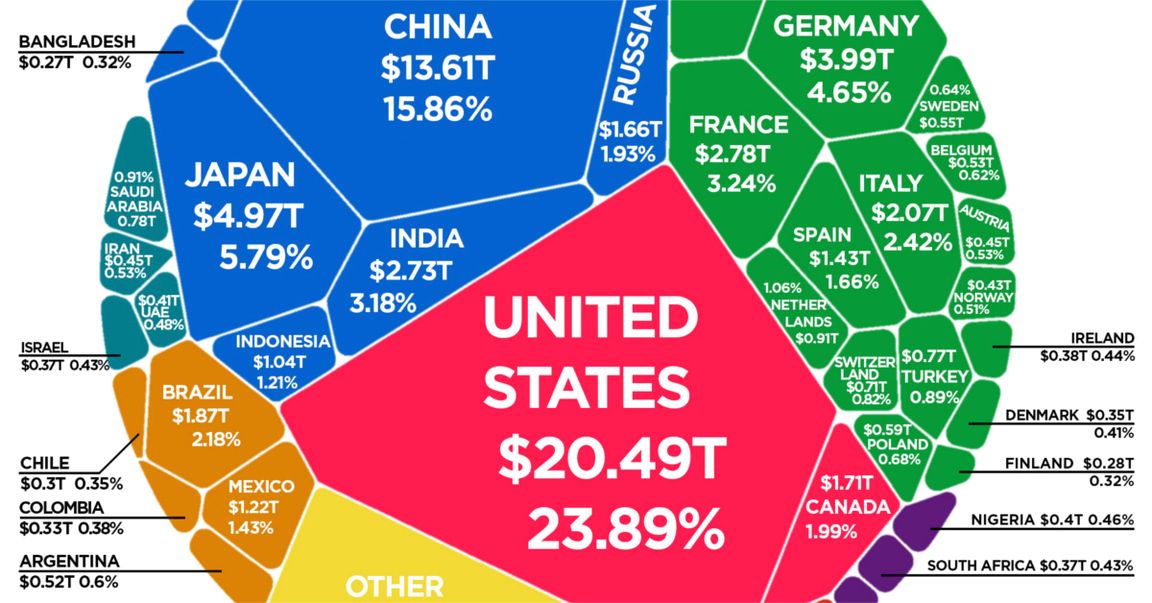
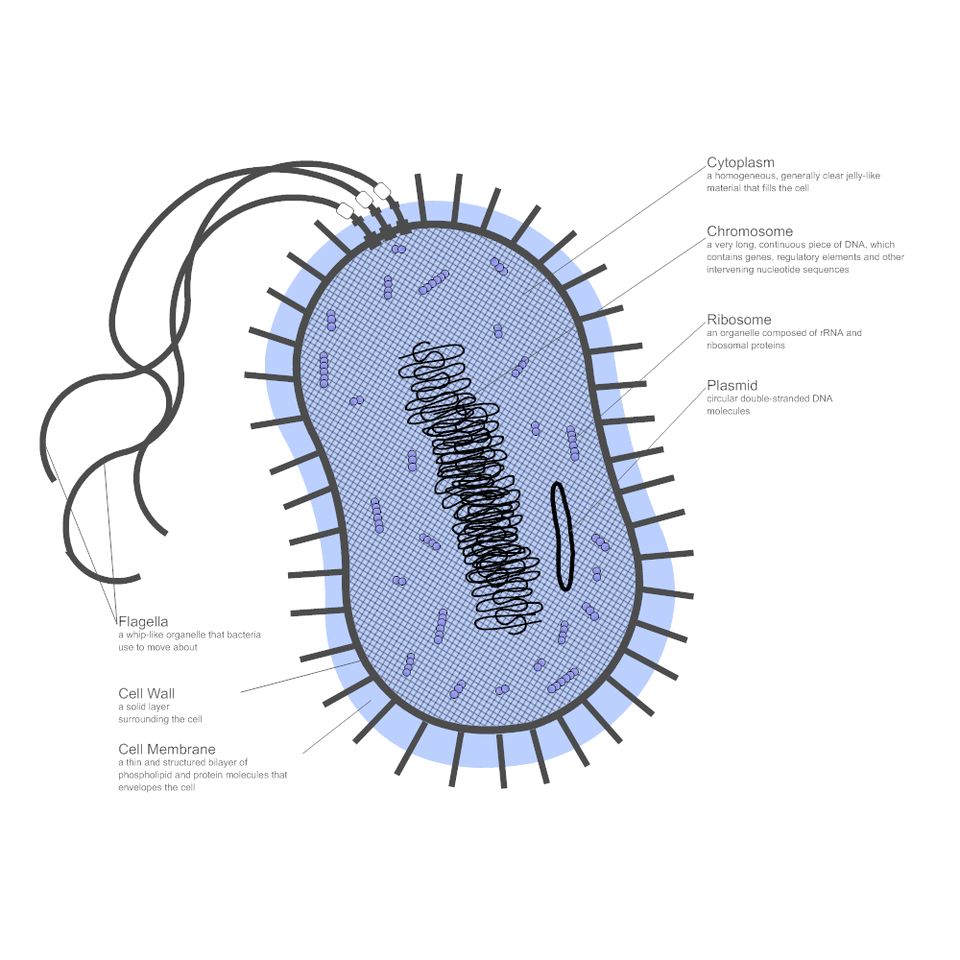
See the below image for the World economy in one diagram. The $86 Trillion World Economy in One Chart The world economy is in a never-ending state of flux. The fact is that billions of variables — both big and small — factor into any calculation of overall economic productivity, and these inputs are changing all of the time.
The World’s Top 10 Economies Rank Country GDP % of Global GDP #1 United States $19.4 trillion 24.4% #2 China $12.2 trillion 15.4% #3 Japan $4.87 trillion 6.1% #4 Germany $3.68 trillion 4.6% 6 more rows …
The $80 Trillion World Economy in One Chart. The latest estimate from the World Bank puts global GDP at roughly $80 trillion in nominal terms for 2017. Today’s chart from HowMuch.net uses this data to show all major economies in a visualization called a Voronoi diagram – let’s dive into the stats to learn more. The World’s Top 10 Economies