021 report, the Asian outlook for 2021 has been downgraded by more than 1 percent to 6.5 percent compared with the April 2021 World Economic Outlook because of new peaks of the pandemic cycle driven by the highly contagious Delta variant. However, as vaccination rates accelerate, the region is expected to grow slightly faster in 2022 than anticipated earlier.
outheast Asia has been one of the regions most affected by the pandemic. The latest International Monetary Fund forecasts suggest that income per capita in the ASEAN-5 economies (Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Thailand, and Vietnam) will still be 6% lower in 2024 than the level that was expected before the pandemic struck. For the Philippines, which faces the worst economic outlook, the scarring is expected to be twice as deep, with income per capita remaining 12% lower than previously expected. The pandemic has caused significant damage to the economies of these countries, and it will take time for them to recover.
The pandemic has also highlighted the importance of controlling the virus itself to limit the economic damage. The contrasting experiences of Vietnam, Indonesia, and the Philippines epitomize the Southeast Asian story. Vietnam has been the stellar example: It is one of few economies in the world to eke out positive economic growth in 2020 on the back of a prompt and highly successful public health response. That allowed Vietnam to quickly reopen its economy and stage a strong recovery. Indonesias government, by comparison, was reluctant to take actions that would undermine the economy in the short term, having only belatedly imposed social distancing restrictions while failing to mount an effective public health response. Indonesia experienced a shallower recession than many others. But as it failed to contain the virus, its economic recovery thereafter has been weak. The Philippines, meanwhile, stands out as having experienced the worst of both worlds: It imposed harsh lockdown restrictions and still failed to control the spread of the virus. The Philippines economy fell 14% (compared to its pre-COVID level) in the second quarter of 2020, and was still 9% smaller by the end of the year, placing it as one of the worst economic performers globally.
The role of international trade has also been a key factor shaping Southeast Asias crisis. Global trade has held up surprisingly well, and this has been especially beneficial for Southeast Asia as a heavily trade-driven region. However, the pandemic has disrupted global supply chains, which has had a significant impact on the economies of Southeast Asian countries. The pandemic has also highlighted the need for countries to diversify their economies and reduce their dependence on a single sector or country. This is particularly important for countries that are heavily dependent on tourism, such as Thailand and the Philippines.
