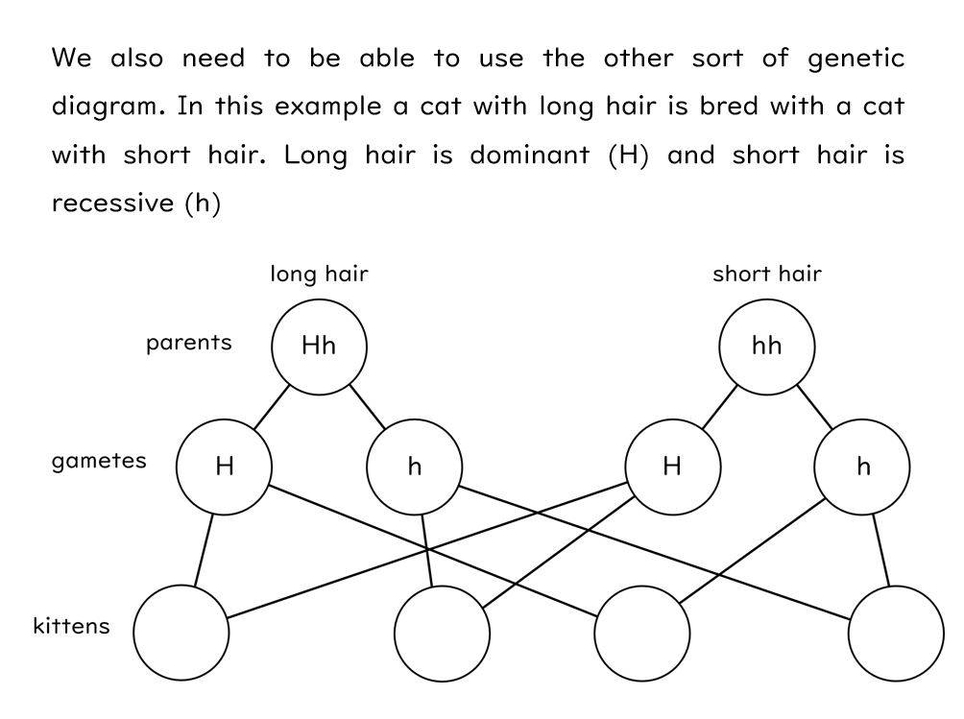
Genetic Diagrams: Genetic diagrams, such as Punnett squares, depict the inheritance of traits from parents to offspring. They are used to predict genetic variations and understand patterns of inheritance in organisms.
Charts, Graphs and Diagrams
The term economic flow refers to the movement of goods, services, and money within an economy. It is a fundamental concept in economics that helps us understand how different sectors of the economy interact with each other. There are two main models that economists use to explain economic flow: the circular flow model and the economic cycle.
The circular flow model is a simplified representation of how money and goods move between households and businesses. In this model, households provide labor to businesses in exchange for wages, which they use to purchase goods and services from businesses. Businesses, in turn, use the revenue generated from these sales to pay for labor and other inputs. This creates a circular flow of money and goods between households and businesses, which is essential for the functioning of a market economy .
The economic cycle, also known as the business cycle, refers to the fluctuations in economic activity that occur over time. The cycle is characterized by four stages: expansion, peak, contraction, and trough. During the expansion phase, the economy grows rapidly, with low unemployment rates and high levels of consumer spending. The peak phase marks the end of the expansion and the beginning of a contraction, during which economic activity slows down, unemployment rates rise, and consumer spending decreases. The trough phase is the bottom of the cycle, where the economy is at its weakest. Finally, the cycle enters the expansion phase again, and the process repeats itself .
The economic cycle is driven by a variety of factors, including changes in interest rates, government policies, and technological innovations. Understanding the economic cycle is important for investors and businesses, as it can help them make informed decisions about when to invest and when to pull back. It is also important for policymakers, who can use fiscal and monetary policies to stabilize the economy during times of contraction .
In conclusion, the concept of economic flow is essential for understanding how different sectors of the economy interact with each other. The circular flow model and the economic cycle are two important models that economists use to explain economic flow. By understanding these models, we can gain a better understanding of how the economy works and make informed decisions about our investments and policies.
