Shifting cultivation is a form of agriculture that involves moving from one plot of land to another after a period of cultivation. It is practiced in many parts of the world, especially in the humid and sub-humid tropics, where it covers about 280 million hectares of land. Shifting cultivation has both advantages and disadvantages for the environment and the people who practice it.
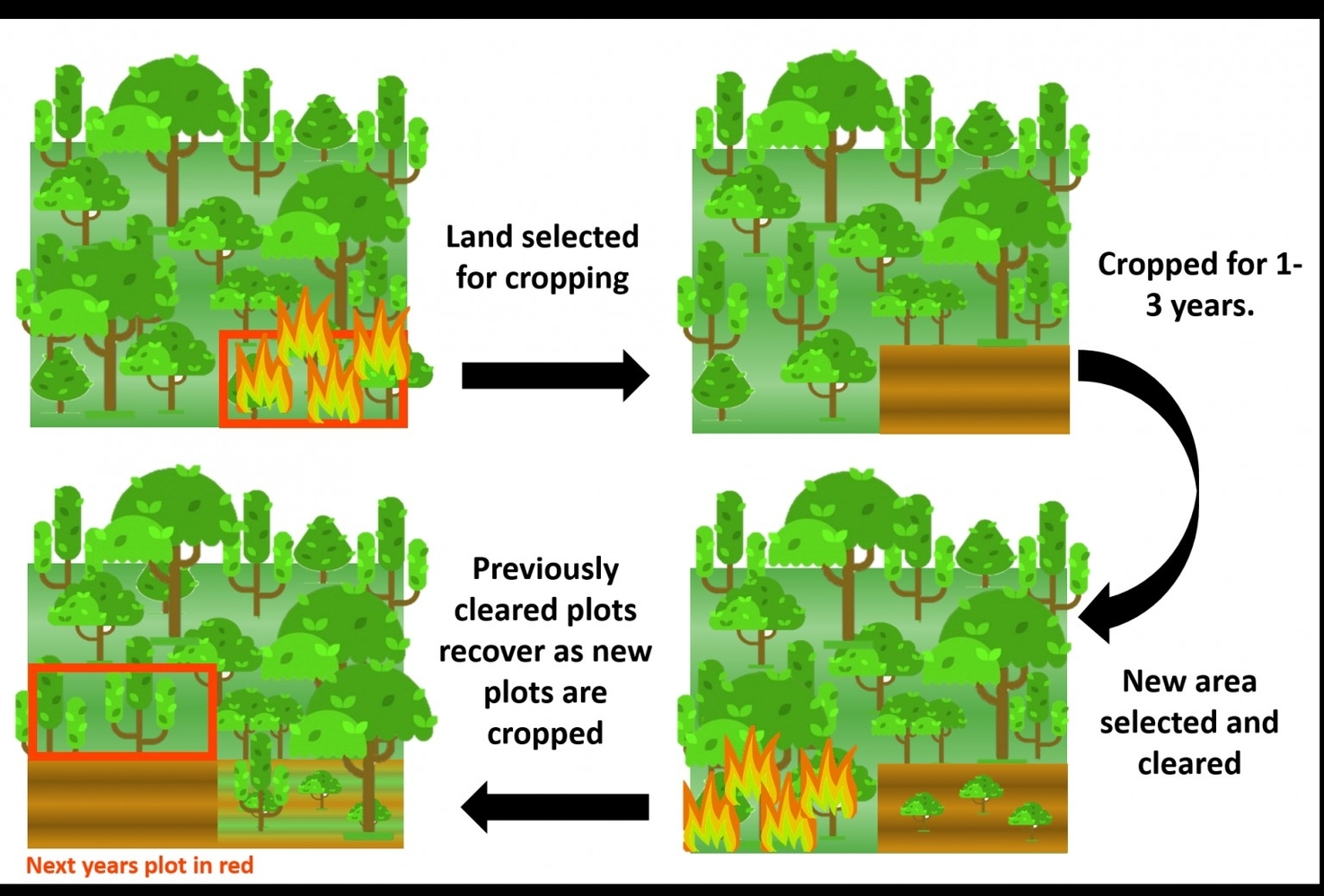
The main steps of shifting cultivation are:
– Clearing: The cultivator selects a plot of land, usually in a forested area, and cuts down the trees and bushes. This is often done by slash-and-burn methods, which means setting fire to the vegetation after slashing it. This creates a layer of ash that adds nutrients to the soil.
– Cultivating: The cultivator plants crops on the cleared land, using simple tools like hoes and digging sticks. The crops are usually mixed and diverse, such as maize, cassava, rice, beans, bananas, and vegetables. The cultivator may also plant fruit and nut trees, or protect some of the natural vegetation, to provide additional food and resources.
– Fallowing: After a few years, the soil becomes less fertile and more prone to weeds and pests. The cultivator then abandons the plot and moves to a new one, leaving the old one to regenerate naturally. The fallow period can last from a few years to several decades, depending on the local conditions and the type of vegetation. During this time, the fallow plot provides habitat for wildlife, carbon storage, and soil protection.
– Returning: The cultivator may return to the same plot after the fallow period, or may choose a different one. The cycle then repeats itself.
hifting cultivation has some benefits for the environment and the people who practice it, such as:
– It maintains biodiversity and ecosystem services, as the fallow plots allow for the recovery of natural vegetation and wildlife.
– It adapts to the local conditions and needs of the people, as they can choose the crops, trees, and fallow periods that suit them best.
– It preserves the traditional knowledge and culture of the people, as they have been practicing shifting cultivation for generations and have developed a close relationship with the land.
hifting cultivation also has some drawbacks for the environment and the people who practice it, such as:
– It contributes to deforestation and greenhouse gas emissions, as the clearing and burning of vegetation releases carbon dioxide and other gases into the atmosphere.
– It reduces the productivity and sustainability of the land, as the soil becomes degraded and eroded over time.
– It faces pressure and competition from