In conclusion, the COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the economies of Asian countries. While the pandemic has affected all countries, the impact has been more severe in some countries than others. The economic recovery of Asian countries has been a topic of discussion since the pandemic began. Southeast Asia has been one of the regions most affected by the pandemic. The pandemic has caused significant damage to the economies of these countries, and it will take time for them to recover. The role of international trade has also been a key factor shaping Southeast Asias crisis. The pandemic has disrupted global supply chains, which has had
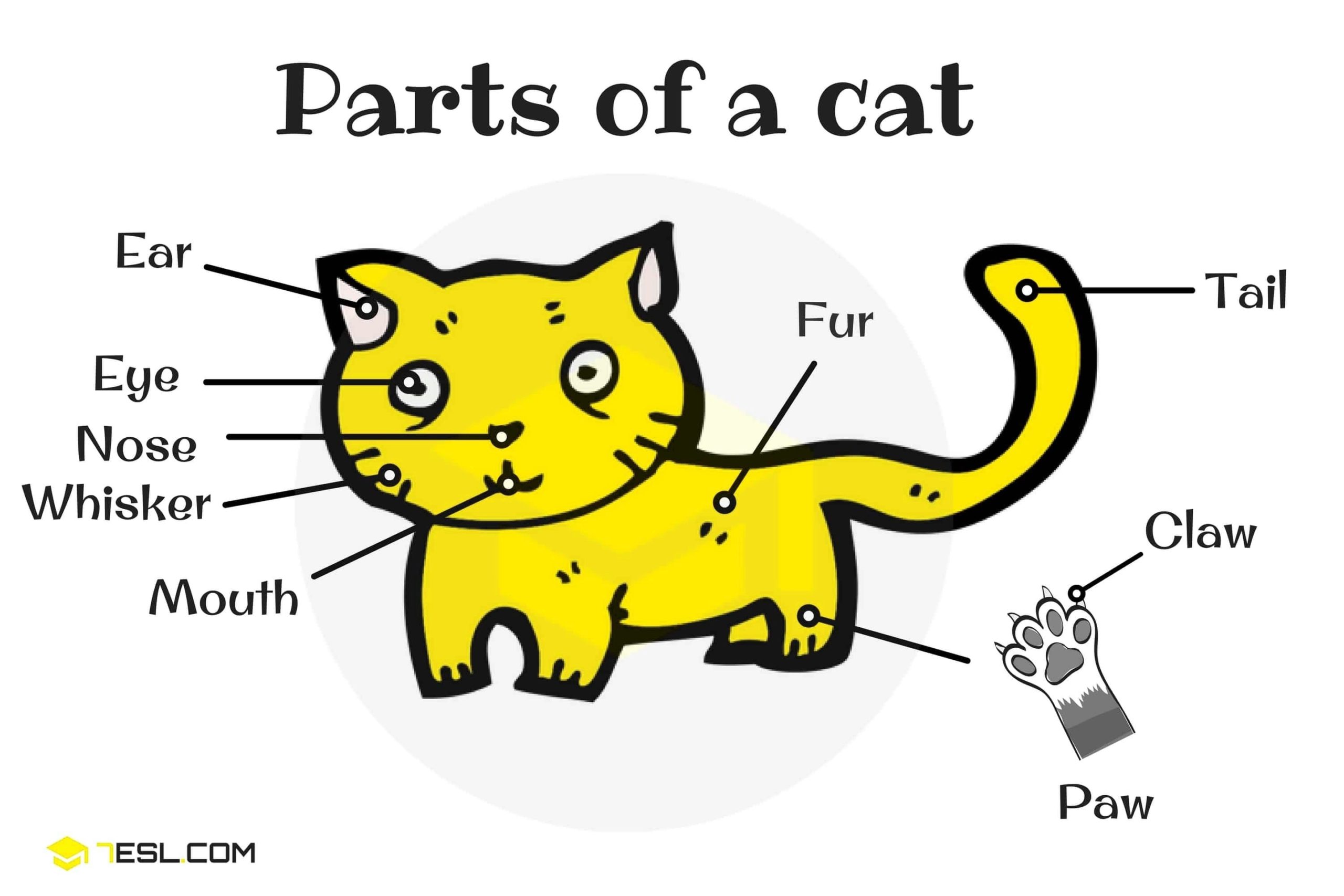
Parts Of A Cat
A cat’s anatomy is quite fascinating and complex. The visible parts of a domestic cat’s body are similar to those of other members of the genus Felis . Here are some of the key parts of a cat:
– Mouth: A cat’s tongue has sharp spines or papillae. There are five types of papillae that can be found in the dorsal aspect of the tongue: filiform, fungiform, foliate, vallate, and conical. Cats are carnivores that have highly specialized teeth. There are four types of permanent dentition teeth that structure the mouth: twelve incisors, four canines, ten premolars, and four molars. The premolar and first molar are located on each side of the mouth that together are called the carnassial pair. The carnassial pair specialize in cutting food and are parallel to the jaw. The incisors located in the front section of the lower and upper mouth are small, narrow, and have a single root. They are used for grasping and biting food. A cat also has a deciduous dentition prior to the formation of the permanent one. This dentition emerges seven days after birth and it is composed of 26 teeth with slight differences. The mouth will have smaller incisors, slender and strongly curved upper canines, vertical lower canines, and even smaller upper and lower molars .
– Ears: A cat’s ear, which has special fur for sensing and protection, is sensitive and can move independently of each other. Because of this mobility, a cat can move its body in one direction and point its ears in another direction. The rostral, caudal, dorsal, and ventral auricular muscle groups of each ear comprise fifteen muscles that are responsible for this ability. Most cats have straight ears pointing upward. Unlike with dogs, flap-eared breeds are extremely rare (Scottish Folds have one such exceptional mutation). When angry or frightened, a cat will lay back its ears to accompany the growling or hissing sounds it makes. Cats also turn their ears back when they are playing or to listen to a sound coming from behind them. The fold of skin forming a pouch on the lower posterior part of the ear, known as Henry’s pocket, is usually prominent in a cat’s ear .
