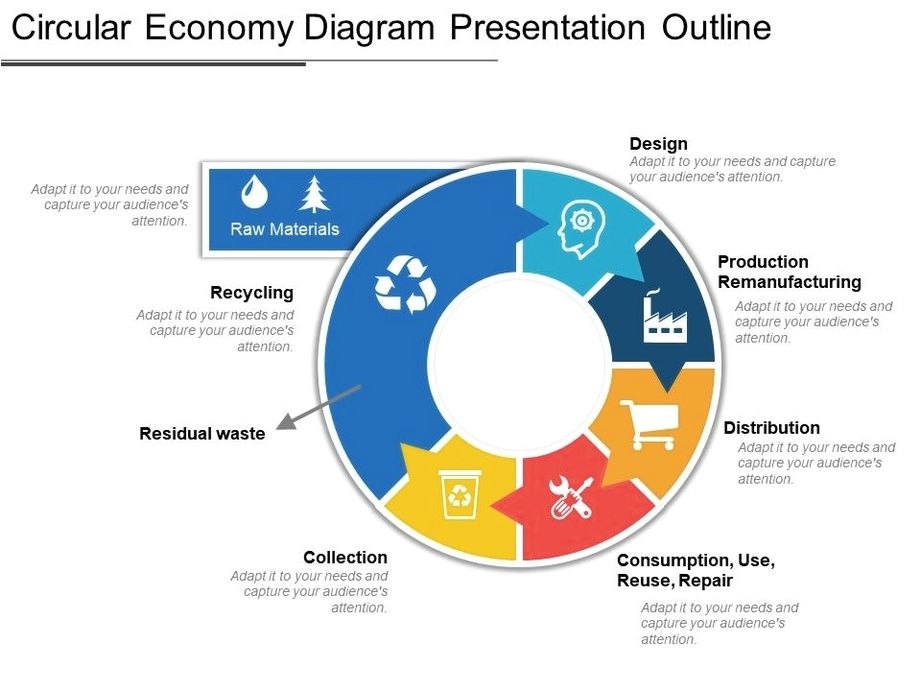
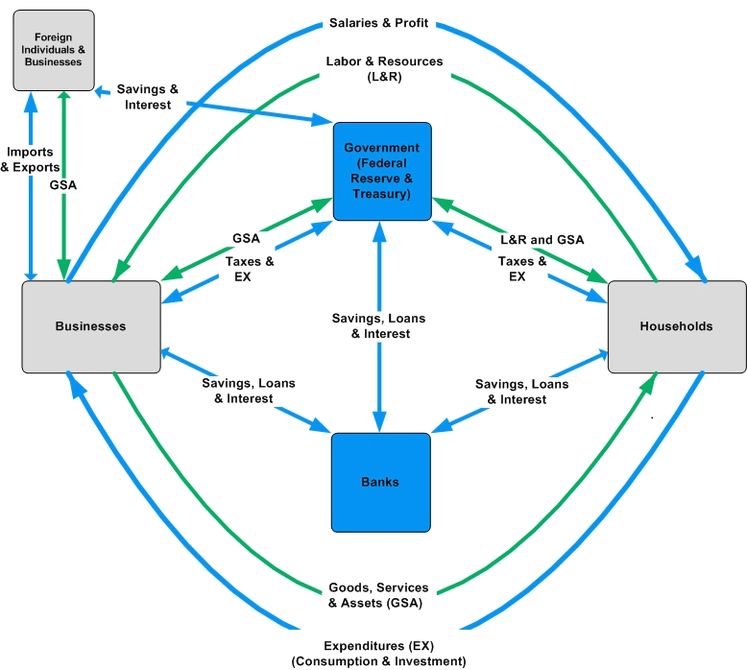
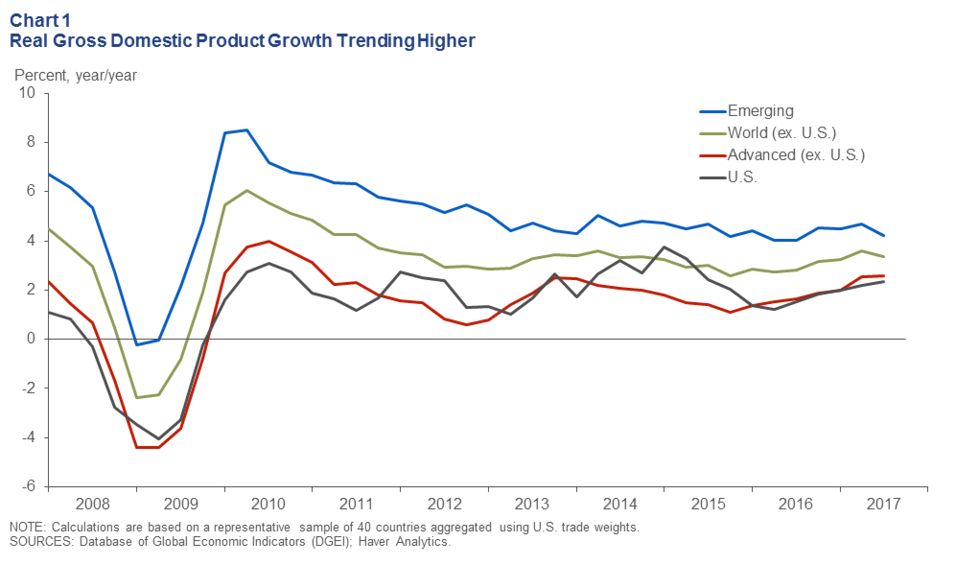
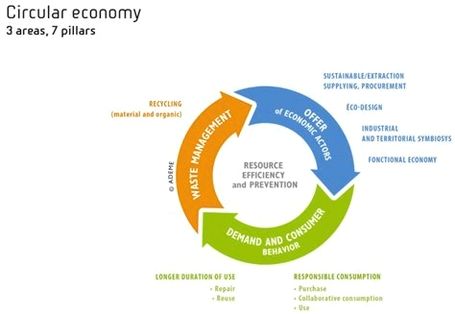
See the below image for the Global economy pie diagram. Starting now, PIIE will track the state of the global economy and the success of policy measures adopted to rebuild it in an accessible online format, to provide ongoing assessment of progress. Constructive economic solutions to the existential threats we face are possible, but they must be targeted at practical rebuilding, and they must be global.
