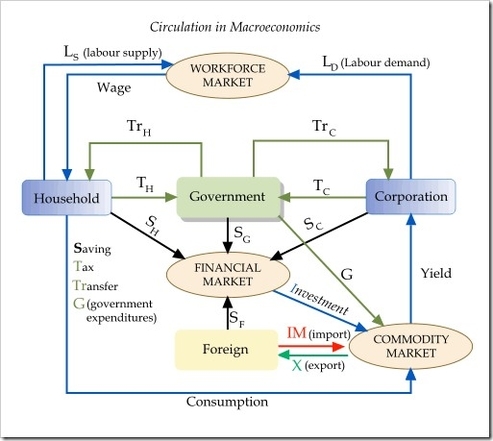
The Circular Flow Model is a fundamental concept in macroeconomics that describes how money, goods, and services move between sectors in an economic system . The model is used to measure a country’s national income or Gross Domestic Product (GDP) . The model is based on the idea that there are two cycles flowing in opposite directions: one cycle involves goods and services flowing from businesses to individuals, and individuals providing resources for production (labor force) back to the businesses. In the other direction, money flows from individuals to businesses as consumer expenditures on goods and services and flows back to individuals as personal income (wages, dividends, etc.) for the labor force provided .
The basic circular flow model consists of two sectors: households and businesses . In this model, it is assumed that households spend all their incomes as consumer expenditures and purchase the goods and services produced by businesses. Thus, there are no taxes, savings, or investments that are associated with other sectors . The five-sector model consists of households (the public sector), businesses, government, the foreign sector, and the financial sector . In this model, money flows from households and businesses to the government in the form of taxes. The government pays back in the form of government expenditures through subsidies, benefit programs, public services, etc. .
The circular flow model is used to measure a nation’s income, as the circular flow model measures both cash coming into and exiting a nation’s economy . The model is also used to gauge the interdependence of different sectors in an economy . The model is crucial for calculating national income and is a key concept in macroeconomics .
In summary, the circular flow model describes how money and economic resources flow in cycles between different sectors in an economic system. The model is used to measure a country’s national income or GDP and to gauge the interdependence of different sectors in an economy. The model is a fundamental concept in macroeconomics and is crucial for calculating national income .
