Month: July 2021
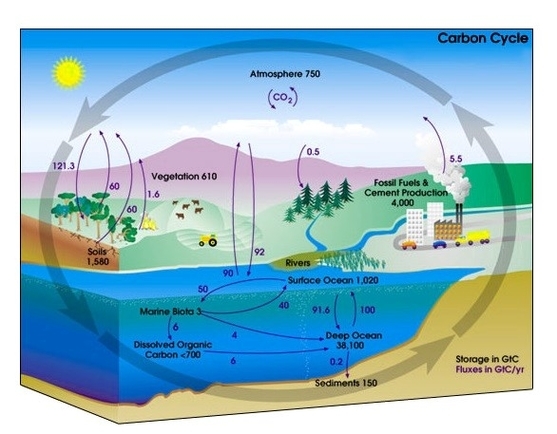
Carbon Cycle Diagram
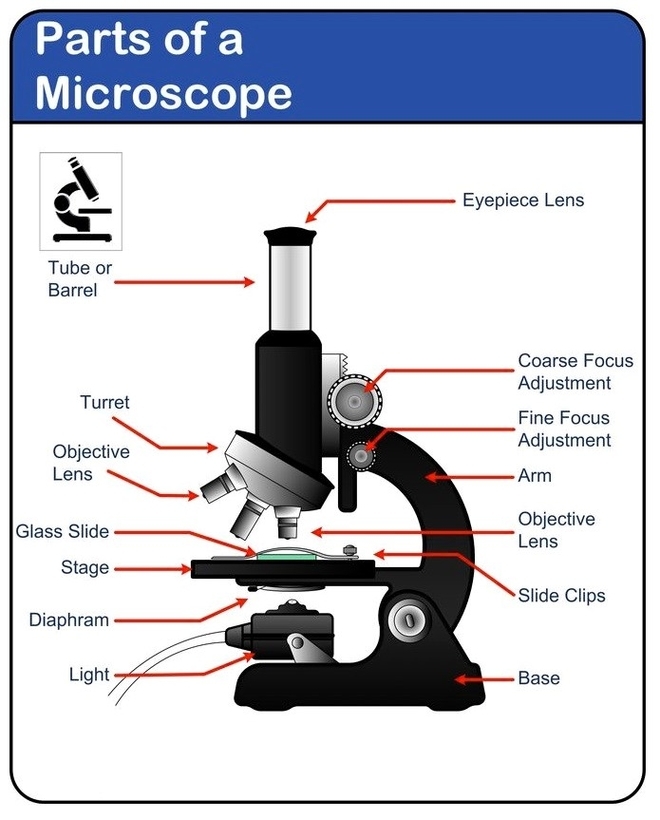
Miscroscope diagram
To better understand the structure and function of a microscope, we need to take a look at the labeled microscope diagrams of the compound and electron microscope. These diagrams clearly explain the functioning of the microscopes along with their respective parts. Man’s curiosity has led to great inventions. The microscope is one of them.
Here, unlabeled microscope diagrams have been provided for your perusal, which will help you practice and test your understanding of the instrument. Depending on the source of illumination, microscopes can be divided into two categories. They are:
A simple microscope’s parts have two classifications: the mechanical part and the optical parts. What are the mechanical parts? Mechanical parts pertain to the parts of the microscope that support the optional parts. They help in the adjustment so as to accurately magnify the object. Mechanical parts include the following:
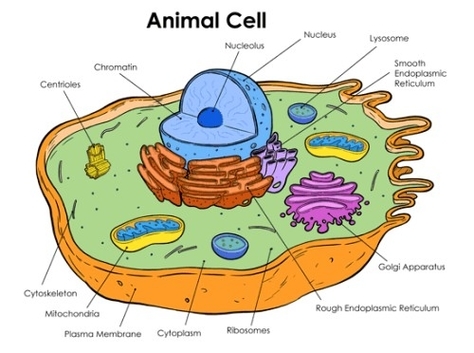
Animal Cell
Animal Cell Definition: Animal cells, which are the fundamental units of life in the Animal Kingdom, are eukaryotic cells. This means that they contain a true (membrane-bound nucleus) along with other membrane-bound organelles.
An animal cell is a type of cell that differs from plant or fungi cells. Like plant and fungi cells, an animal cell is eukaryotic, but animal cells lack the cell wall structure found in plant and fungi cell types. Animal cells also do not contain chloroplasts as plant cells do, as animal cells are heterotrophic and do not perform photosynthesis.
Animal cells, which are the fundamental units of life in the Animal Kingdom, are eukaryotic cells. This means that they contain a true (membrane-bound nucleus) along with other membrane-bound organelles.