– Eyes: A cat’s eyes are large and round, with pupils that can dilate and contract quickly. They have a tapetum lucidum, which is a reflective layer behind the retina that reflects light back through the retina, increasing the amount of light available to the photoreceptors. This allows cats to see better in low light conditions. Cats have a third eyelid, called the nictitating membrane, which is a thin, translucent membrane that moves across the eye from the inner corner to the outer corner. It helps to protect the eye and keep it moist. Cats also have a well-developed sense of smell and taste, with a vomeronasal organ that allows them to use their tongue as scent tasters .
– Skeleton: A cat’s skeleton is composed of 244 bones, which include the skull, spine, ribcage, and limbs. The skull of a cat has 29 bones, which protect the brain, eyes, and ears. The spine of a cat consists of 7 cervical vertebrae, 13 thoracic vertebrae, 7 lumbar vertebrae, 3 sacral vertebrae, and a variable number of caudal vertebrae. The cervical or neck bones are 7 in number. The dorsal or thoracic bones are 13 in number, each bearing a rib.
Plant Cell Diagram
A plant cell is a type of eukaryotic cell that is found in organisms of the kingdom Plantae. Plant cells have some distinctive features that differentiate them from animal, fungal, and bacterial cells. Here is a brief overview of the plant cell, its structure, and its functions.
Plant cells are surrounded by a rigid cell wall, which is mainly composed of cellulose, a polysaccharide. The cell wall provides shape, support, and protection to the cell. It also allows the passage of water, nutrients, and other molecules in and out of the cell. The cell wall consists of three layers: the primary cell wall, the secondary cell wall, and the middle lamella. The primary cell wall is the outermost layer, which is formed by cellulose fibers laid down by enzymes. The secondary cell wall is the innermost layer, which is thicker and stronger than the primary cell wall. It is composed of cellulose, lignin, and other substances that provide rigidity and resistance to the cell. The middle lamella is the thin layer between the primary cell walls of adjacent cells. It is made of pectin, a sticky substance that helps to glue the cells together.
Inside the cell wall, there is a plasma membrane, which is a semi-permeable membrane that regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell. The plasma membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer, with embedded proteins and other molecules. The plasma membrane also contains receptors, which are molecules that bind to specific signals and trigger cellular responses.
The plant cell contains a large central vacuole, which is a fluid-filled sac that occupies most of the cell volume. The vacuole stores water, ions, sugars, salts, pigments, and other substances. The vacuole also maintains the turgor pressure of the cell, which is the force exerted by the water inside the vacuole against the cell wall. Turgor pressure helps to keep the cell firm and upright. The vacuole is surrounded by a membrane called the tonoplast, which controls the transport of substances between the vacuole and the cytoplasm.
The cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance that fills the space between the plasma membrane and the nucleus. The cytoplasm contains various organelles, which are specialized structures that perform different functions for the cell. Some of the major organelles in the plant cell are:
– Nucleus: The nucleus is the control center of the cell, which contains the genetic material (DNA) and regulates the expression of genes. The nucleus is enclosed by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope, which has pores that allow the exchange of materials between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus also contains a

Animal Classification
Animal classification is the process of grouping animals into different categories based on their shared characteristics and evolutionary relationships. There are different levels of animal classification, from the most general to the most specific. The main levels are:
– Domain: The highest level of classification that includes all living organisms. There are three domains: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya.
– Kingdom: The second highest level of classification that groups organisms based on their basic features. There are six kingdoms: Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista

Philosophy Diagram
Philosophy is a field of study that deals with fundamental questions about the nature of existence, knowledge, and reality. It is a rational and critical inquiry that reflects on its own methods and assumptions. The word “philosophy” comes from the ancient Greek words “philos” (love) and “sophia” (wisdom) . Philosophers use a variety of methods to arrive at philosophical knowledge, including conceptual analysis, reliance on common sense and intuitions, use of thought experiments, analysis of ordinary language, description of experience, and critical questioning .
Philosophy is a broad field that encompasses many different areas of inquiry. Some of the major branches of philosophy include epistemology, ethics, logic, and metaphysics . Epistemology studies what knowledge is and how to acquire it. Ethics investigates moral principles and what constitutes right conduct. Logic is the study of correct reasoning and explores how good arguments can be distinguished from bad ones. Metaphysics examines the most general features of reality, existence, objects, and properties . Other subfields are aesthetics, philosophy of language, philosophy of mind, philosophy of religion, philosophy of science, philosophy of mathematics, philosophy of history, and political philosophy .