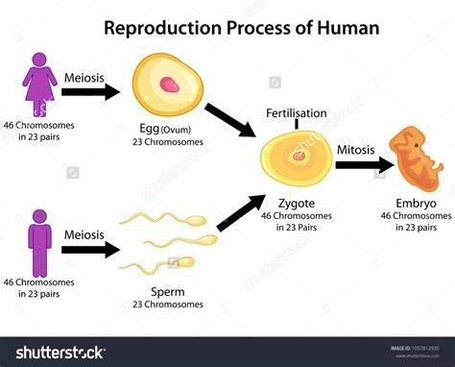
Human Reproduction Diagram: A human reproduction diagram displays the male and female reproductive systems, labeled with structures such as the testes, vas deferens, penis, ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, and vagina. Additional diagrams may show fertilization, embryo development, and menstrual cycle phases. These illustrations help explain the complex biological process of reproduction, from gamete formation to childbirth, and are fundamental in health education and biology curricula.
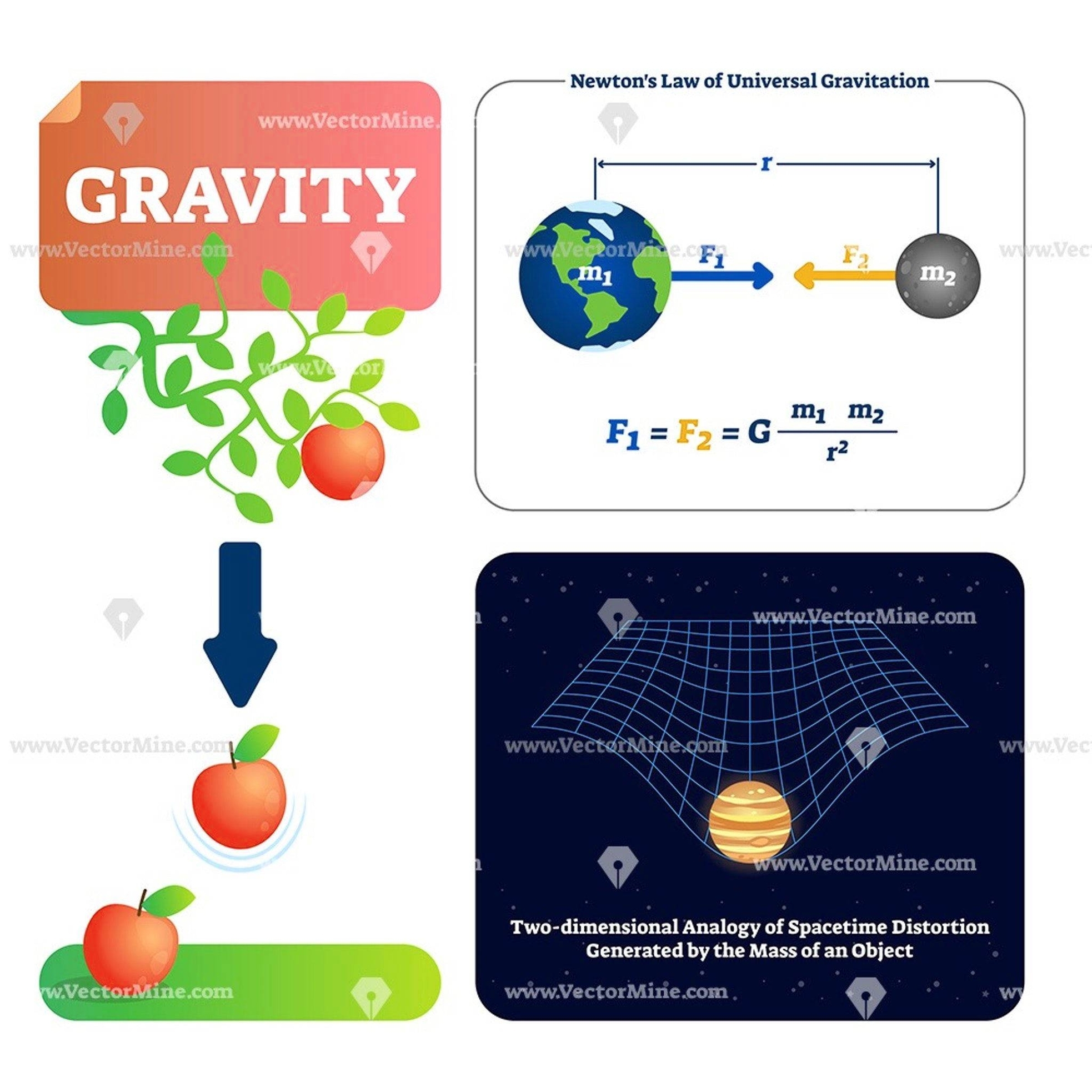
Gravity Explanation Diagram With Formula Physics Gravitation Concept Map: A gravity explanation diagram with formulas and a concept map illustrates the principles of gravitational force. It includes key formulas, such as Newtons law of gravitation, and visual representations of gravitational interactions.
