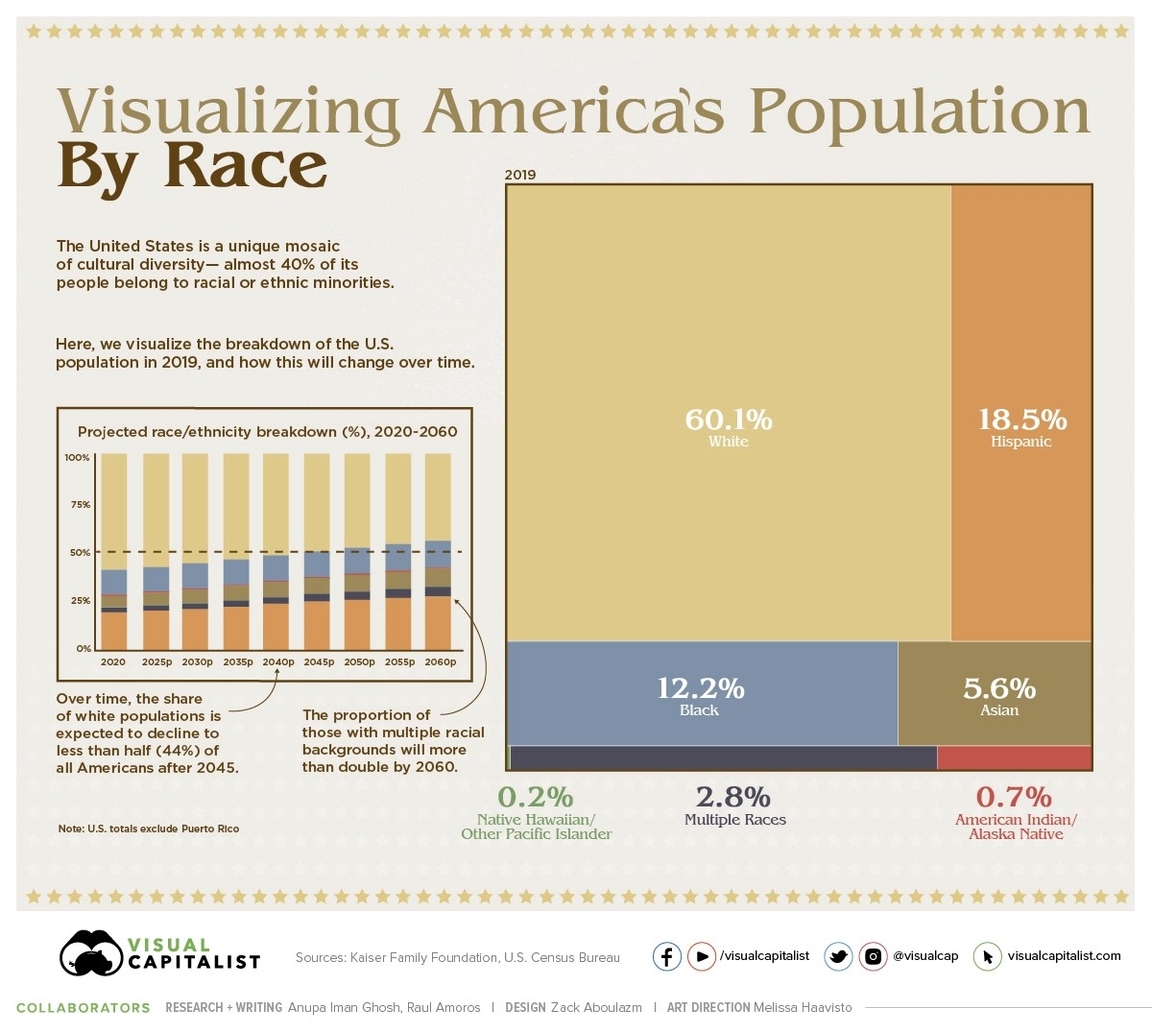
The United States is a diverse country with a population of over 332 million people. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the country’s population is becoming increasingly diverse. The 2020 Census used two separate questions to collect the races and ethnicities of the U.S. population, following the standards set by the U.S. Office of Management and Budget (OMB) in 1997. The following table shows the racial and ethnic composition of the U.S. population as of 2019:
| Race/Ethnicity | Percentage of Population |
|—————–|————————–|
| White | 60.1% |
| Hispanic | 18.5% |
| Black | 12.2% |
| Asian | 5.6% |
| Multiple Races | 2.8% |
| American Indian/Alaska Native | 0.7% |
| Native Hawaiian/Other Pacific Islander | 0.2% |
It is important to note that the above percentages are based on self-identification and may not be an accurate representation of the actual population. The overall racial and ethnic diversity of the country has increased since 2010, according to U.S. Census Bureau analyses. The concept of “diversity” refers to the representation and relative size of different racial and ethnic groups within a population and is maximized when all groups are represented in an area and have equal shares of the population.