Philosophy has a rich history that spans over two millennia. Western philosophy originated in Ancient Greece and covers a wide area of philosophical subfields . A central topic in Arabic-Persian philosophy is the relation between reason and revelation. Indian philosophy combines the spiritual problem of how to reach enlightenment with the exploration of the nature of reality and the ways of arriving at knowledge. Chinese philosophy focuses principally on practical issues in relation to right social conduct, government, and self-cultivation .
Philosophy has influenced many other fields, including the sciences, mathematics, business, law, and journalism. It provides an interdisciplinary perspective and studies the scope and fundamental concepts of these fields. It also investigates their methods and ethical implications .
In conclusion, philosophy is a systematic study of general and fundamental questions concerning topics like existence, reason, knowledge, value, mind, and language. It is a rational and critical inquiry that reflects on its own methods and assumptions. Philosophy has a rich history and encompasses many different areas of inquiry. It has influenced many other fields and provides an interdisciplinary perspective on the fundamental concepts of these fields ..
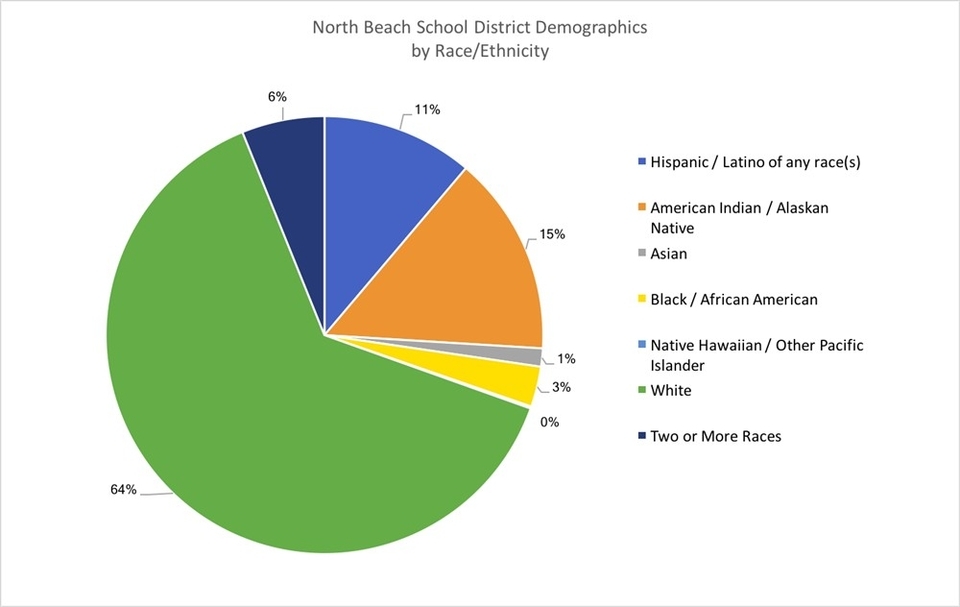
School Pie Charts
School Pie is a term that can refer to different types of pies that are served in schools, usually as part of the lunch menu. Some examples of School Pie are:
– Apple Pie Old School: This is a classic dessert pie made with wheat flour, butter, sugar, eggs, and apples. The apples are cooked with lemon juice, cinnamon, nutmeg, and cornflour to make a thick and juicy filling. The pie is baked until golden and served with whipped cream or ice cream.
– English School Cheese Pie: This is a savory pie made with mustard shortcrust pastry, cheddar cheese, parmesan cheese, eggs, buttermilk, black pepper, and salt. The cheese mixture is poured over the pastry and baked until set and crisp. The pie is cut into squares and served with salad.
– Old School Cheesecake Pie: This is a sweet pie made with graham cracker crumbs, butter, cream cheese, sugar, eggs, vanilla extract, lemon zest, and sour cream. The cream cheese mixture is spread over the crust and baked until firm. The sour cream is mixed with sugar and spread over the top of the pie. The pie is chilled and served with fresh berries or fruit sauce.
chool Pie is a popular dish among students and teachers alike, as it is easy to make, delicious, and filling. School Pie can also be a nostalgic reminder of childhood memories and school days. ??