Physics 24 is a rapid learning course that covers the fundamentals of physics in 24 chapters. The course is designed to help students learn physics quickly and efficiently. The course is offered by Rapid Learning Center, which is a leading provider of online education.
The course is divided into 24 chapters, each of which covers a different topic in physics. The topics covered in the course include mechanics, waves, thermodynamics, electricity, magnetism, and optics. The course is designed to be self-paced, so students can work through the material at their own speed.
Each chapter of the course includes a core concept tutorial, which is a visual presentation of the key concepts covered in the chapter. The tutorials are designed to be engaging and easy to understand. They include animations, illustrations, and examples to help students grasp the material.
In addition to the core concept tutorials, each chapter includes problem-solving drills and review sheets. The problem-solving drills are designed to help students practice applying the concepts they have learned. The review sheets are designed to help students review the material they have covered in the chapter.
The course is suitable for high school and college students who are studying physics. It is also suitable for anyone who wants to learn physics for personal enrichment or professional development.
The course is available online and can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection. Students can work through the material on their own schedule and at their own pace. The course is designed to be flexible and adaptable to the needs of individual students.
In conclusion, Physics 24 is a rapid learning course that covers the fundamentals of physics in 24 chapters. The course is designed to be engaging, easy to understand, and self-paced. It is suitable for high school and college students, as well as anyone who wants to learn physics for personal enrichment or professional development.
Physical science is the study of matter, energy, and the interactions between them. Physical science display ideas are ways to showcase the concepts and phenomena of physical science in a creative and engaging way. Here are some possible physical science display ideas for you:
– Electricity and Magnetism: You can demonstrate the principles of electricity and magnetism by creating circuits, electromagnets, motors, generators, speakers, and more. You can use wires, batteries, magnets, light bulbs, coils, and other materials to make your display interactive and fun. You can also explain how electricity and magnetism are related, and how they are used in everyday devices.
– Sound and Light: You can explore the properties of sound and light by making musical instruments, optical illusions, kaleidoscopes, prisms, mirrors, lenses, and more. You can use different materials to show how sound and light travel, reflect, refract, diffract, interfere, and change frequency and wavelength. You can also explain how sound and light are forms of energy, and how they are used for communication and entertainment.
– Forces and Motion: You can investigate the effects of forces and motion by building rockets, cars, planes, catapults, pendulums, roller coasters, and more. You can use different materials to show how forces and motion depend on mass, speed, direction, gravity, friction, air resistance, and other factors. You can also explain how forces and motion are related to Newton’s laws, and how they are used in transportation and engineering.
– Chemical Reactions: You can demonstrate the changes that occur during chemical reactions by making volcanoes, slime, crystals, soap, baking soda and vinegar, and more. You can use different substances to show how chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of atoms, the release or absorption of energy, and the formation of new products. You can also explain how chemical reactions are involved in cooking, cleaning, medicine, and other applications.
These are some examples of physical science display ideas that you can try. You can also combine different topics and experiment with different materials to create your own unique display. Physical science display ideas are a great way to learn about the natural world and express your creativity. Have fun! ??
Chemistry And Computer Science: Chemistry and computer science intersect in the field of computational chemistry, where computer simulations assist in solving chemical problems. This interdisciplinary approach helps in understanding molecular structures, creating drugs, and optimizing various chemical processes.