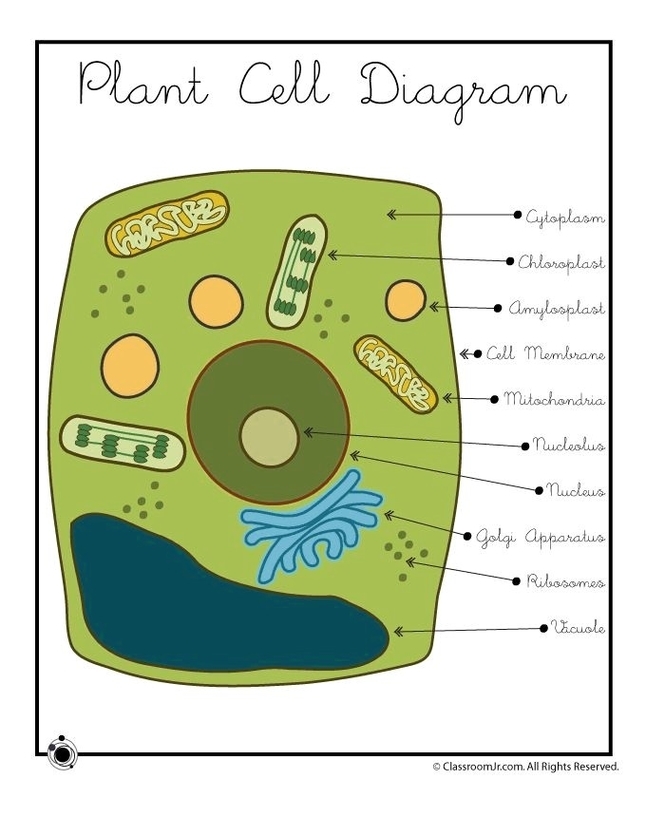
Plant Cell Diagram
Worm Anatomy Diagram
Worm Anatomy A worms body is made up of many segments called ‘annuli’. The length of a worms body has muscles which contract and relax which enables the worm to move along a surface. The ‘annuli’ are covered in tiny hairs called ‘setae’ which help the worms movement.
Not necessarily in that order:) The worm has a pointed head and a slightly rounded body. The rings on its body are called segments. Earthworms have no protruding body parts making the worm very contour which enables them to pass through the soil with ease and to also squeeze in between tiny cracks.
Place earthworm in the dissecting tray & rinse off the excess preservative. Identify the dorsal side, which is the worm’s rounded top, and the ventral side, which is its flattened bottom. Turn the worm ventral side up, as shown in the earthworm anatomy diagram below. 3.

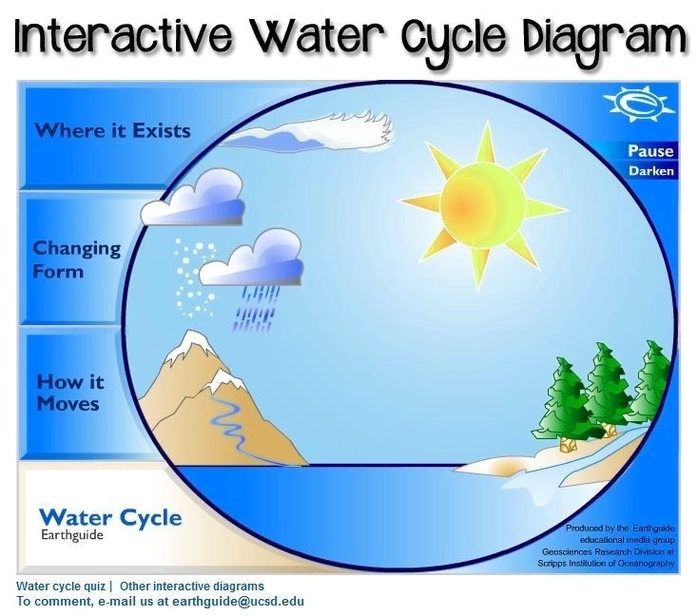
Water Cycle Diagram
In this activity, students will create their own water cycle diagrams. You can differentiate or scaffold this activity by adding or removing information from the template or instructions. Students are also encouraged to provide a description of each step or the cycle as a whole using textables or the cell and description layout.
Our interactive diagrams allow you to “mouse around” the parts of the water cycle and view explanations, pictures, and more. Our interactive diagram allows you to “mouse around” the parts of the water cycle and view explanations, pictures, and more online. The diagram is available for three levels of students:
Written By: Water cycle, also called hydrologic cycle, cycle that involves the continuous circulation of water in the Earth-atmosphere system. Of the many processes involved in the water cycle, the most important are evaporation, transpiration, condensation, precipitation, and runoff.