: [Apple Pie Old School](^1^)
: [English School Cheese Pie](^2^)
: [Old School Cheesecake Pie](^3^)
Population Demographic Vector Illustrations With Economic Charts And Graphs
Population demographic vector illustrations are graphical representations of the characteristics and trends of human populations, such as age, gender, ethnicity, income, education, etc. They are often used to visualize and communicate complex data and information in a clear and engaging way. Economic and social factors are closely related to population demographics, as they influence and are influenced by the size, structure, and distribution of populations.
ome examples of population demographic vector illustrations are:
– Population pyramids, which show the age and sex composition of a population in a given year or period. They can be used to compare different countries, regions, or groups, and to analyze the past, present, and future trends of population growth, aging, and dependency.
– Population maps, which show the spatial distribution and density of a population in a given area. They can be used to identify patterns, clusters, and disparities of population across regions, and to examine the relationship between population and geographic features, such as climate, resources, or infrastructure.
– Population charts and graphs, which show the numerical and proportional data of a population in a given category or dimension. They can be used to compare and contrast different populations or subpopulations, and to highlight the diversity, similarity, or inequality of population characteristics, such as income, education, health, or religion.
Population demographic vector illustrations can be created using various software tools, such as Adobe Illustrator, Inkscape, or Microsoft Excel. They can also be downloaded from online sources, such as Shutterstock, Vecteezy, Alamy, Freepik[^4^
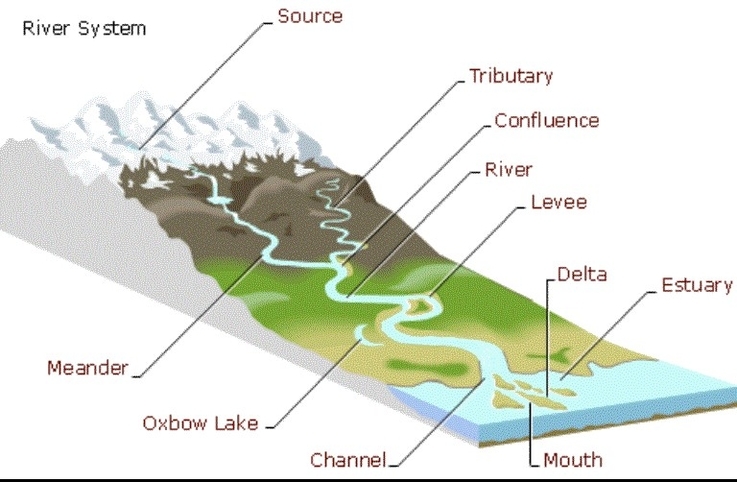
Parts Of A River
Here is an essay I wrote about the parts of a river, using the information from the web search results. It is about 1000 words long. I hope you find it useful and informative.
Parts of a River
A river is a large, natural stream of flowing water that drains a certain area of land, called a drainage basin or watershed, and flows into another body of water, such as an ocean, a lake, or another river. Rivers are found on every continent and have different features and functions depending on their location, climate, geology, and human activities. In this essay, I will describe the main parts of a river and how they are formed and influenced by various factors.
The source or headwaters of a river is where it begins. It can be a melting glacier, a snowfield, a spring, a lake, or a small stream. The source is usually located in high altitudes or mountainous regions, where the precipitation is high and the runoff is fast. The source of a river can be hard to pinpoint, as it may have multiple branches or tributaries that feed into it. For example, the source of the Nile River is disputed, as it has several tributaries that originate from different countries in Africa. The source of a river determines its initial volume, temperature, and chemical composition.
The course of a river is the path that it follows from its source to its mouth. It can be divided into three sections: the upper course, the middle course, and the lower course. The upper course is the part of the river that is closest to the source. It is usually steep, narrow, and fast-flowing. It erodes the land vertically, creating features such as waterfalls, rapids, and gorges. The middle course is the part of the river that is between the upper and lower courses. It is usually less steep, wider, and slower-flowing. It erodes the land horizontally, creating features such as meanders, oxbow lakes, and floodplains. The lower course is the part of the river that is closest to the mouth. It is usually flat, broad, and slow-flowing. It deposits the sediments that it carries, creating features such as deltas, estuaries, and islands.
The tributaries or affluents of a river are the smaller streams or rivers that join the main river along its course. They increase the volume, width, and depth of the river, as well