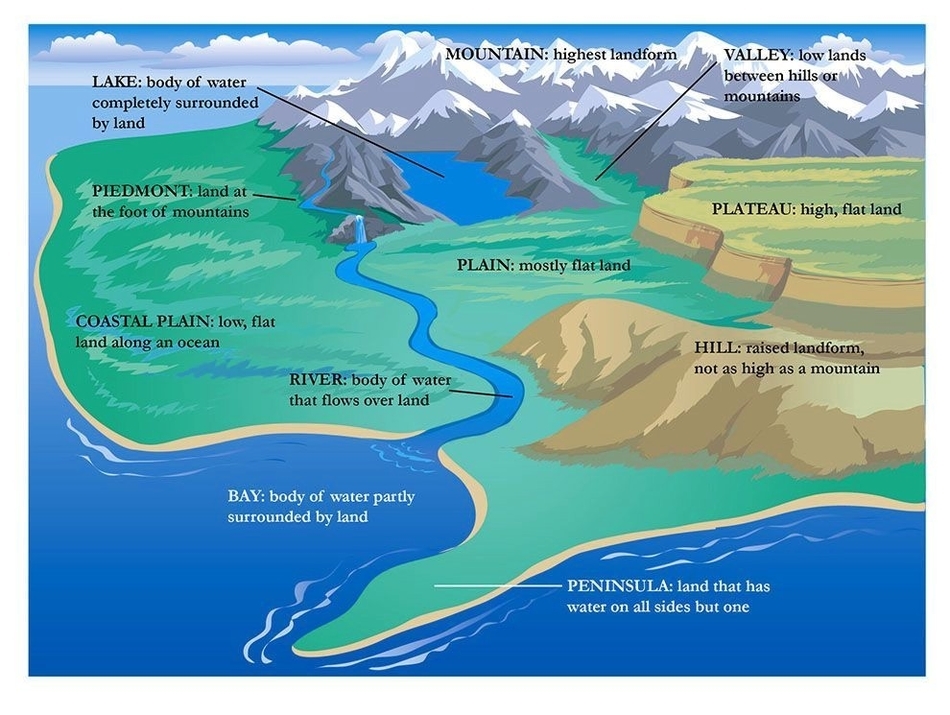
Landforms are natural features of the Earth’s surface that have been formed by various geological processes. They are an essential part of the Earth’s geography and play a crucial role in shaping the planet’s ecosystems. Landforms can be classified into several categories based on their characteristics, such as their elevation, slope, and shape. Some of the most common landforms include mountains, hills, valleys, plateaus, plains, deserts, and canyons.
Mountains are landforms that rise above the surrounding terrain and have steep slopes and high elevations. They are formed by tectonic forces that cause the Earth’s crust to fold and uplift. The highest mountain in the world is Mount Everest, which stands at an elevation of 29,031.7 feet above sea level. Hills are similar to mountains but are smaller in size and have gentler slopes. They are formed by the same geological processes as mountains.
Valleys are low-lying areas between mountains or hills. They are formed by the erosion of the surrounding terrain by water or ice. Valleys can be narrow or wide and can be home to rivers, lakes, or other bodies of water. Plateaus are flat, elevated landforms that are higher than the surrounding terrain. They are formed by the uplift of the Earth’s crust and can be found on every continent. The Tibetan Plateau is the highest plateau in the world, with an average elevation of over 14,800 feet.
Plains are flat, low-lying areas that are generally covered by grasses or other vegetation. They are formed by the deposition of sediment by rivers, wind, or glaciers. Plains can be found on every continent and are often used for agriculture. Deserts are dry, barren areas that receive very little rainfall. They are formed by the interaction of atmospheric and geological processes and can be found on every continent. The Sahara Desert in Africa is the largest hot desert in the world, covering over 3.6 million square miles.
Canyons are deep, narrow valleys with steep sides. They are formed by the erosion of rock by water or wind. Canyons can be found in many parts of the world and are often home to rivers or other bodies of water. The Grand Canyon in the United States is one of the most famous canyons in the world, with a depth of over a mile and a length of over 277 miles.