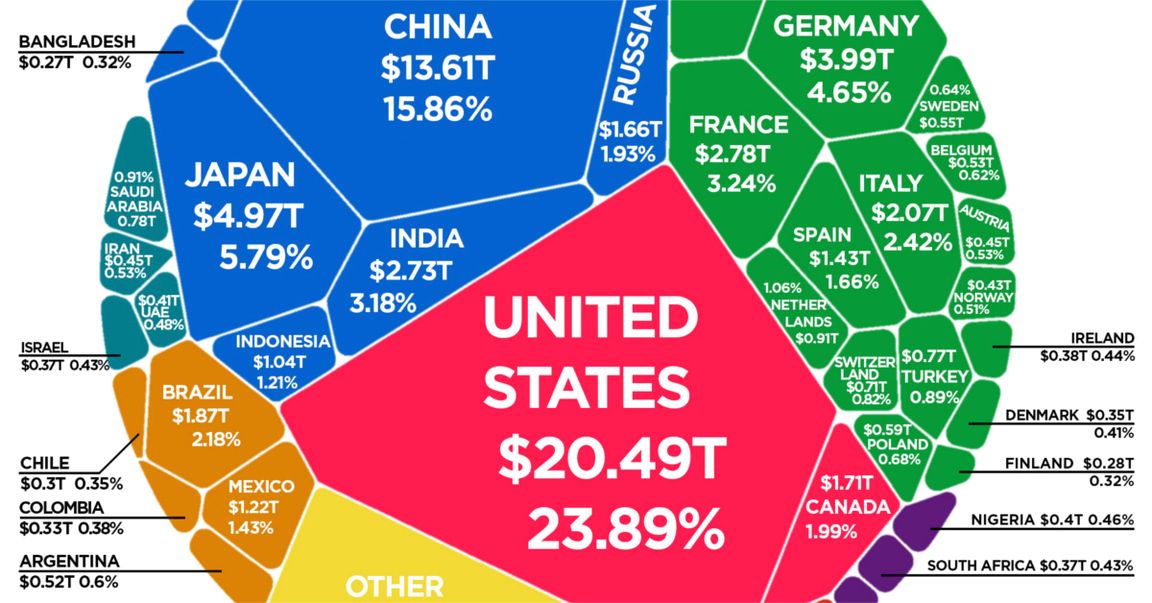
Surpassing the $100 trillion mark is a new milestone for global economic output. We’ve covered this topic in the past when the world’s GDP was $88 trillion (2020) and then $94 trillion (2021), and now according to the latest projections, the IMF expects the global economy to reach nearly $104 trillion in nominal value by the end of 2022.
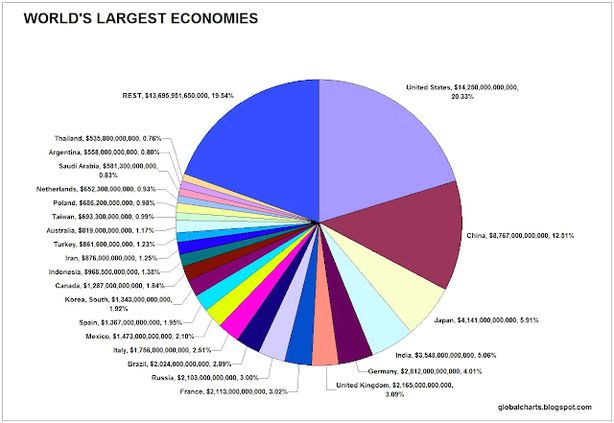
In the one-year period since the last release of official data in 2018, the global economy grew approximately $2 trillion in size—or about 2.3%. The United States continues to have the top GDP, accounting for nearly one-quarter of the world economy.