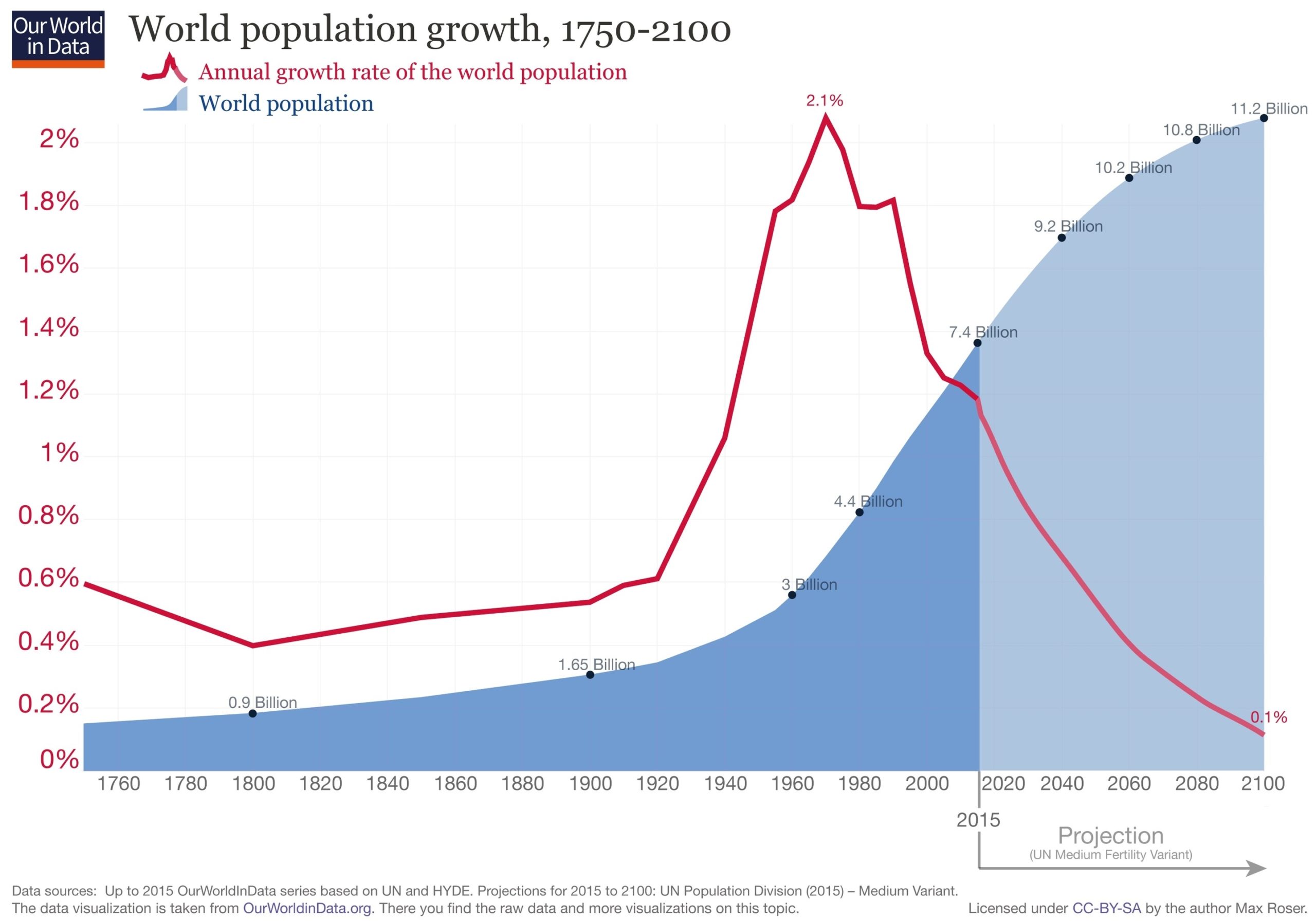
World population growth is the change in the number of people living on Earth over time. It is influenced by factors such as birth rates, death rates, migration, and environmental changes. Here is a brief overview of world population growth in about 1000 words:
The world population has increased rapidly in recent centuries, reaching 8.1 billion people in 2024. However, the growth rate has slowed down from its peak of around 2% per year in the late 1960s to around 0.9% per year in 2024. This slowdown is mainly due to the decline in fertility rates, which is the average number of children per woman, across most regions of the world. Fertility rates have fallen from about 5 children per woman in 1950 to about 2.4 children per woman in 2020. This decline is influenced by various factors, such as education, health, contraception, urbanization, and women’s empowerment.
The current population increase is estimated at around 73 million people per year. This means that every day, there are about 200,000 more people on the planet than the day before. The majority of this population growth occurs in low- and middle-income countries, especially in Africa and Asia, where fertility rates are still relatively high and mortality rates are declining due to improvements in health and sanitation. In contrast, high-income countries have low or negative population growth, as fertility rates are below the replacement level of 2.1 children per woman and migration is not enough to offset the aging and shrinking of the population.
The future of world population growth is uncertain, as it depends on the trends and projections of fertility, mortality, and migration, which are influenced by various social, economic, and environmental factors. The latest UN projections suggest that the world population could grow to around 8.5 billion in 2030 and 9.7 billion in 2050, before reaching a peak of around 10.4 billion people during the 2080s. The population is expected to remain at that level until 2100[^