Volcano Eruption Diagram
In this topic, we look at how movements in the earth’s crust can cause both volcanic eruptions and earthquakes. It also looks at different types of plate boundary and where volcanoes are located. It then goes on to look at the different features of volcanoes by looking at a cross-section of a volcano.
Label a volcano diagram. Free to download. Click on the image above. What is a volcano? What is a volcano? In this topic, we look at how movements in the earth’s crust can cause both volcanic eruptions and earthquakes.
178 volcano diagram illustrations & vectors are available royalty-free. Volcano cross section with hot lava and volcanic ash cloud vector diagram. Illustration of volcano mountain, volcanic lava flow Volcano Types Infographic Diagram.
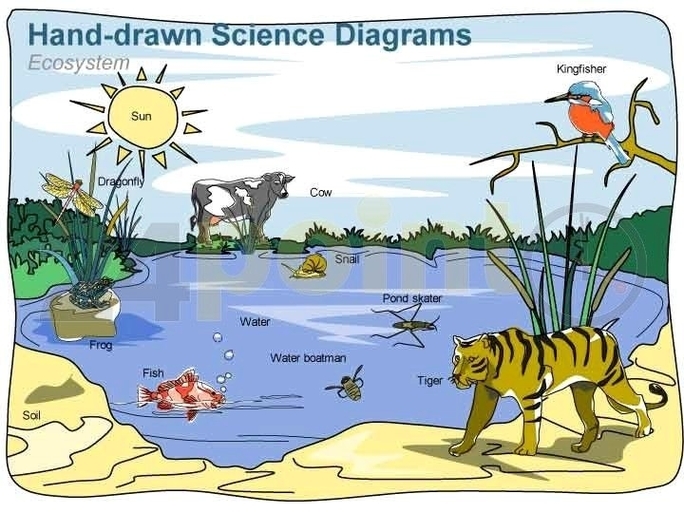
Ecosystem diagram
An ecosystem is a discrete structural, functional and life sustaining environmental system. The environmental system consists of biotic and abiotic components in a habitat. Biotic component of the ecosystem includes the living organisms; plants, animals and microbes whereas the abiotic component includes inorganic matter and energy.
“The organisms and the physical features of the habitat form an ecological complex or more briefly an ecosystem.” (Clarke, 1954). The concept of ecosystem was first put forth by A.G. Tansley (1935). Ecosystem is the major ecological unit. It has both structure and functions.
The structure of an ecosystem is basically a description of the organisms and physical features of environment including the amount and distribution of nutrients in a particular habitat. It also provides information regarding the range of climatic conditions prevailing in the area. From the structure point of view, all ecosystems consist of the …
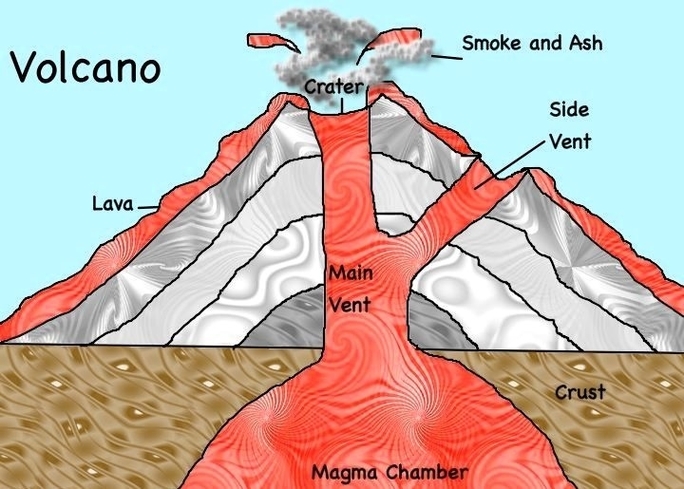
Parts of a volcano
9 Parts of a volcano from the inside. 1 1. Magma chamber. This is the part of the volcano located deepest underground, even beneath the Earth’s crust. The width of the magma chamber ranges … 2 2. Lava dome. 3 3. Magmatic dike. 4 4. Vent. 5 5. Fissure vents. More items
In this anatomy of a volcano, explore the basic geological features of a volcano such as Mt. St. Helens as well as the deadly materials released during volcanic eruptions. To learn more about the various numbered parts of this volcano diagram, read on.
Vent – An opening in Earth’s surface through which volcanic materials escape. Flank – The side of a volcano. Lava – Molten rock that erupts from a volcano that solidifies as it cools. Crater – Mouth of a volcano – surrounds a volcanic vent. Conduit – An underground passage magma travels through. Throat – Entrance of a volcano.