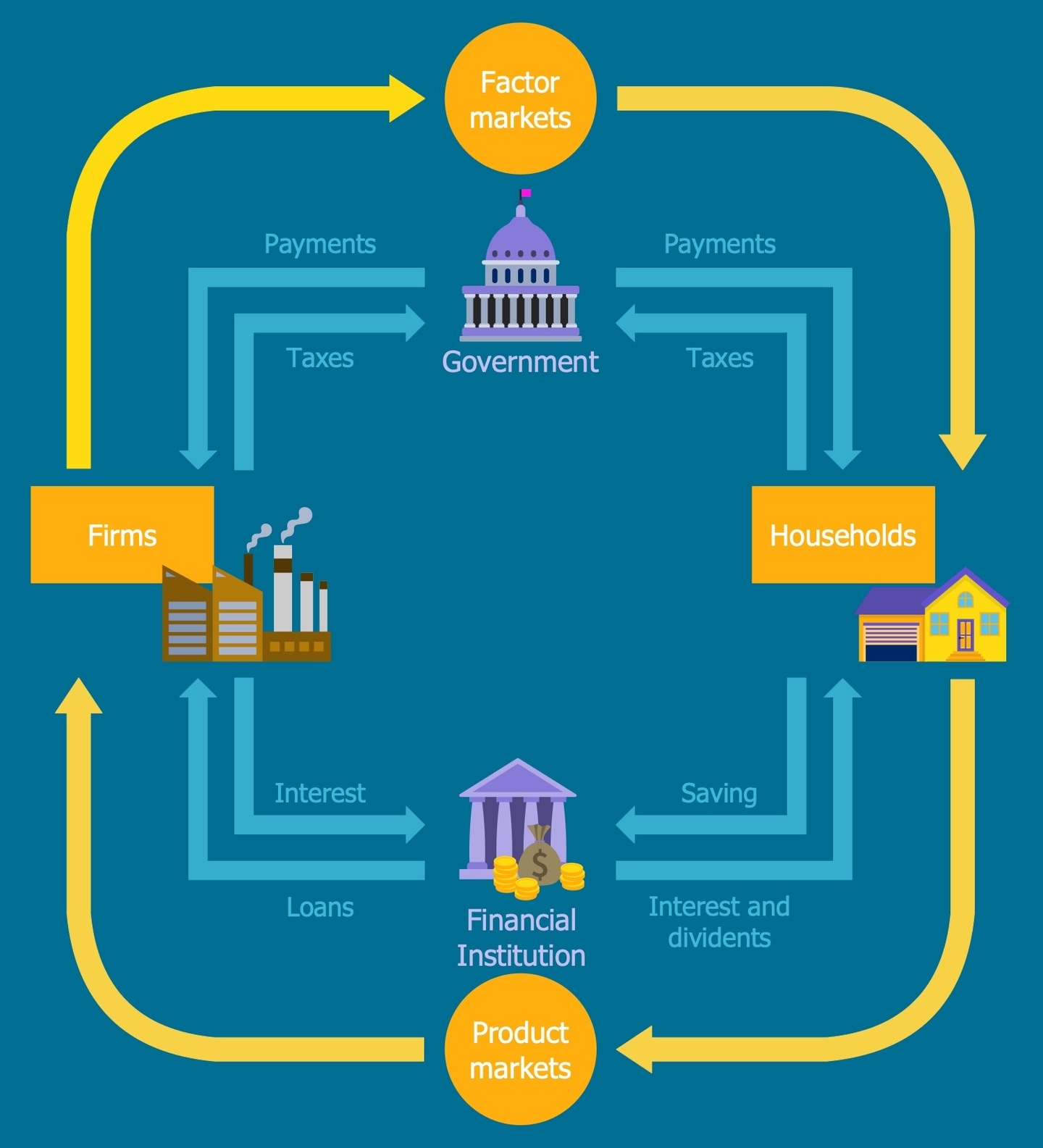
The Four Sector Circular Flow Model is a macroeconomic model that describes the flow of goods and services, income, and expenditure among four primary sectors of an economy: households, businesses, the government, and the foreign sector. This model is considered to be the most realistic one under current world conditions .
In this model, every sector plays a dual role, receiving payments from other sectors while also paying them in one form or another. The household sector is responsible for providing resources to businesses and the public in the form of labor, professionals, and capital. They earn income in the form of rent on owned properties, fees, and remuneration for work and services provided to other sectors as well as to the household segment . The business sector produces goods and services and sells them to households and the government. They also pay wages and salaries to the household sector and taxes to the government . The government sector collects taxes from households and businesses and provides public goods and services such as infrastructure, education, and healthcare. They also make transfer payments to households and businesses in the form of subsidies and welfare activities . Finally, the foreign sector represents the export and import of goods and services. In this model, imports are treated as expenditure and become a leakage, while exports boost national income .
The Four Sector Model is also known as an Open Economy Model because it includes foreign transactions and treats them as an integral part of the economy . The model assumes that there are no restrictions on the import and export of goods and services in general, although specific restrictions may exist based on the trading country, product, etc. . The model also assumes that both domestic and foreign markets feature perfect competition .
The Four Sector Model is an improvement over the Two Sector and Three Sector Models, which represented closed economies that are no longer relevant in current times . The Four Sector Model is more realistic and practical as it consists of four primary sectors, and foreign transactions are included and integrated into the model .
To determine the equilibrium output/income in the Four Sector Model, we need to consider the role of each sector in detail. The household sector is the largest consumer of goods and services, and their consumption expenditure is the largest component of aggregate demand. The business sector is the largest producer of goods and services, and their investment expenditure is the largest component of aggregate demand. The government sector is the largest provider of public goods and services, and their expenditure is the largest component of aggregate demand. The foreign sector is the largest importer and exporter of goods and services, and their net exports are the largest component of aggregate demand .
In conclusion, the Four Sector Circular Flow Model is a macroeconomic model that describes the flow of goods and services, income, and expenditure among four primary sectors of an economy: households, businesses, the government, and the foreign sector. It is the most realistic model under current world conditions and includes foreign transactions as an integral part of the economy. Each sector plays a dual role, receiving payments from other sectors while also paying them in one form or another. The Four Sector Model is an improvement over the Two Sector and Three Sector Models, which represented closed economies that are no longer relevant in current times. The model is used to determine the equilibrium output/income in an economy by considering the role of each sector in detail .