Vellore Institute of Technology (VIT) is a private university located in Vellore, Tamil Nadu, India. The School of Advanced Sciences (SAS) at VIT was established in 1984 and comprises the departments of Mathematics, Physics, and Chemistry. The school aims to provide quality teaching and research that would make an impact at a global level.
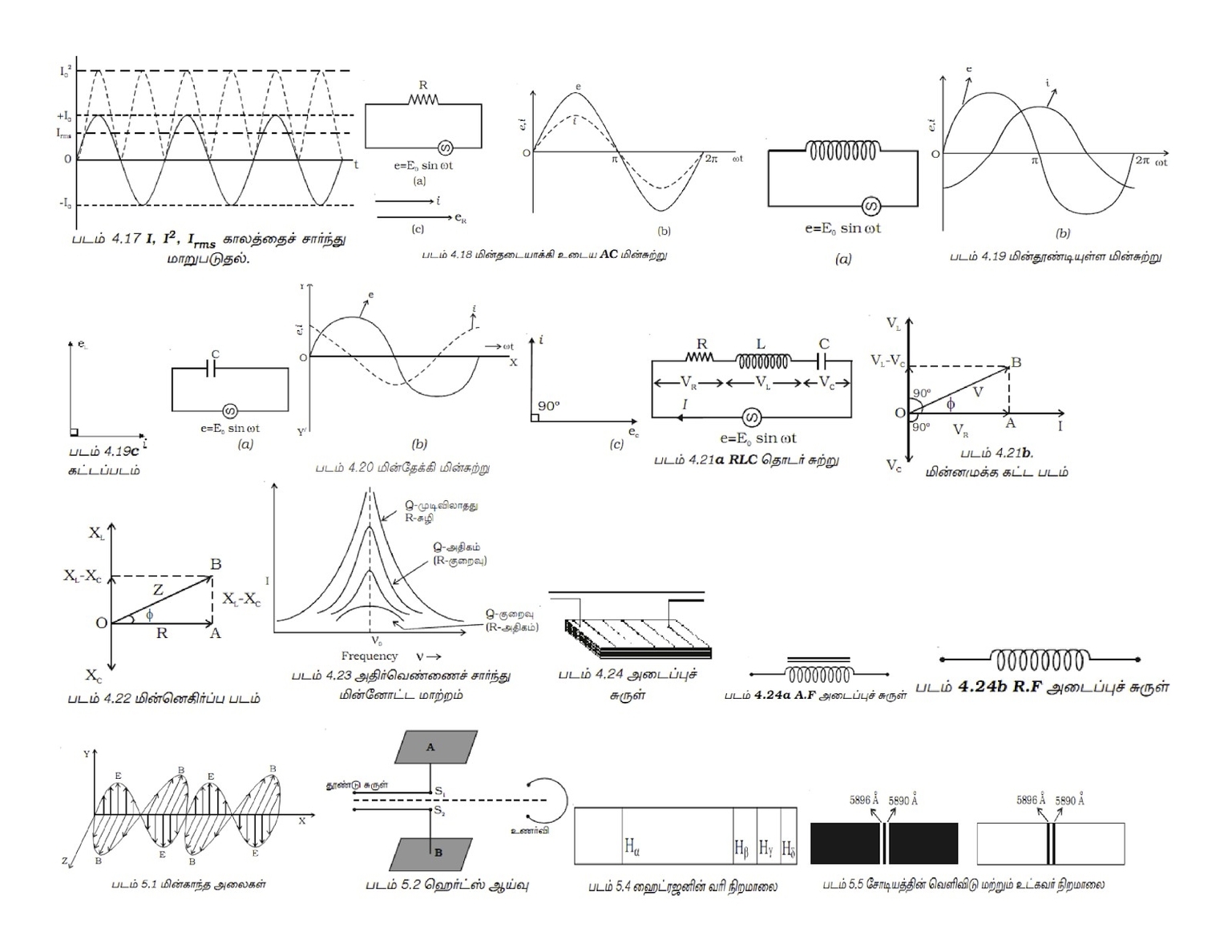
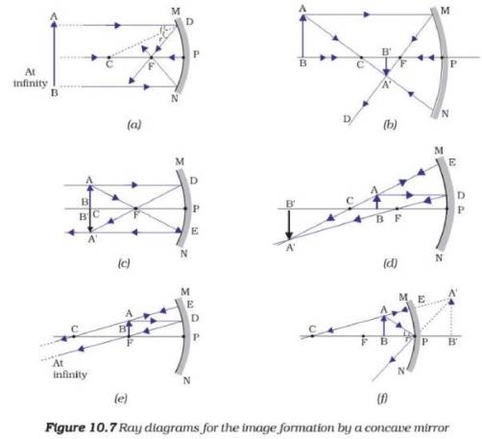
The Physics department at SAS offers a range of undergraduate and postgraduate programs. The undergraduate program offers University core and elective courses in Mathematics, Physics, and Chemistry for all undergraduate programs. The postgraduate program offers M.Sc. programs in Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics. The department also offers core and elective courses for all postgraduate programs. The school also offers Ph.D. programs in frontier research areas.
The Physics department at SAS has a total of 45 experienced and energetic faculty members. Most of them are experts in their research fields. The department has been receiving research grants from various national and international funding agencies like AERB, ARDB, BRNS, CII, CSIR, DBT-RGYI, DRDO, DST, IGCAR, ISRO, NBHM, NRB, and UGC-DAE. The department has ongoing projects to the tune of Rs. 11.5 crores (1.551 million US Dollars) and has successfully completed several projects to the tune of Rs. 27.032 crores (3.643 million US Dollars).
The Physics department at SAS has a strong focus on research and innovation. The department has been recognized by the Department of Science and Technology (DST) for support under the FIST programs. The department has also been actively involved in community activities such as National Science Day, InoVIT (National Science Contest for School students), and VIT Mathematical Meet (A State-level Mathematical Contest for School students).
In conclusion, the Physics department at VIT’s School of Advanced Sciences is a well-established department with a strong focus on research and innovation. The department offers a range of undergraduate and postgraduate programs and has a team of experienced and energetic faculty members. The department has been receiving research grants from